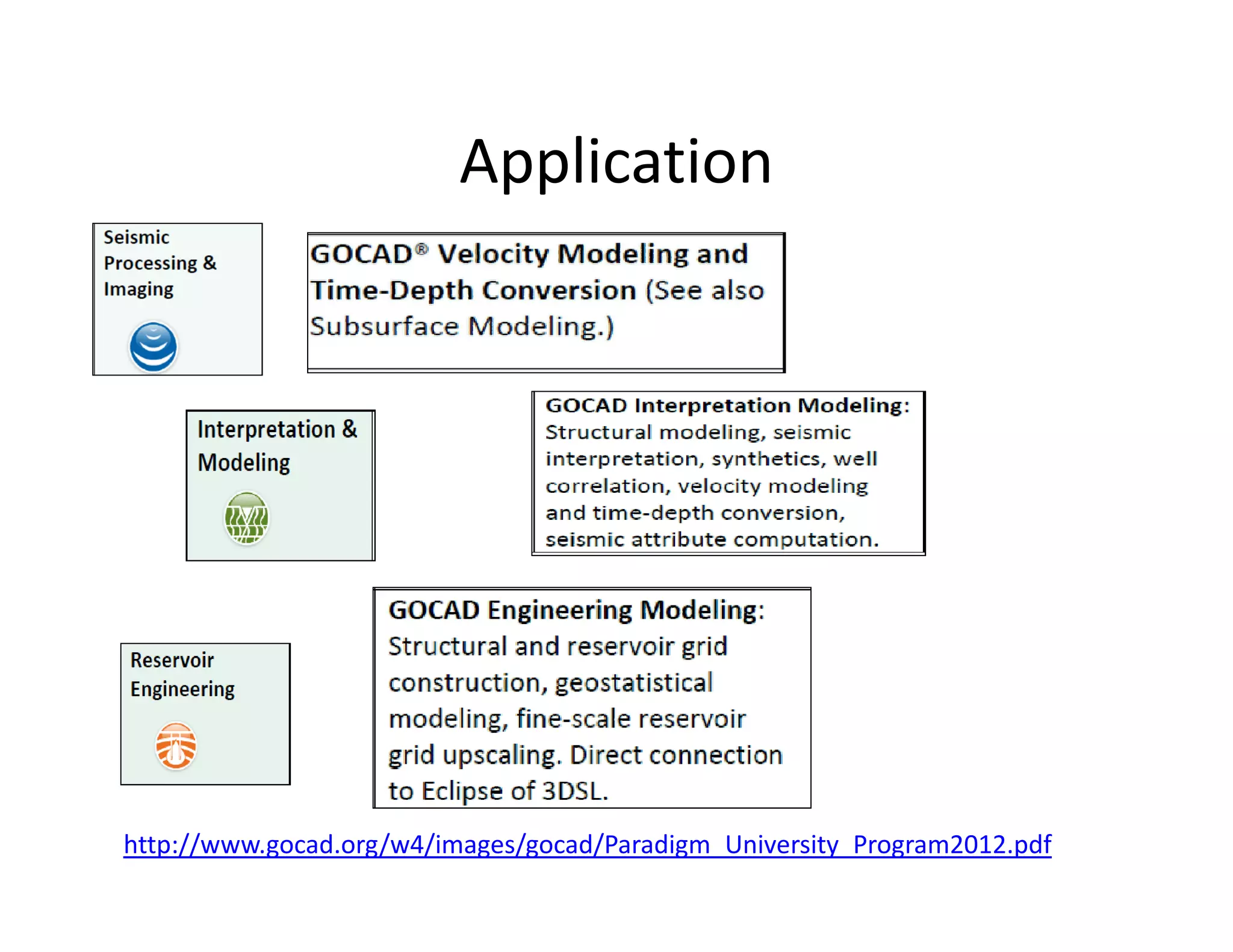
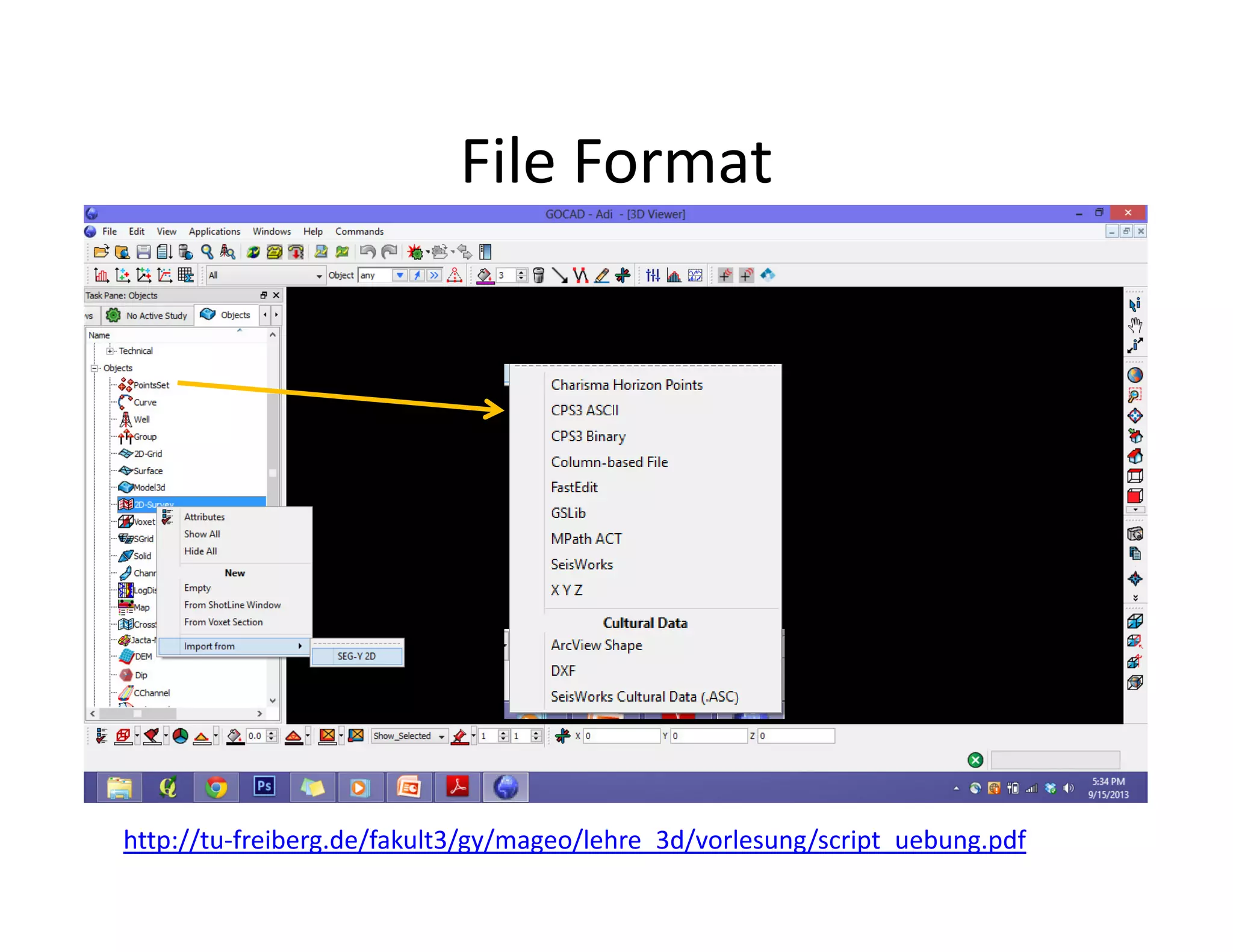
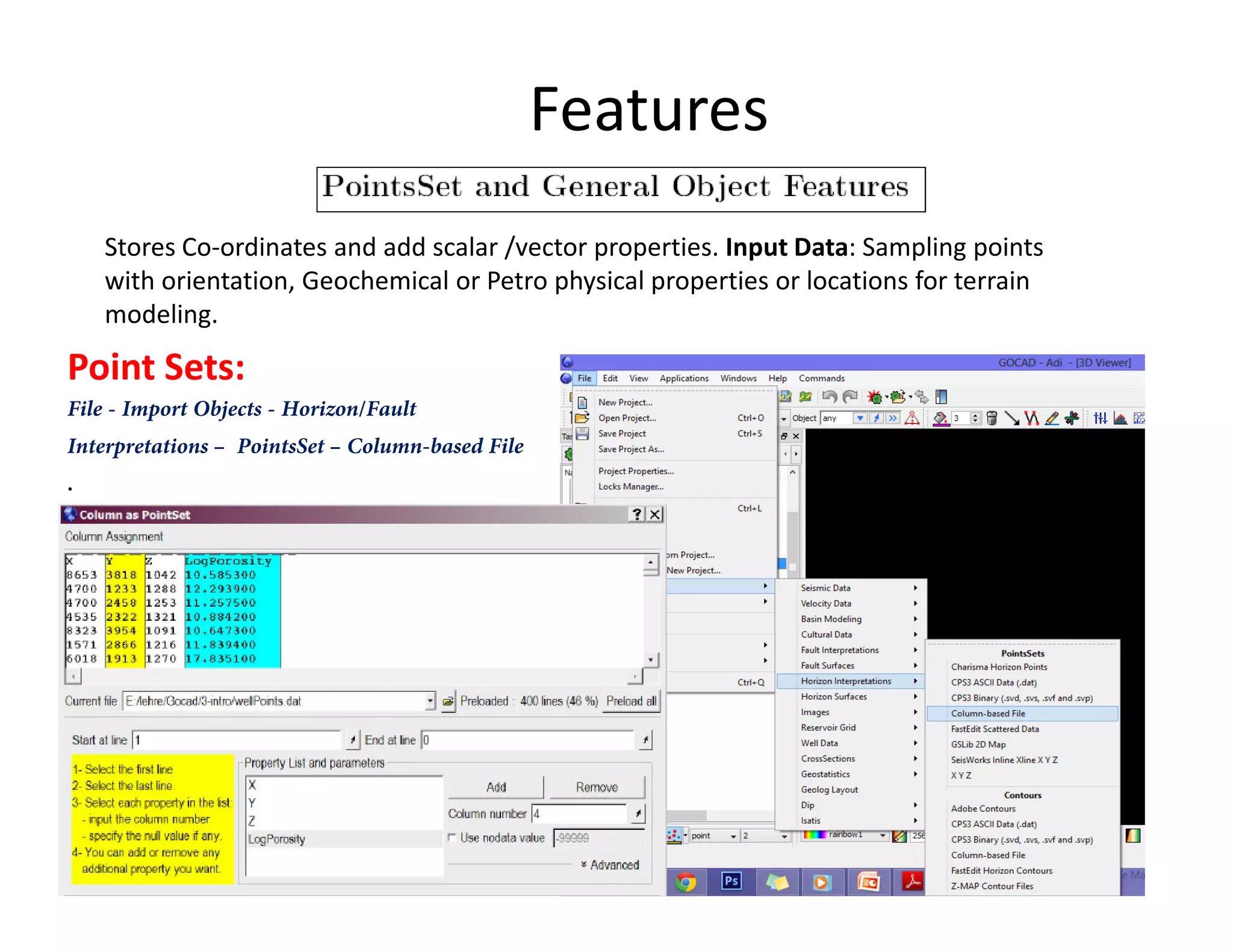
