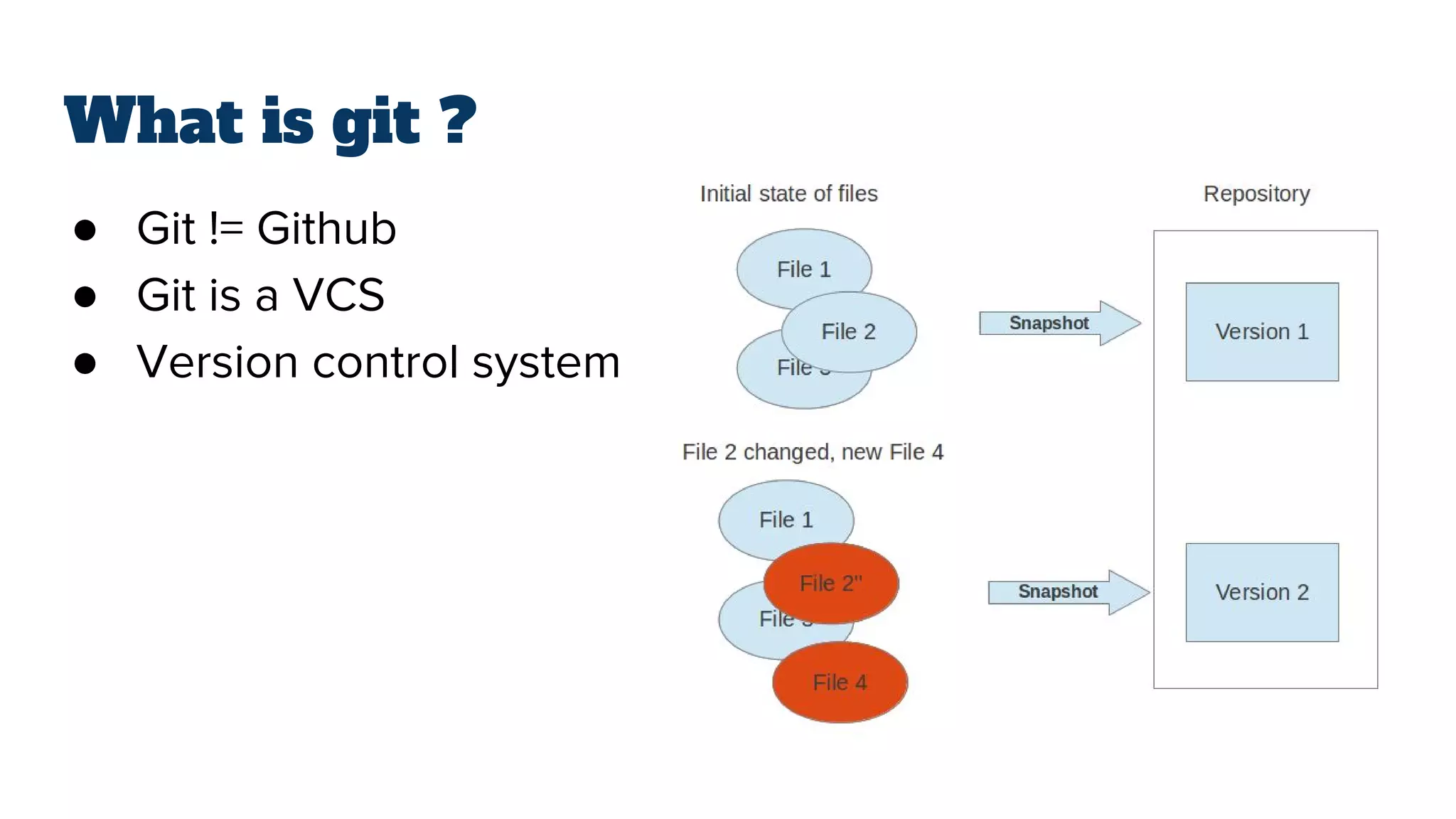
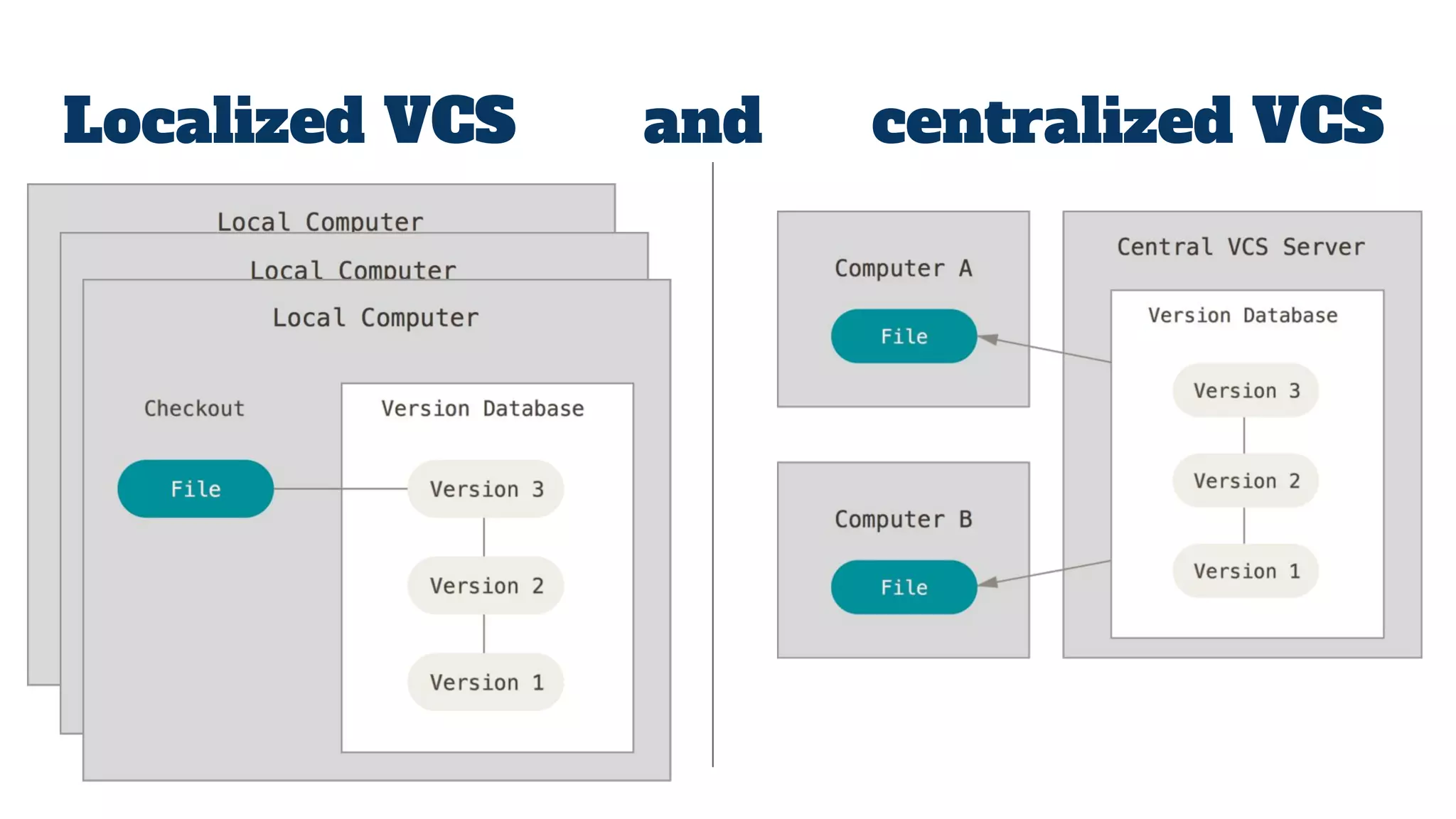
