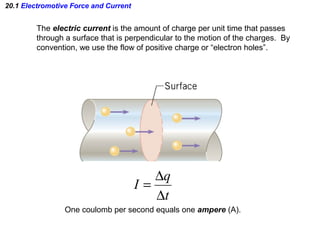
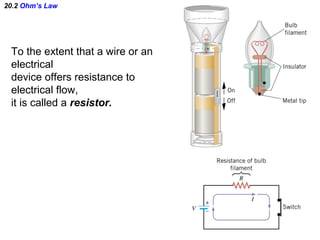
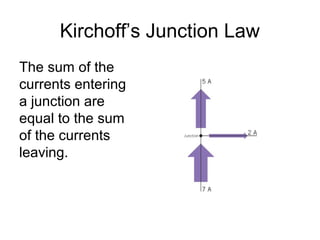
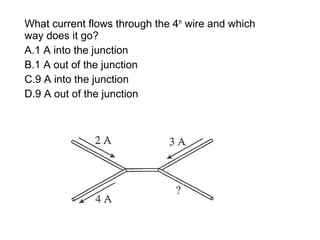
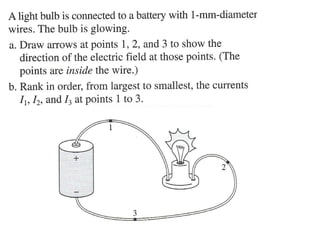
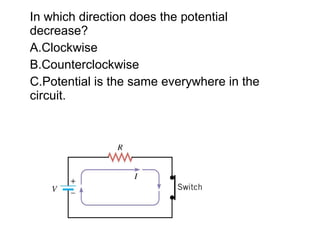
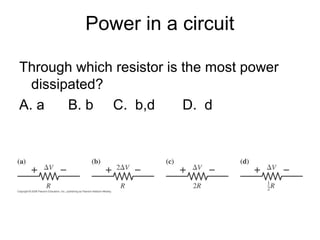
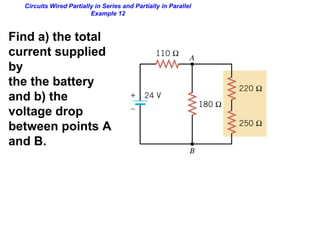
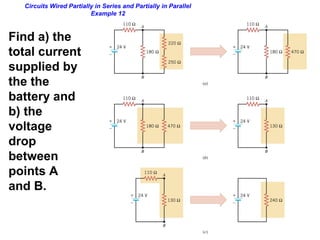
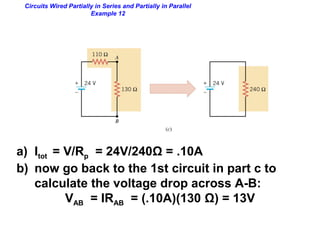
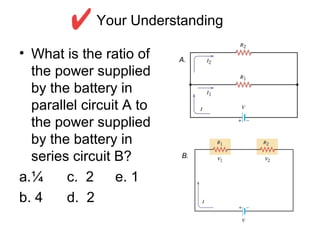
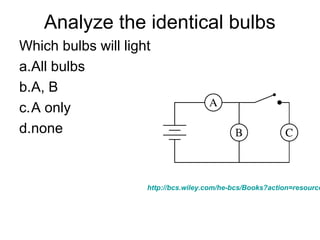
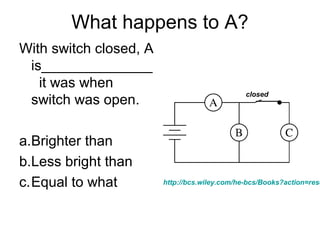
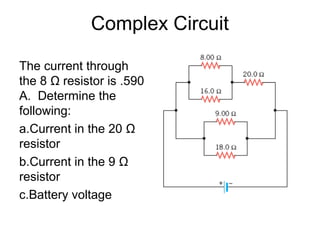
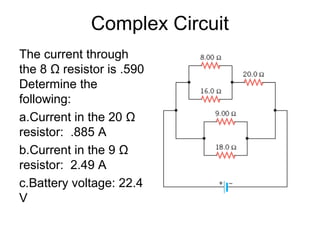
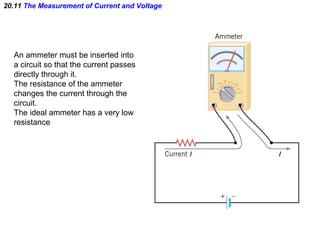
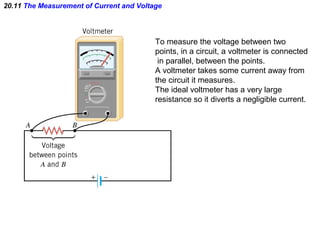
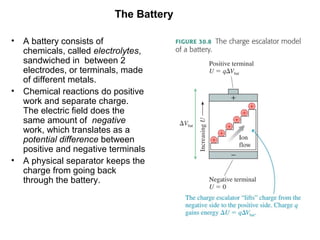
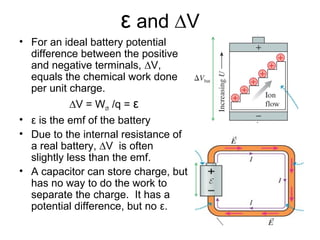
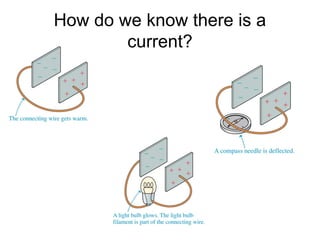
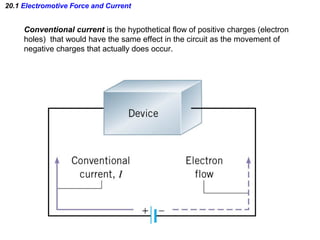
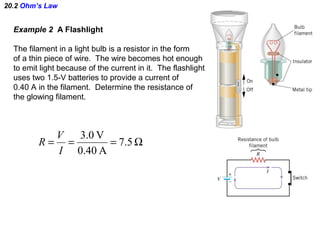
This document discusses electric circuits and Ohm's law. It provides examples of calculating current, resistance, voltage, and power in both series and parallel circuits. Key points covered include:
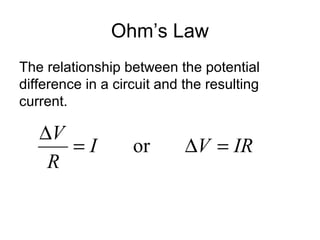
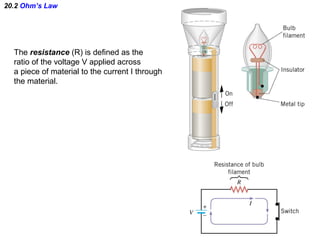
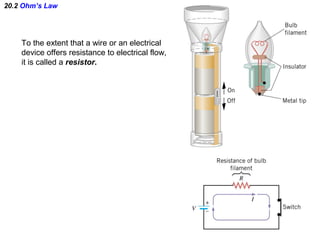
- Ohm's law defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit.
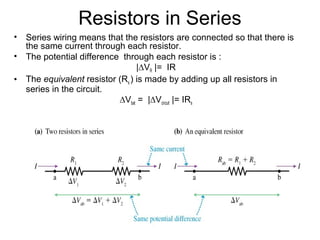
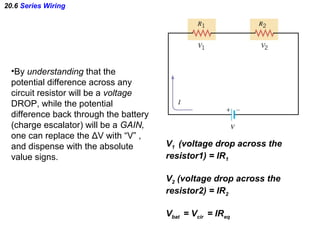
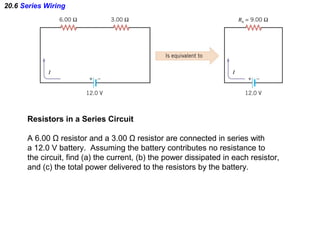
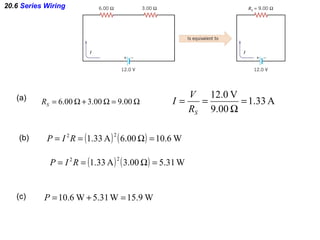
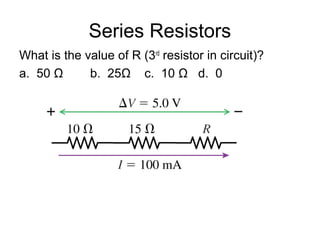
- Components in series experience the same current but their voltages add up. The total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances.
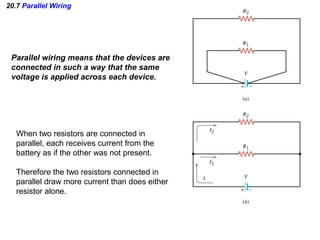
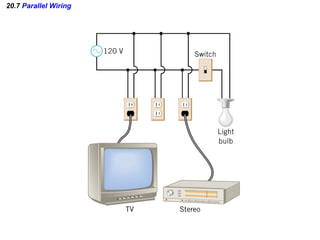
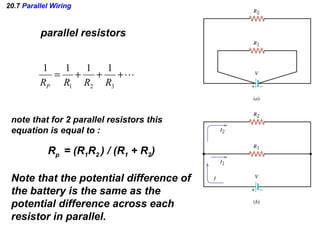
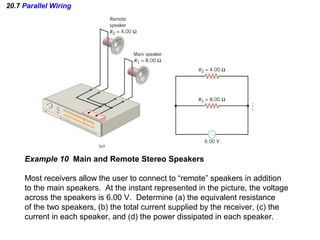
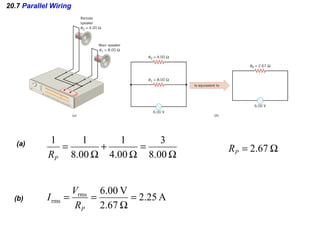
- Components in parallel experience the same voltage but their currents combine. The total resistance is lower than any individual resistance.
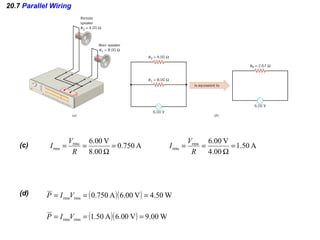
- Power is calculated as the product of voltage and current, and describes how much energy is used by components in a circuit.