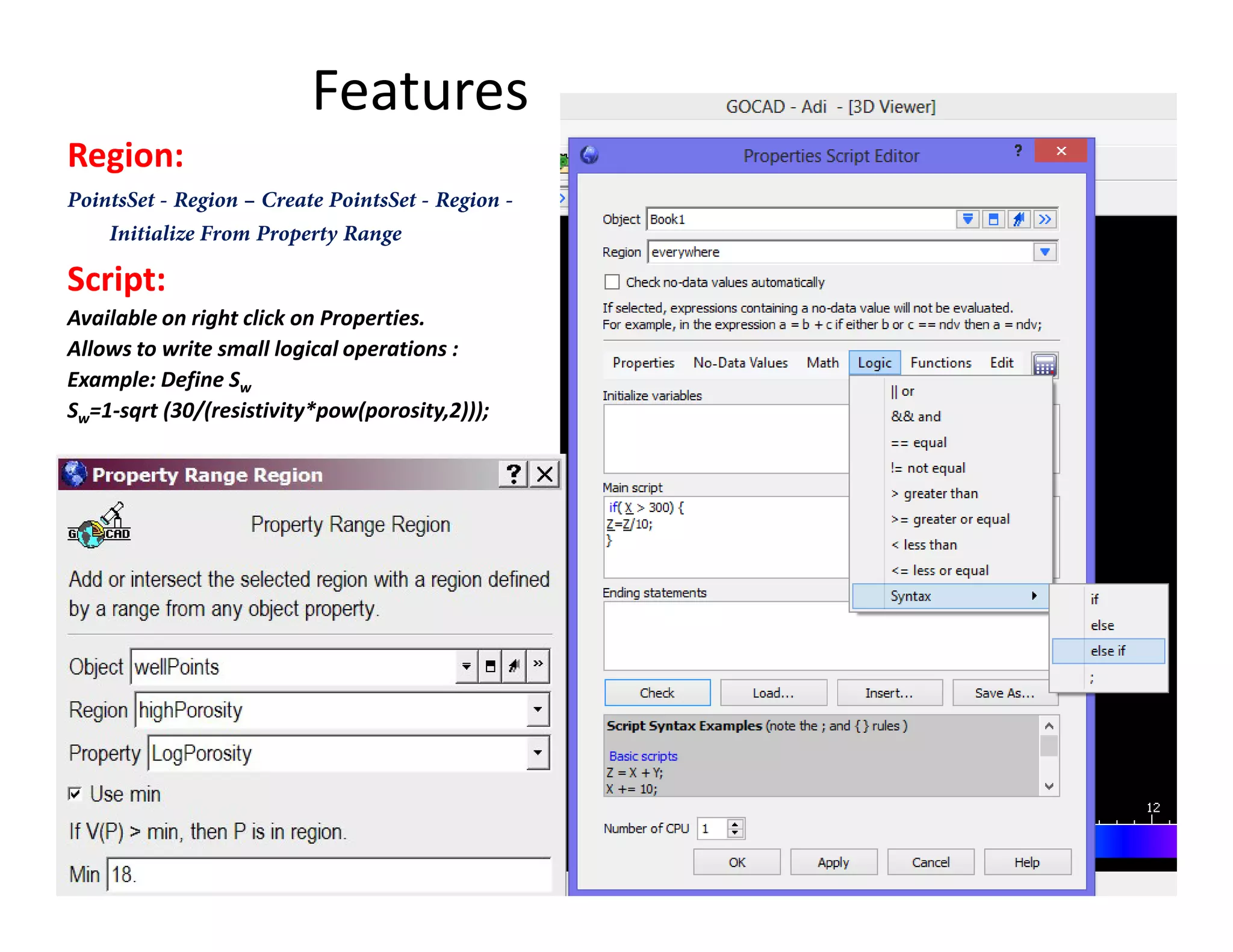
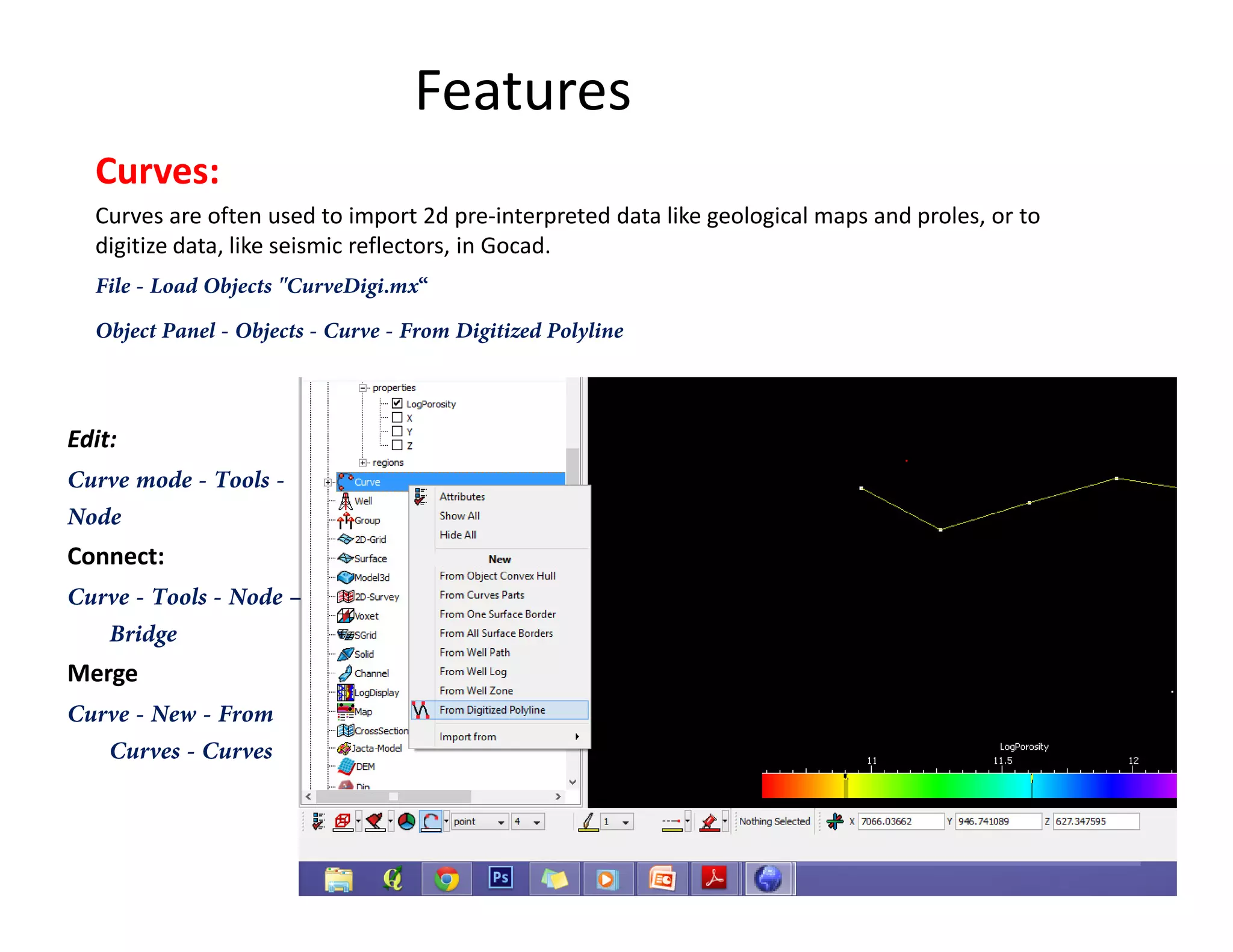