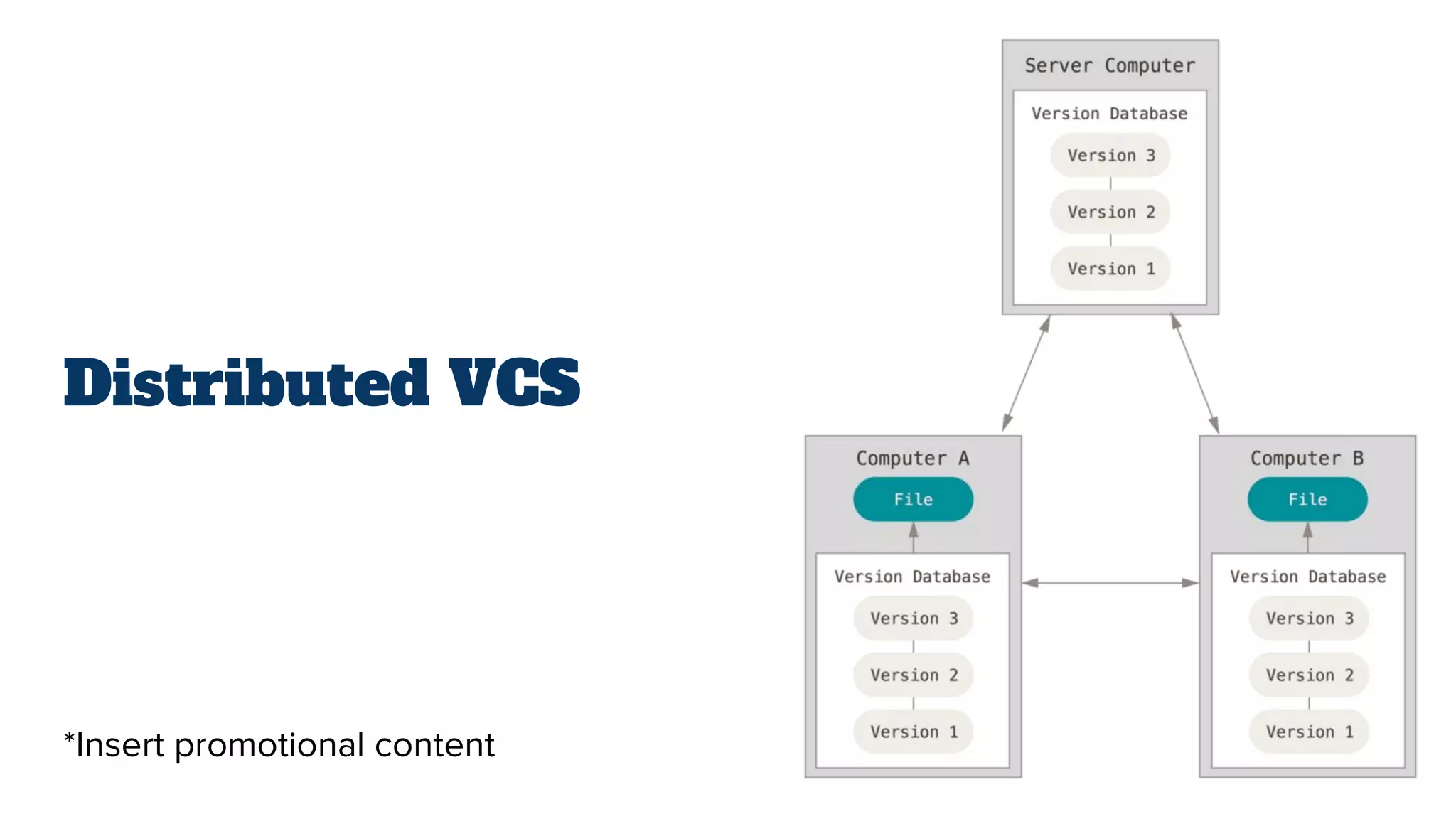
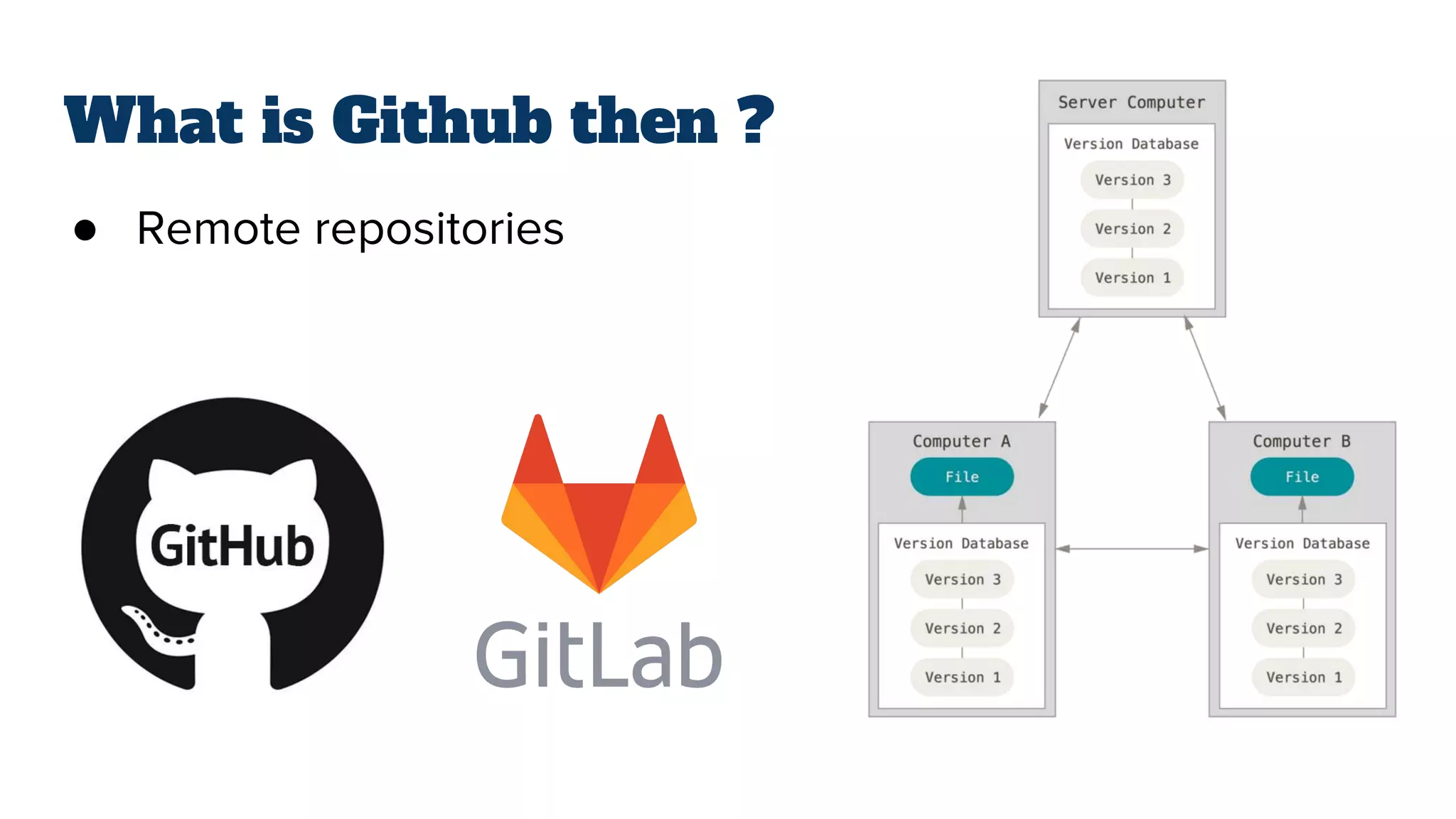
