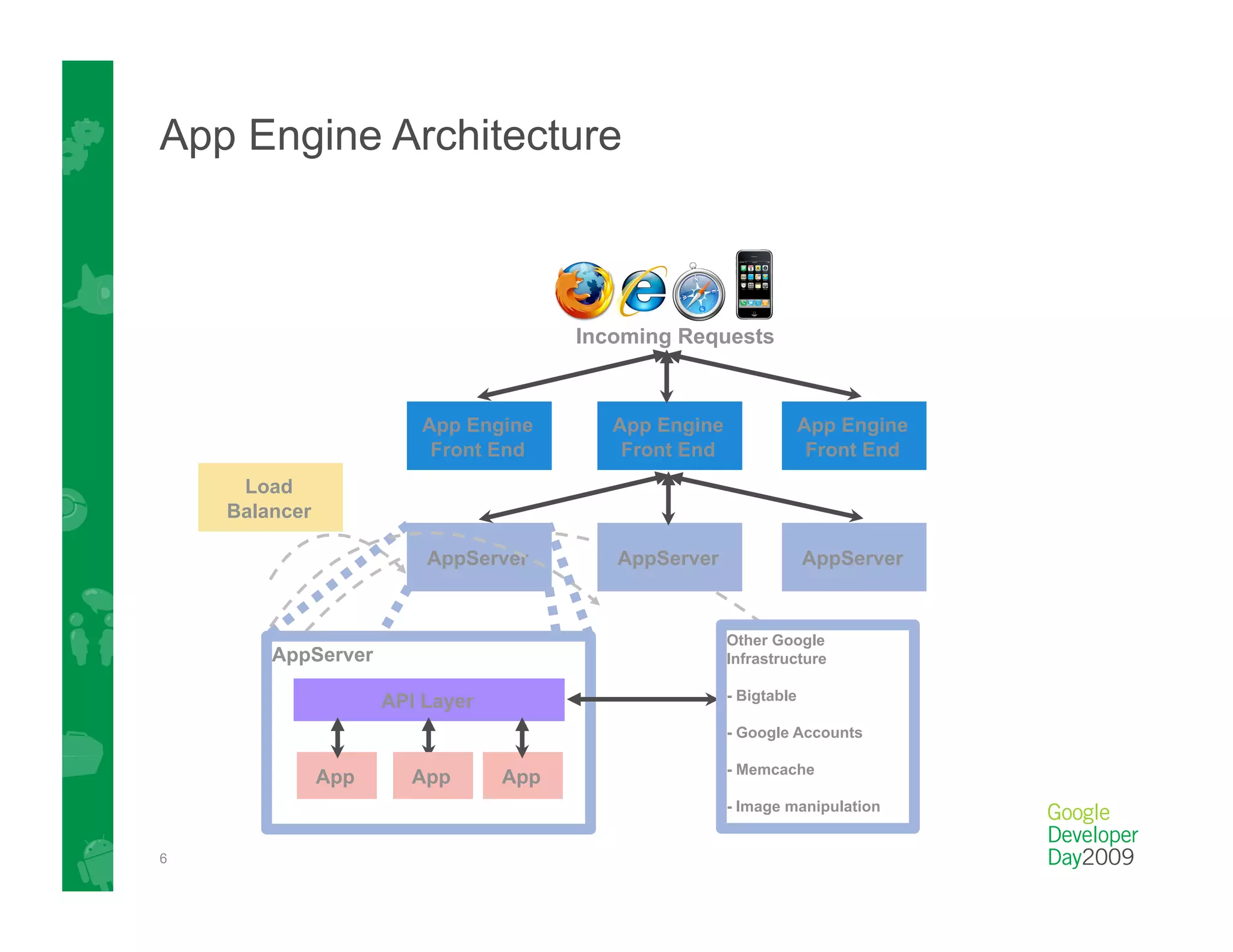
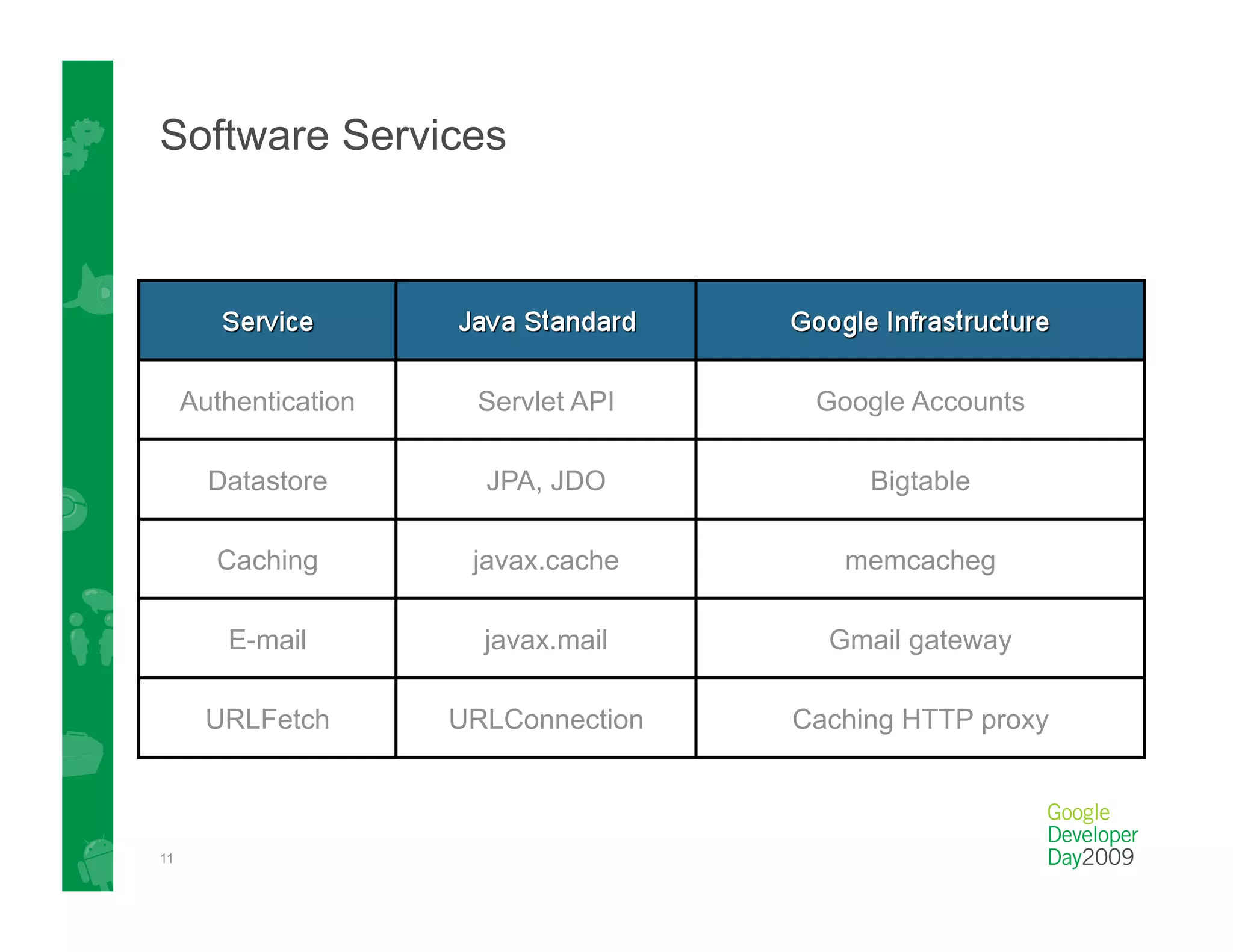
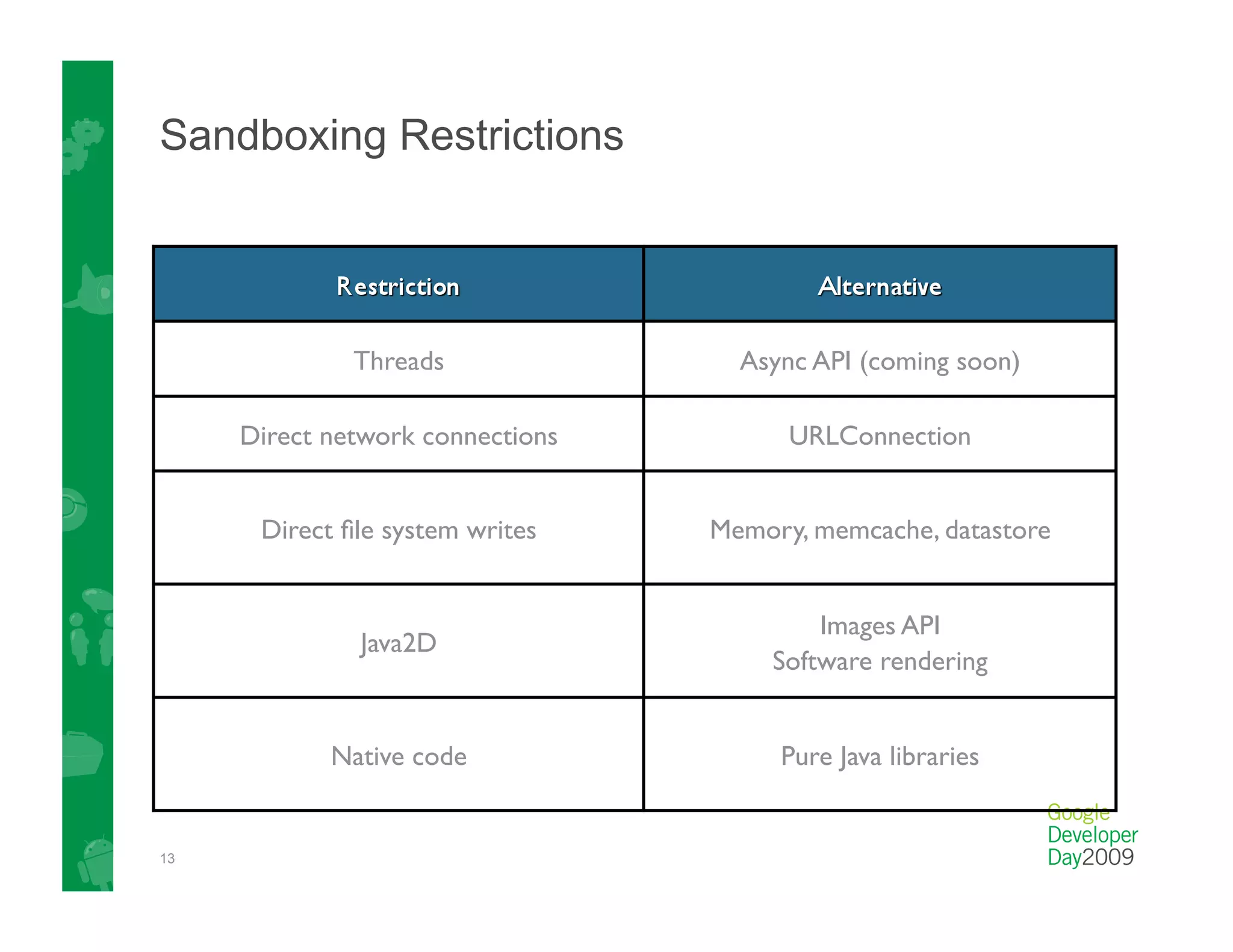