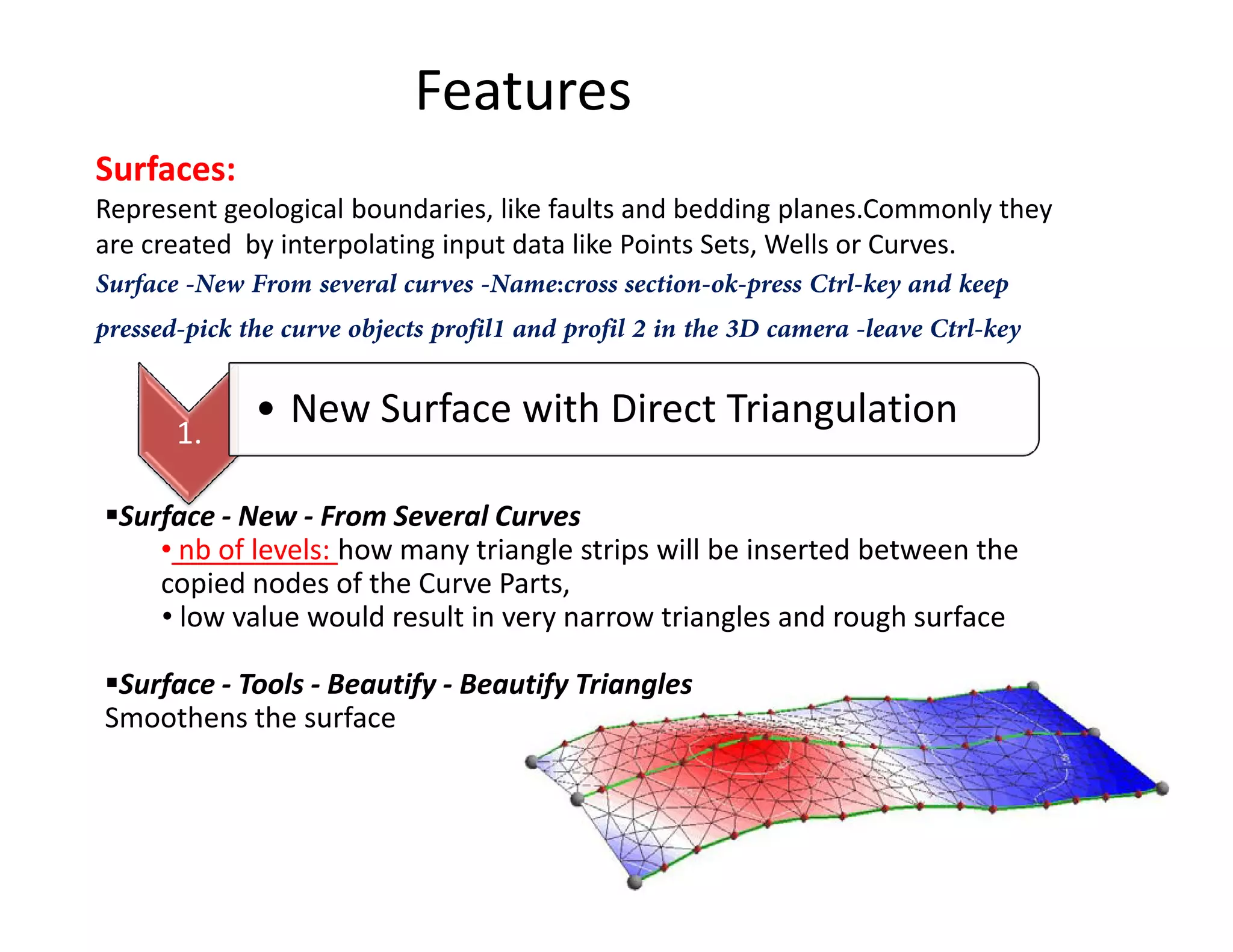
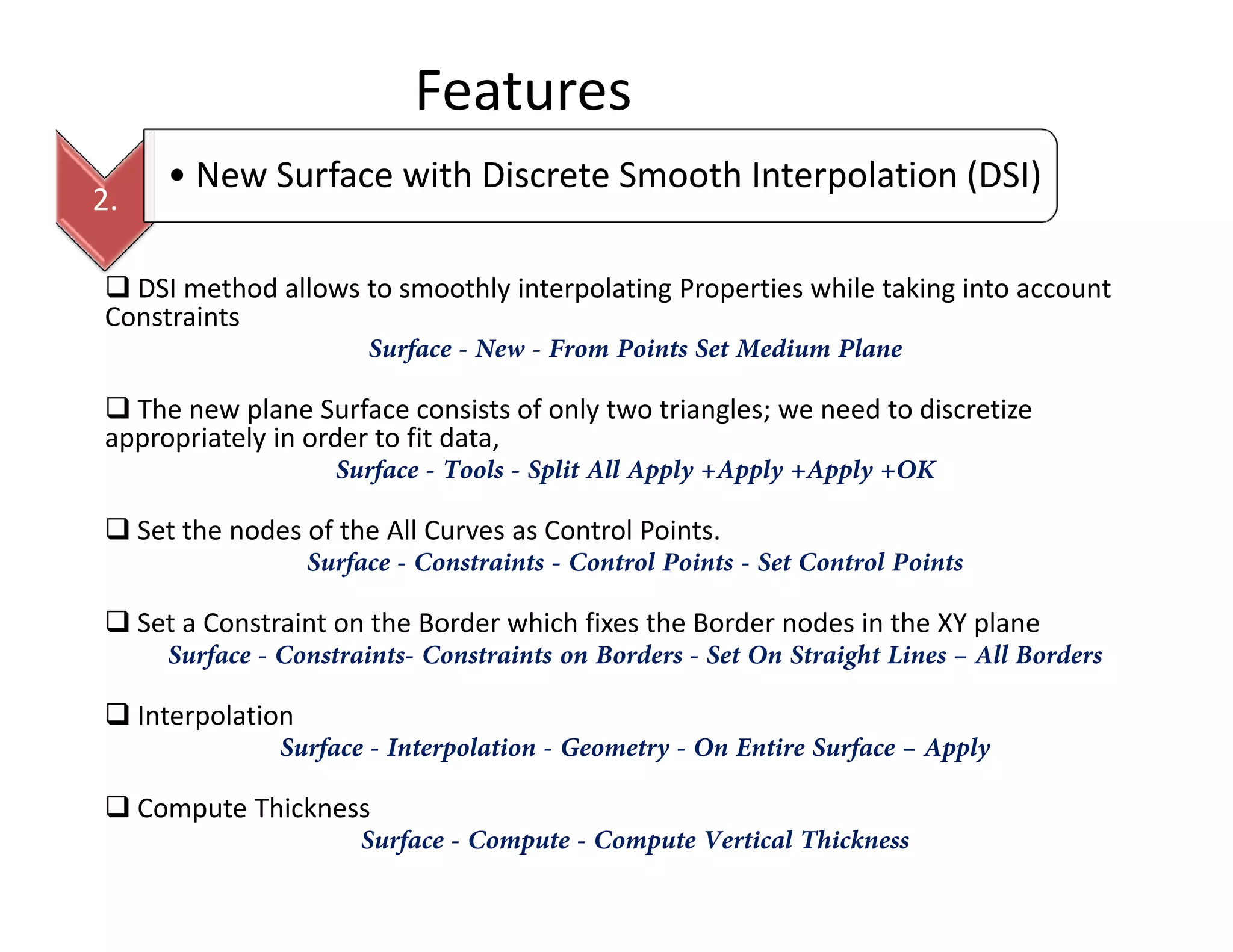
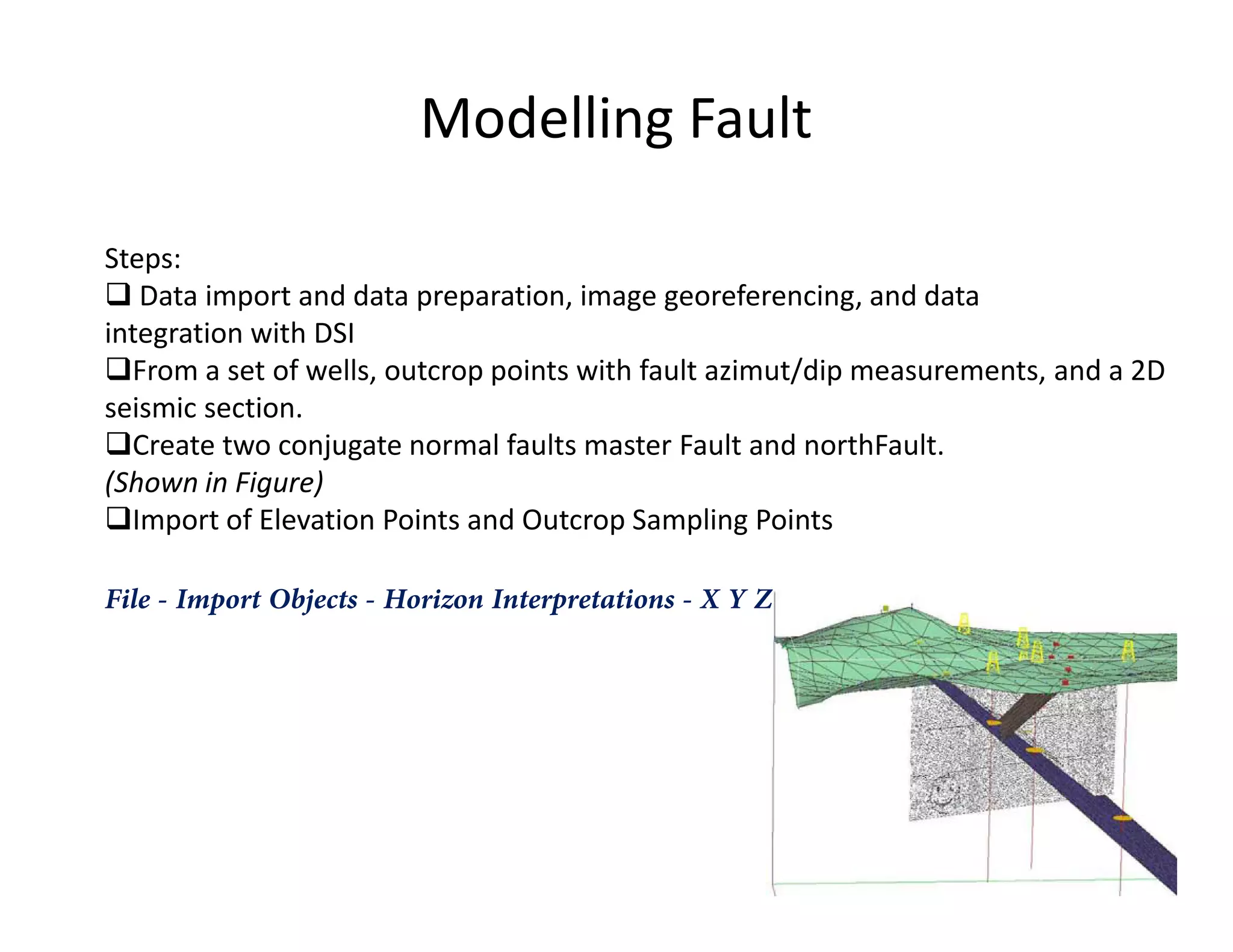