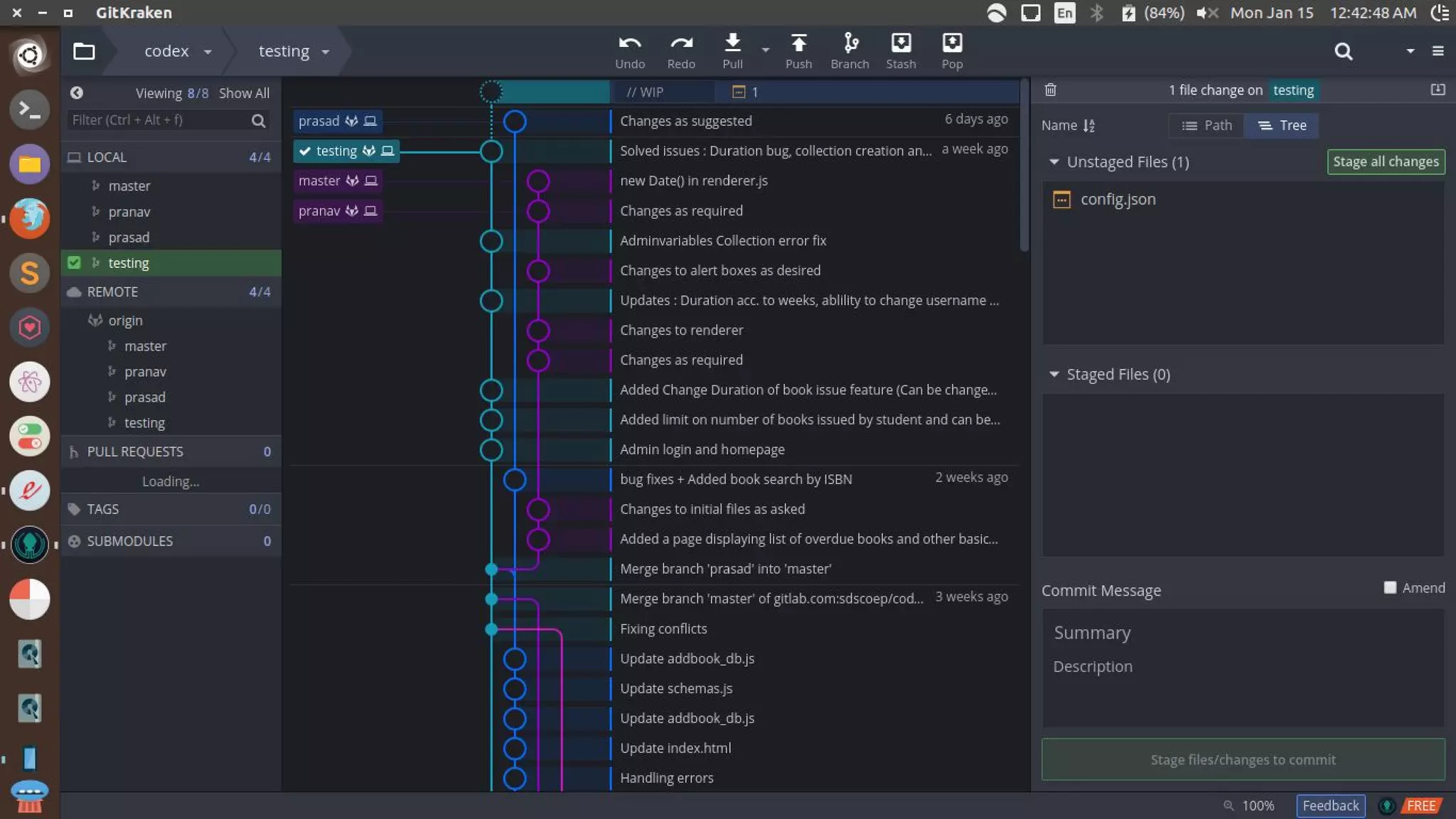
- Git is a version control system (VCS) that allows tracking changes to files and coordinating work across multiple people. It is not the same as GitHub, which is a platform for hosting remote Git repositories.