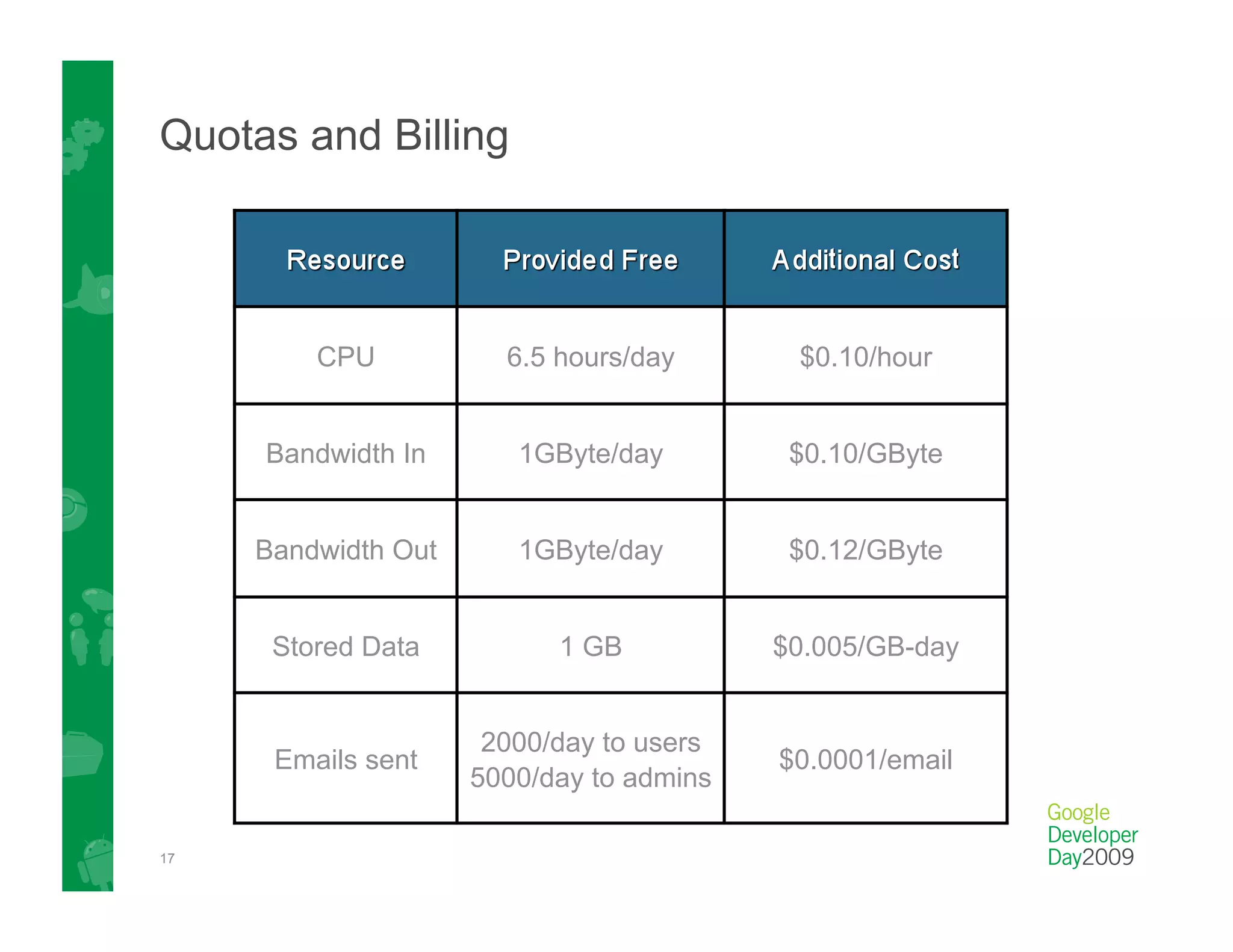
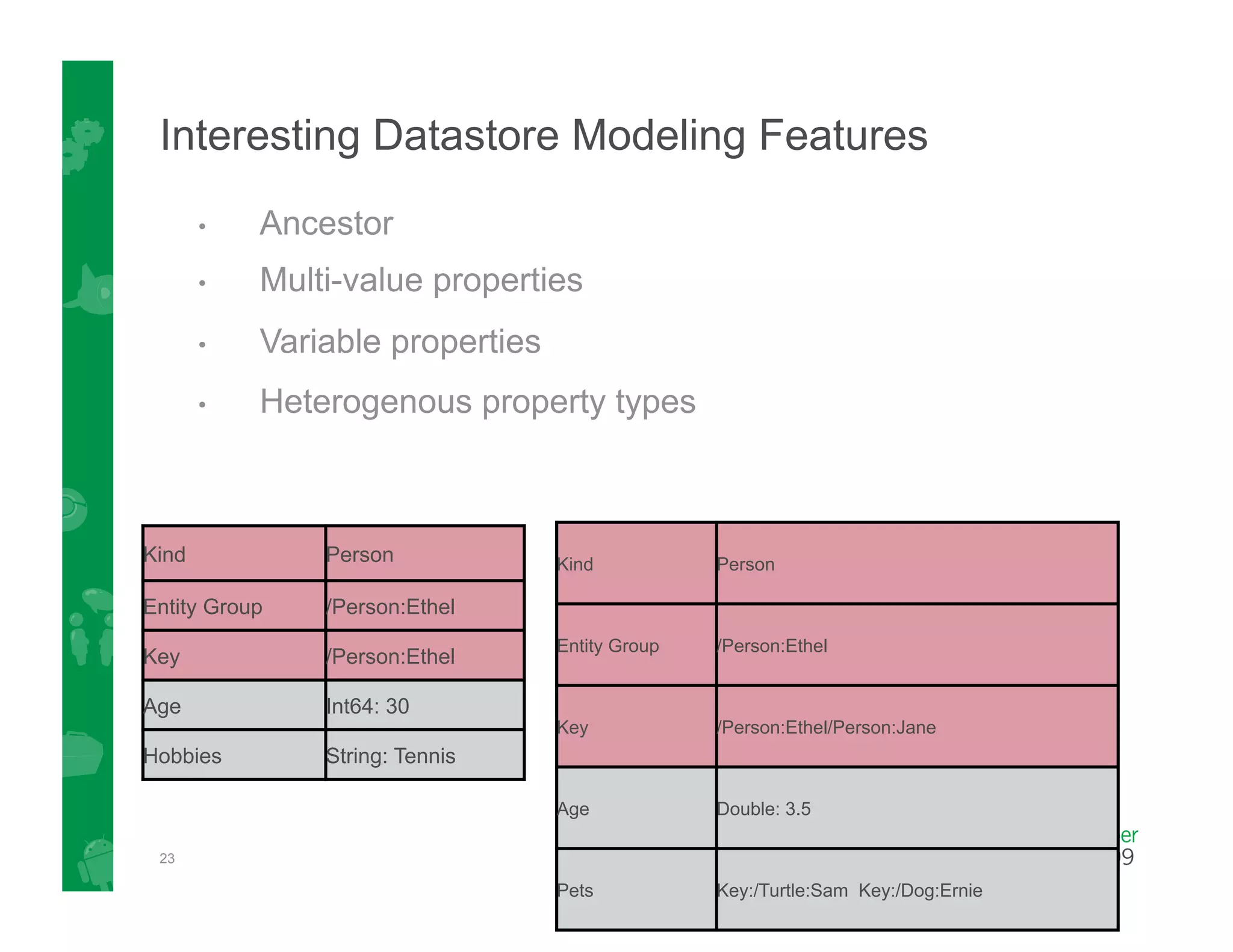
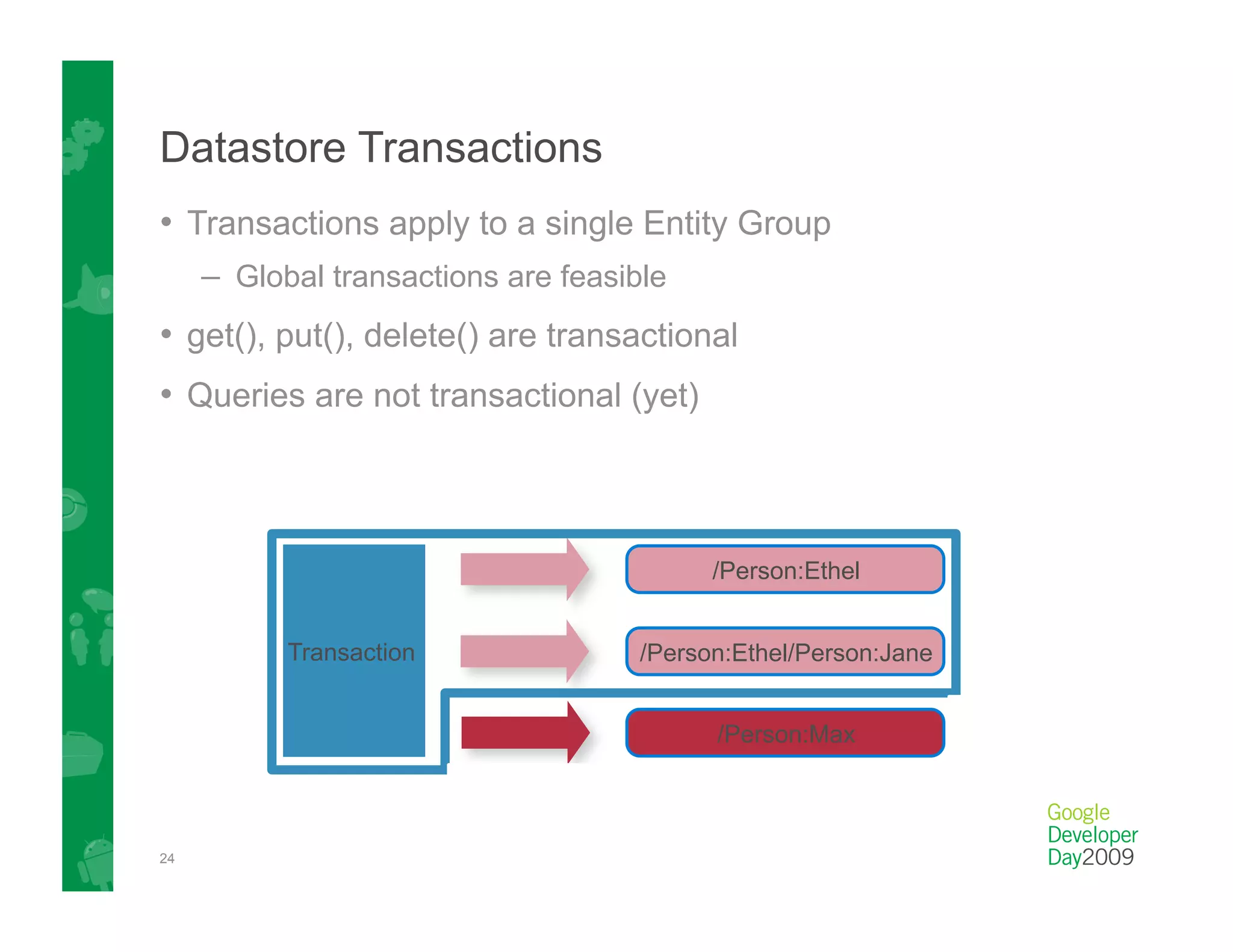