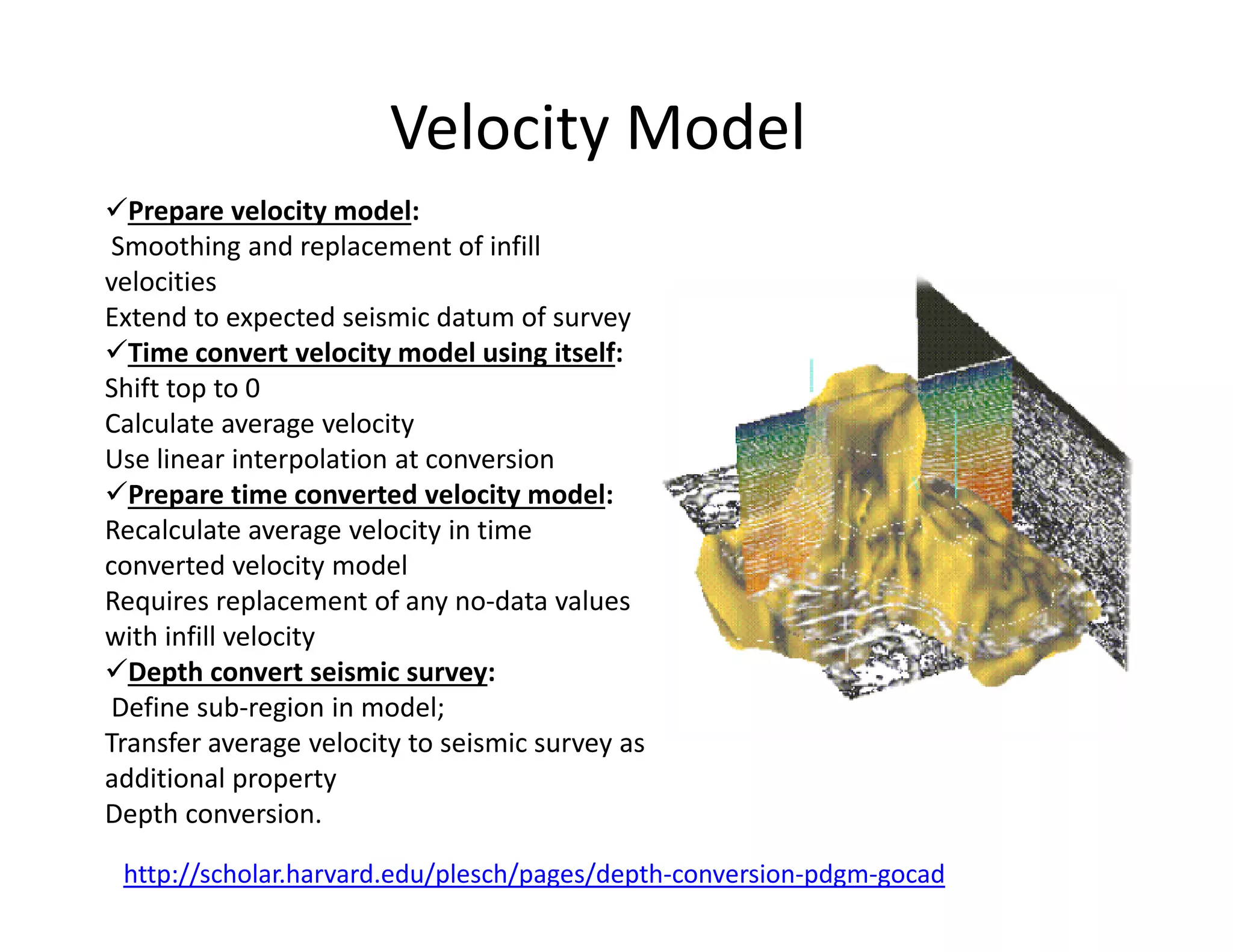
The document provides a comprehensive guide to GOCAD, covering its features for modeling geological data, including interphase file formats, input data types, and specific functionalities such as surface and fault modeling. It discusses the process of depth conversion in seismic surveys, detailing steps for creating velocity models and converting them into time domains. Additionally, it includes references and useful links for further learning about GOCAD applications and methodologies.