This document summarizes a theory seminar on cryptography that covered digital signature schemes. It began with an introduction to hard assumptions like the discrete log problem and computational Diffie-Hellman problem. It then described the ElGamal digital signature scheme, including its key generation, signing, and verification algorithms. It discussed the security of signature schemes in the chosen message attack model and how the ElGamal scheme's unforgeability relies on the hardness of computing discrete logs. It analyzed the probability of an adversary using oracle queries to forge a signature or solve the computational Diffie-Hellman problem. References for the original ElGamal and related signature scheme papers were also provided.





![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Signature Scheme
EDL Scheme
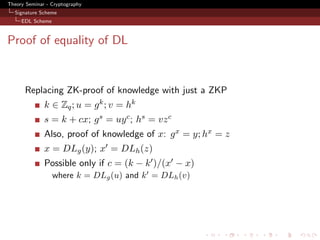
EDL Signature scheme
Proposed originally by [CEVDG88] and [CP93].
Key-generation
sk = x ∈R Zq , pk = y ← g x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-6-320.jpg)
![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Signature Scheme
EDL Scheme
EDL Signature scheme
Proposed originally by [CEVDG88] and [CP93].
Key-generation
sk = x ∈R Zq , pk = y ← g x
Sign(x, M )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-7-320.jpg)
![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Signature Scheme
EDL Scheme
EDL Signature scheme
Proposed originally by [CEVDG88] and [CP93].
Key-generation
sk = x ∈R Zq , pk = y ← g x
Sign(x, M )
1 r ∈R {0, 1}nr , h ← H(M, r) , z ← hx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-8-320.jpg)
![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Signature Scheme
EDL Scheme
EDL Signature scheme
Proposed originally by [CEVDG88] and [CP93].
Key-generation
sk = x ∈R Zq , pk = y ← g x
Sign(x, M )
1 r ∈R {0, 1}nr , h ← H(M, r) , z ← hx
2 NI-ZKP DLh (z) = DLg (y)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-9-320.jpg)
![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Signature Scheme
EDL Scheme
EDL Signature scheme
Proposed originally by [CEVDG88] and [CP93].
Key-generation
sk = x ∈R Zq , pk = y ← g x
Sign(x, M )
1 r ∈R {0, 1}nr , h ← H(M, r) , z ← hx
2 NI-ZKP DLh (z) = DLg (y)
3 k ∈R Zq , u ← g k , v ← hk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-10-320.jpg)
![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Signature Scheme
EDL Scheme
EDL Signature scheme
Proposed originally by [CEVDG88] and [CP93].
Key-generation
sk = x ∈R Zq , pk = y ← g x
Sign(x, M )
1 r ∈R {0, 1}nr , h ← H(M, r) , z ← hx
2 NI-ZKP DLh (z) = DLg (y)
3 k ∈R Zq , u ← g k , v ← hk
4 c ← H (g, h, y, z, u, v) ∈ Zq](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-11-320.jpg)
![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Signature Scheme
EDL Scheme
EDL Signature scheme
Proposed originally by [CEVDG88] and [CP93].
Key-generation
sk = x ∈R Zq , pk = y ← g x
Sign(x, M )
1 r ∈R {0, 1}nr , h ← H(M, r) , z ← hx
2 NI-ZKP DLh (z) = DLg (y)
3 k ∈R Zq , u ← g k , v ← hk
4 c ← H (g, h, y, z, u, v) ∈ Zq
5 s ← k + cx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-12-320.jpg)
![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Signature Scheme
EDL Scheme
EDL Signature scheme
Proposed originally by [CEVDG88] and [CP93].
Key-generation
sk = x ∈R Zq , pk = y ← g x
Sign(x, M )
1 r ∈R {0, 1}nr , h ← H(M, r) , z ← hx
2 NI-ZKP DLh (z) = DLg (y)
3 k ∈R Zq , u ← g k , v ← hk
4 c ← H (g, h, y, z, u, v) ∈ Zq
5 s ← k + cx
6 σ ← (z, r, s, c)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-13-320.jpg)
![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Signature Scheme
EDL Scheme
EDL Signature scheme
Proposed originally by [CEVDG88] and [CP93].
Key-generation
sk = x ∈R Zq , pk = y ← g x
Sign(x, M )
1 r ∈R {0, 1}nr , h ← H(M, r) , z ← hx
2 NI-ZKP DLh (z) = DLg (y)
3 k ∈R Zq , u ← g k , v ← hk
4 c ← H (g, h, y, z, u, v) ∈ Zq
5 s ← k + cx
6 σ ← (z, r, s, c)
Verify](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-14-320.jpg)
![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Signature Scheme
EDL Scheme
EDL Signature scheme
Proposed originally by [CEVDG88] and [CP93].
Key-generation
sk = x ∈R Zq , pk = y ← g x
Sign(x, M )
1 r ∈R {0, 1}nr , h ← H(M, r) , z ← hx
2 NI-ZKP DLh (z) = DLg (y)
3 k ∈R Zq , u ← g k , v ← hk
4 c ← H (g, h, y, z, u, v) ∈ Zq
5 s ← k + cx
6 σ ← (z, r, s, c)
Verify
h ← H(M, r) , u ← g s y −c , v ← h s z −c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-15-320.jpg)
![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Signature Scheme
EDL Scheme
EDL Signature scheme
Proposed originally by [CEVDG88] and [CP93].
Key-generation
sk = x ∈R Zq , pk = y ← g x
Sign(x, M )
1 r ∈R {0, 1}nr , h ← H(M, r) , z ← hx
2 NI-ZKP DLh (z) = DLg (y)
3 k ∈R Zq , u ← g k , v ← hk
4 c ← H (g, h, y, z, u, v) ∈ Zq
5 s ← k + cx
6 σ ← (z, r, s, c)
Verify
h ← H(M, r) , u ← g s y −c , v ← h s z −c
?
c = H (g, h , y, z, u , v ). Check c = c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-16-320.jpg)

![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Security
Unforgeability
Unforgeability
Random oracle model - solve CDH. (Proof is from [?])
Setup: y = g a (a is unknown)
H queries: embed - H(M, r) = h = (g b )d , d - random
H queries: all random.
Sign queries:
r ∈R {0, 1}nr . If H(M, r) is queried - abort.
κ ∈R Z . Set, z = y κ , h = g κ and H(M, r) = h
DLh (z) = DLg (y)
c ∈R Zq , s ∈R Zq ,. Set u = g s y −c and v = hs z −c
Store H (g, h, y, z, u, v) = c
σ = (z, r, s, c)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-19-320.jpg)

![Theory Seminar - Cryptography
Security
Probability
Analysis - Probability of solving CDH
Abort cases
1 H(M, r) was queried! ⇒ P r = qH 2−nr
- Aborting in Step1 of signature P r = qsig · qH · 2−nr
2 Abort at Step4 of signature H (g, g k , y, y k , u, uk ) queried!
- Probability of collision (qH + qsig ) · 2−2nq
- Final : P r = qsig · (qH + qsig ) · 2−2nq
Cannot solve CDH on successful forgery (because of DL)
1 Pr[N H ∧ ¬N Q] = 2−nq
2 Pr[N Q] = qH · 2−nq
NH - event that the attacker does not query H-oracle.
NQ - event that DLg (y) = DLh (z)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gohjarecki-110510090657-phpapp02/85/A-Signature-Scheme-as-Secure-as-the-Diffie-Hellman-Problem-21-320.jpg)