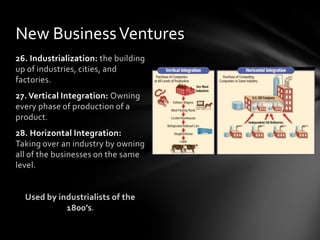
The document summarizes key aspects of the Gilded Age and Progressive Era in the United States, including immigration patterns and issues immigrants faced, the rise of factories and related labor issues, union organizing efforts, muckraking journalism, and the responses of Progressive reformers and presidents like Roosevelt, Taft, and Wilson. It covers topics such as political machines and corruption, trustbusting, and women's suffrage.