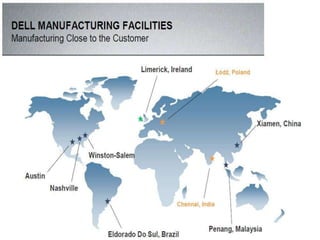
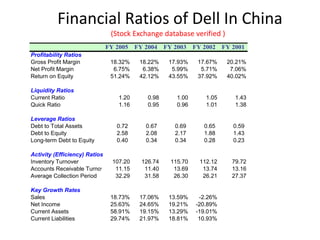
Dell entered the Chinese market in 1995 and has since established local manufacturing and distribution operations. It focuses on selling PCs to enterprise customers, governments, and schools. Dell utilizes strategies like lowering prices, offering free products, and shipping to gain sales. It faces competition from Lenovo and local Chinese brands. Dell's strengths include its reputation and direct sales model, while weaknesses are a lack of low-cost advantage and brand recognition challenges. Opportunities exist in China's growing economy and PC market, while threats include intellectual property risks and intense competition.