This document discusses several classical philosophies and their implications for business practices:
1. Confucian philosophy emphasized morality, social relationships, justice and sincerity. These values like obedience and respect can benefit entrepreneurship if applied correctly, such as in human resources management.
2. Socrates' use of questioning assumptions and testing theories can help entrepreneurs evaluate their beliefs about opportunities and products.
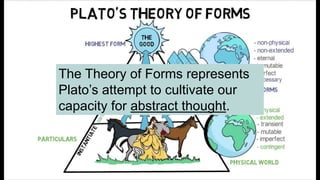
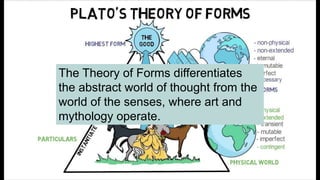
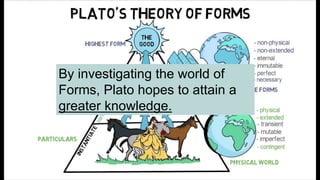
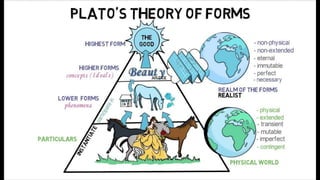
3. Plato's Theory of Forms values abstract thought over art/mythology. He saw education as important for a healthy state.
4. Aristotle believed virtue and happiness were the highest goals. Leaders should create an environment where people can reach their potential.
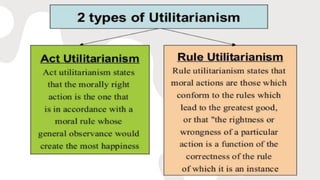
5. Other philosophies discussed include