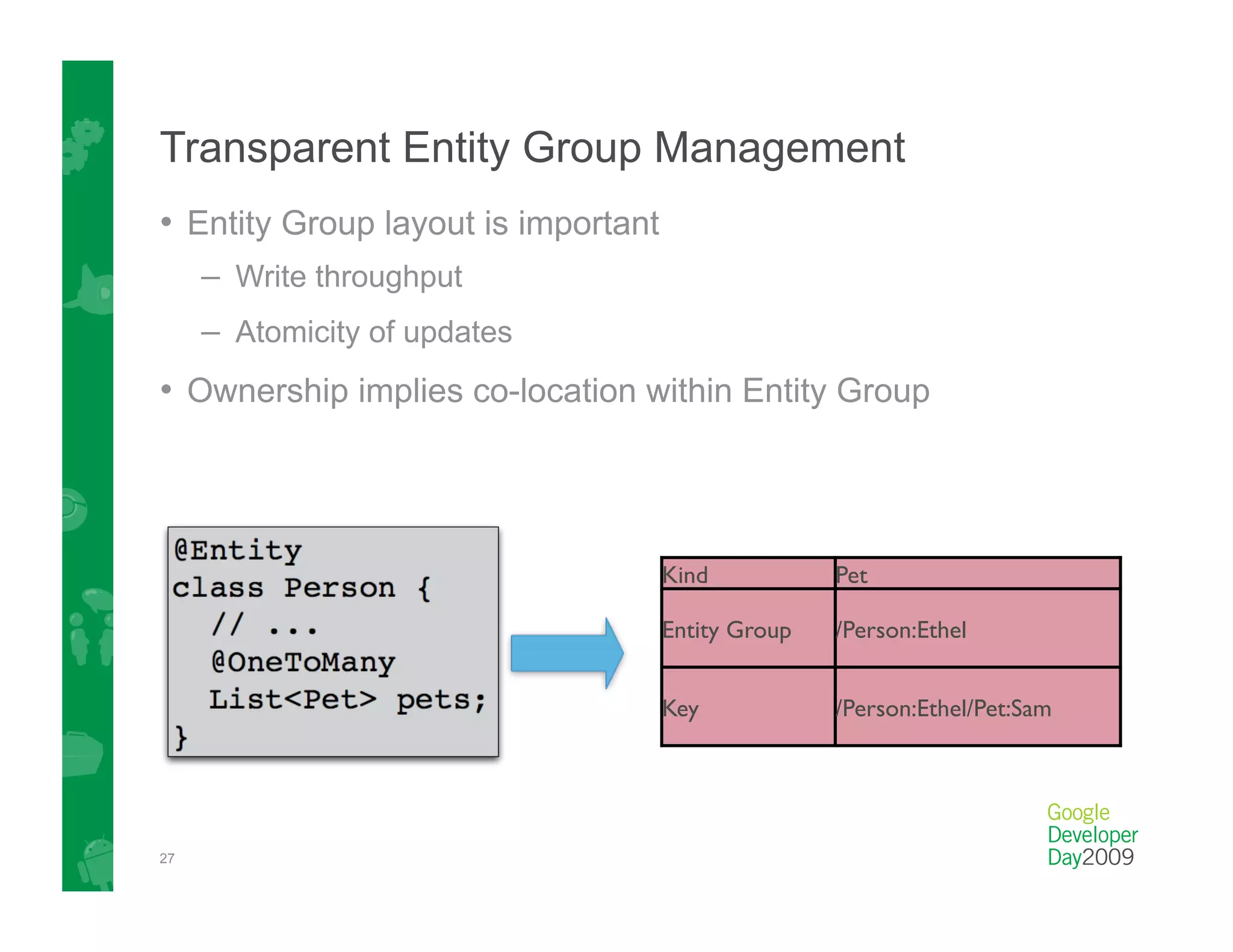
This document provides an overview of Google App Engine and its support for Java applications. It discusses key features like automatic scaling, usage-based billing, and built-in services. It explains that App Engine runs web apps on Google's infrastructure without requiring installation or maintenance of servers. The document demonstrates the App Engine architecture and development tools. It also summarizes the Datastore service and how it differs from relational databases while providing scalable storage and queries.