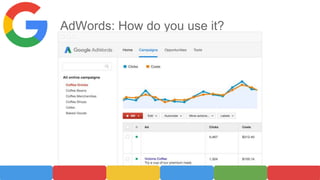
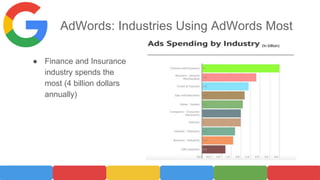
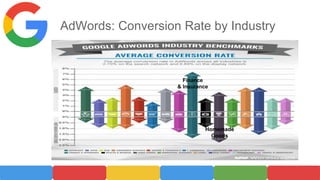
AdWords is Google's advertising service that allows businesses to display ads on Google search results pages. When launched in 2000, it only had 350 advertisers, but now has over 1 million advertisers generating tens of billions in annual revenue for Google. To use AdWords, businesses create an account, add their website and keywords, set a budget and bid for keywords. Google determines ad position through an auction system that ranks ads based on bid amount times quality score. While flexible and able to target specific audiences, AdWords risks include high costs, competition raising prices, poor quality scores lowering ad visibility, and targeting the wrong keywords to miss the intended audience.