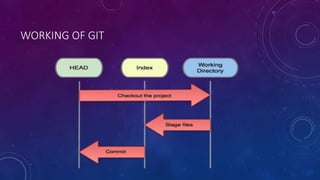
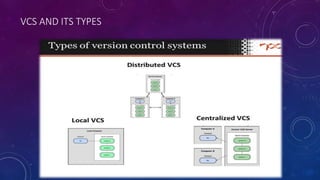
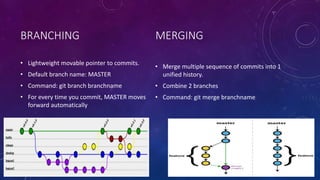
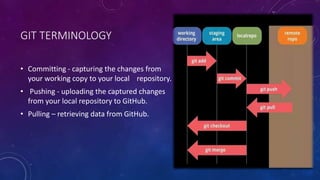
Git is a free and open-source distributed version control system created by Linus Torvalds in 2005. It allows tracking changes to files and coordinating work among teams of developers. GitHub is a web-based hosting service for Git repositories that offers both free and paid plans. Git uses a decentralized model with local repositories that can be synced and shared, supporting thousands of parallel branches. It provides commands for cloning repositories, tracking changes, committing updates, and merging branches.