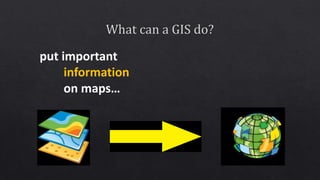
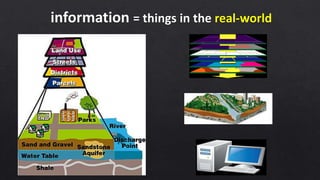
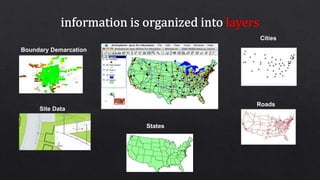
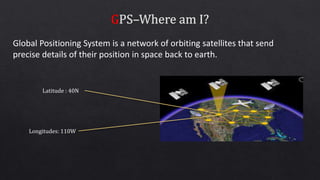
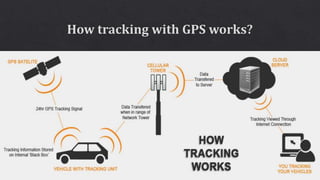
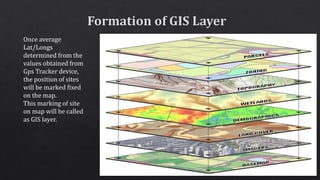
This document discusses geographic information systems (GIS) and global positioning systems (GPS). GIS puts important location-based information like states, roads, and city boundaries onto maps. GPS uses satellites to provide precise location coordinates, with most consumer GPS having an accuracy of around 10 meters. The document outlines how surveyors will use GPS-enabled devices and trackers to obtain multiple location readings for assets, which will then be averaged and mapped as a GIS layer to mark the fixed positions of sites on a map.