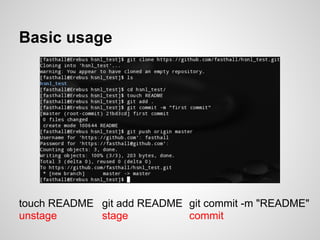
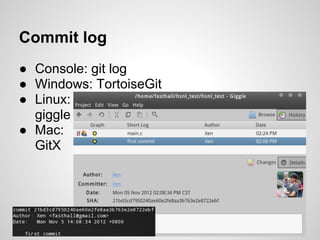
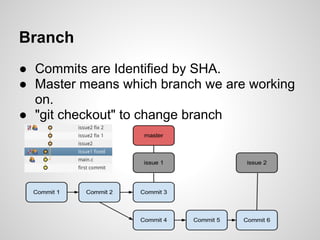
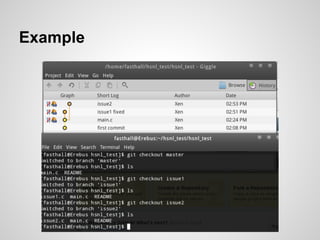
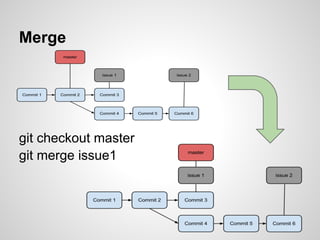
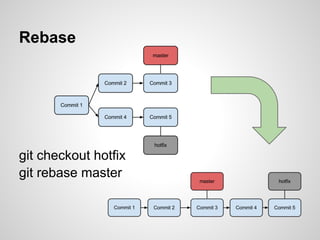
Git is an open source distributed version control system that allows for branching, committing changes, and rolling back changes. It is distributed, so users can work offline and sync changes later. Users can initialize local repositories from existing remote ones using cloning. Basic commands include add, commit, log, checkout, merge, and rebase to manage branches and integrate changes.