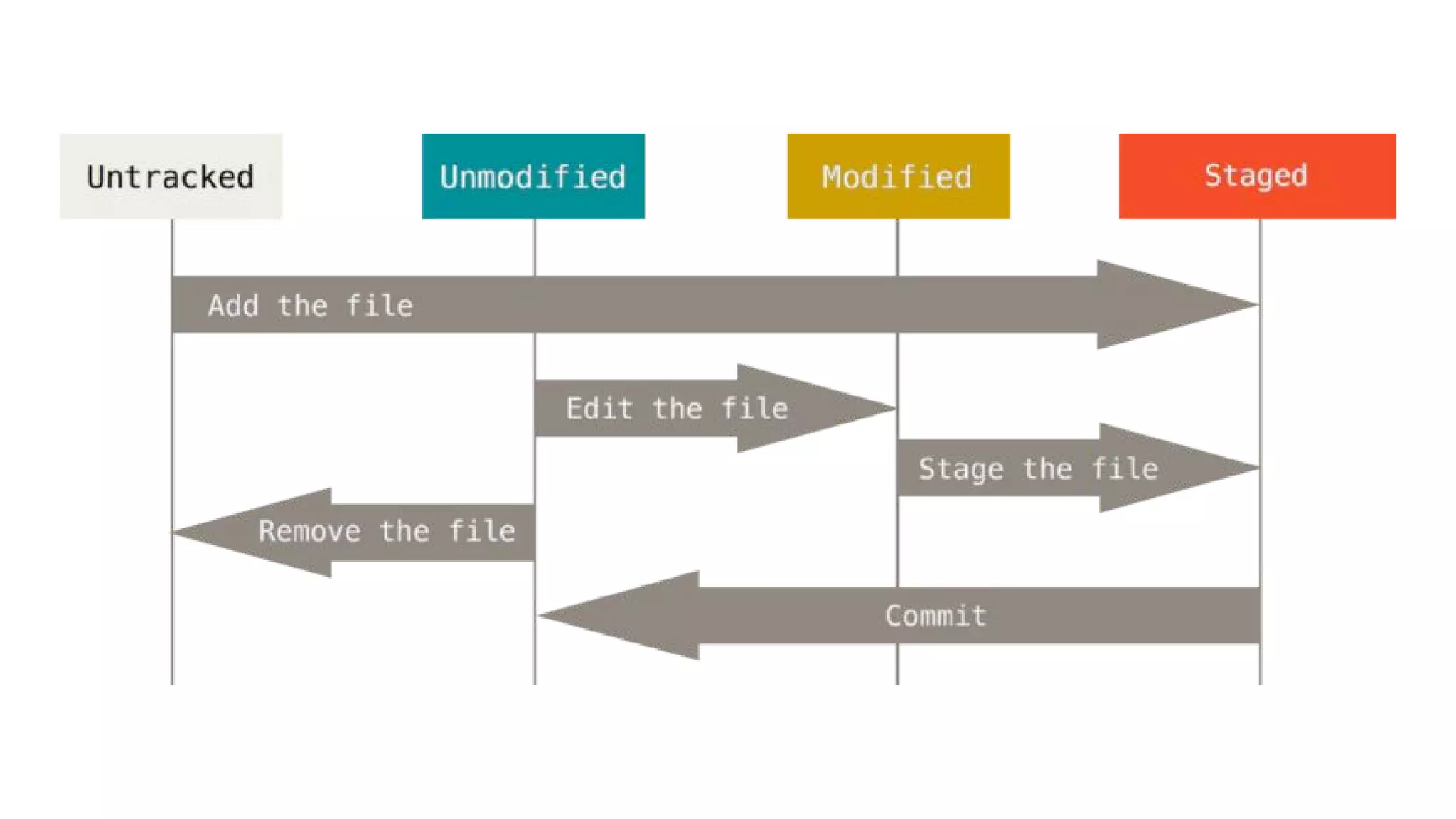
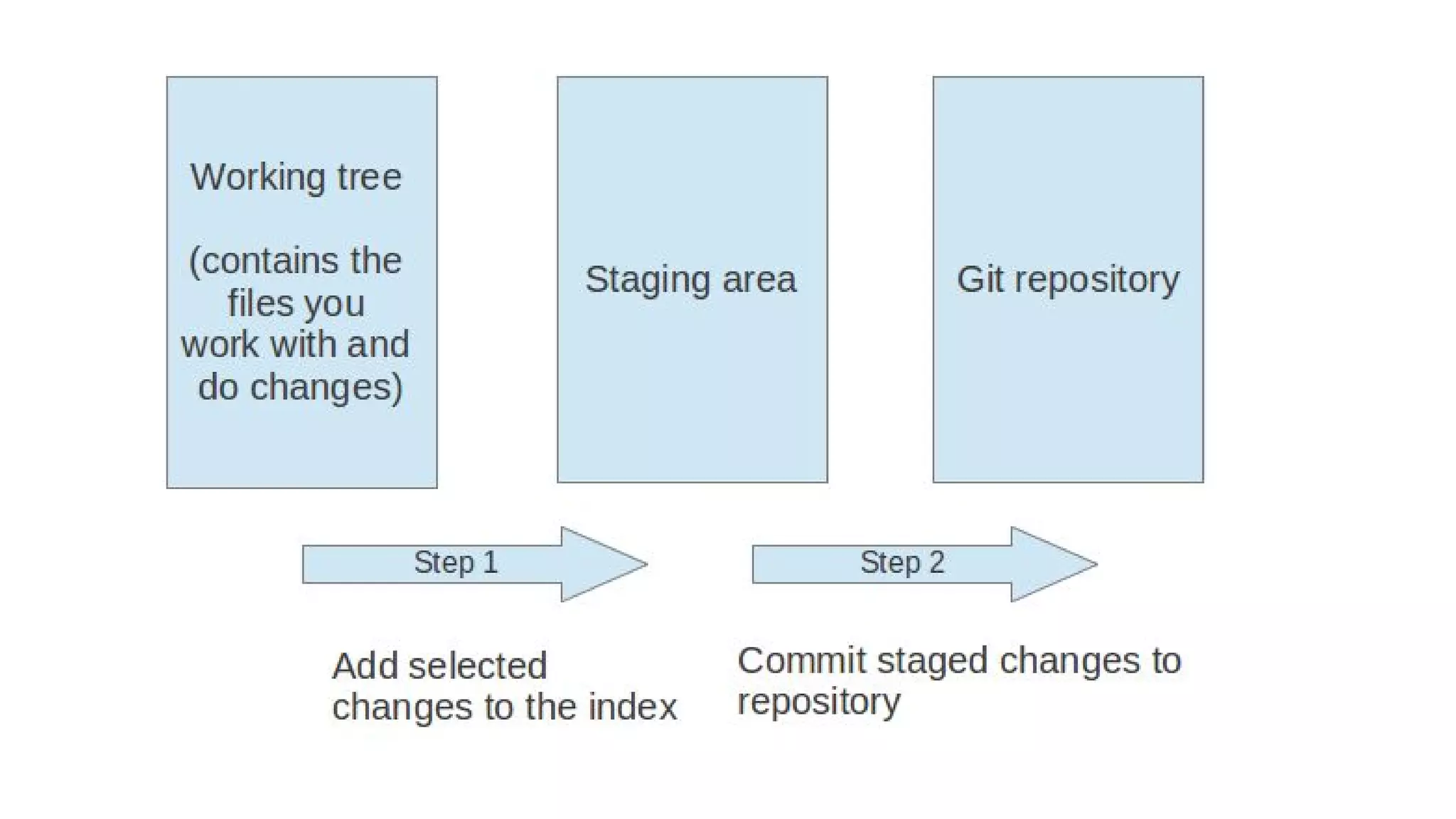
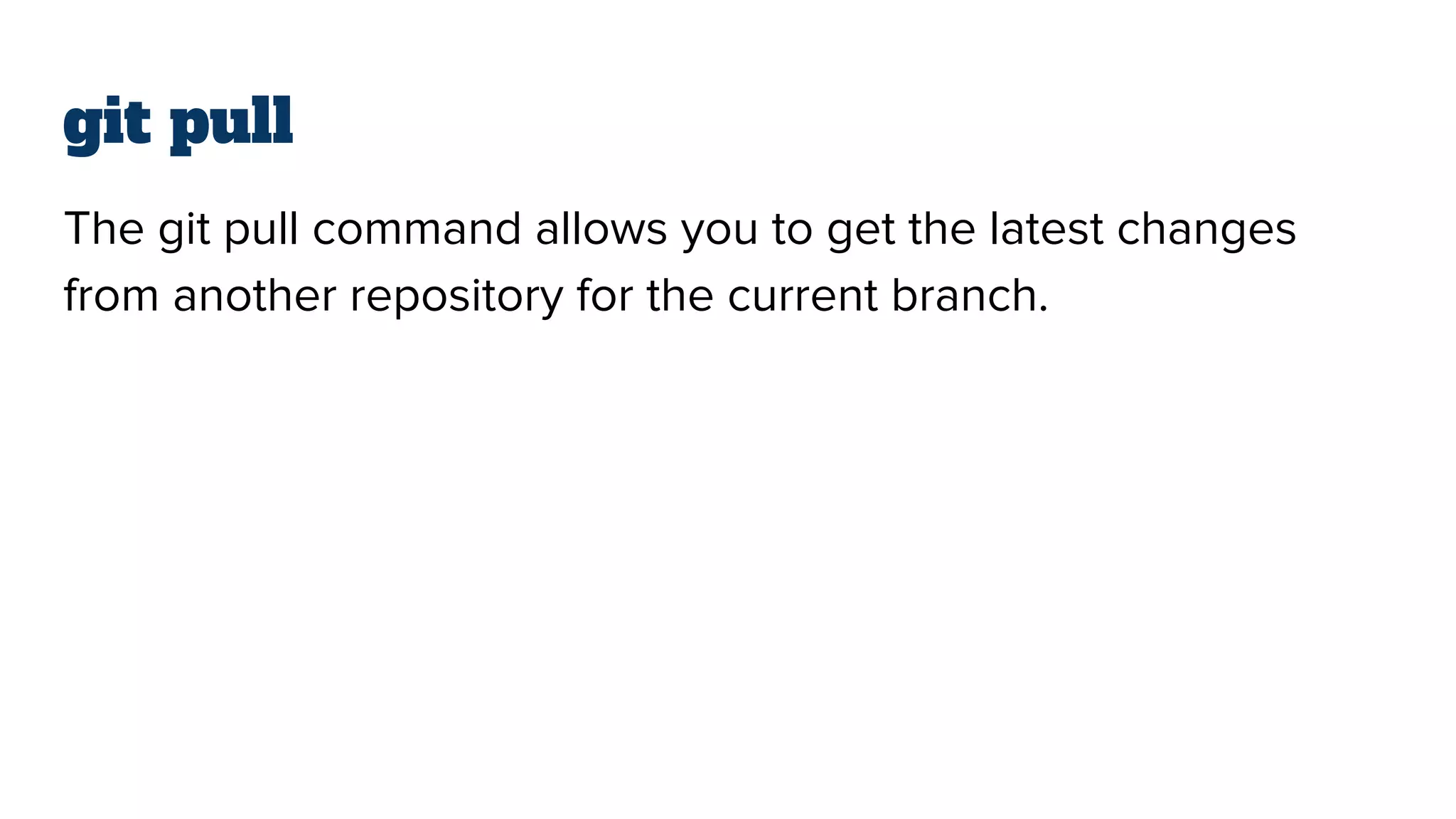
- The basic Git commands are git init to create a local repository, git add to stage files for the next commit, git commit to save file changes to the local repository, git clone to copy a remote repository, git pull to retrieve changes from the remote, and git push to upload local changes to the remote.
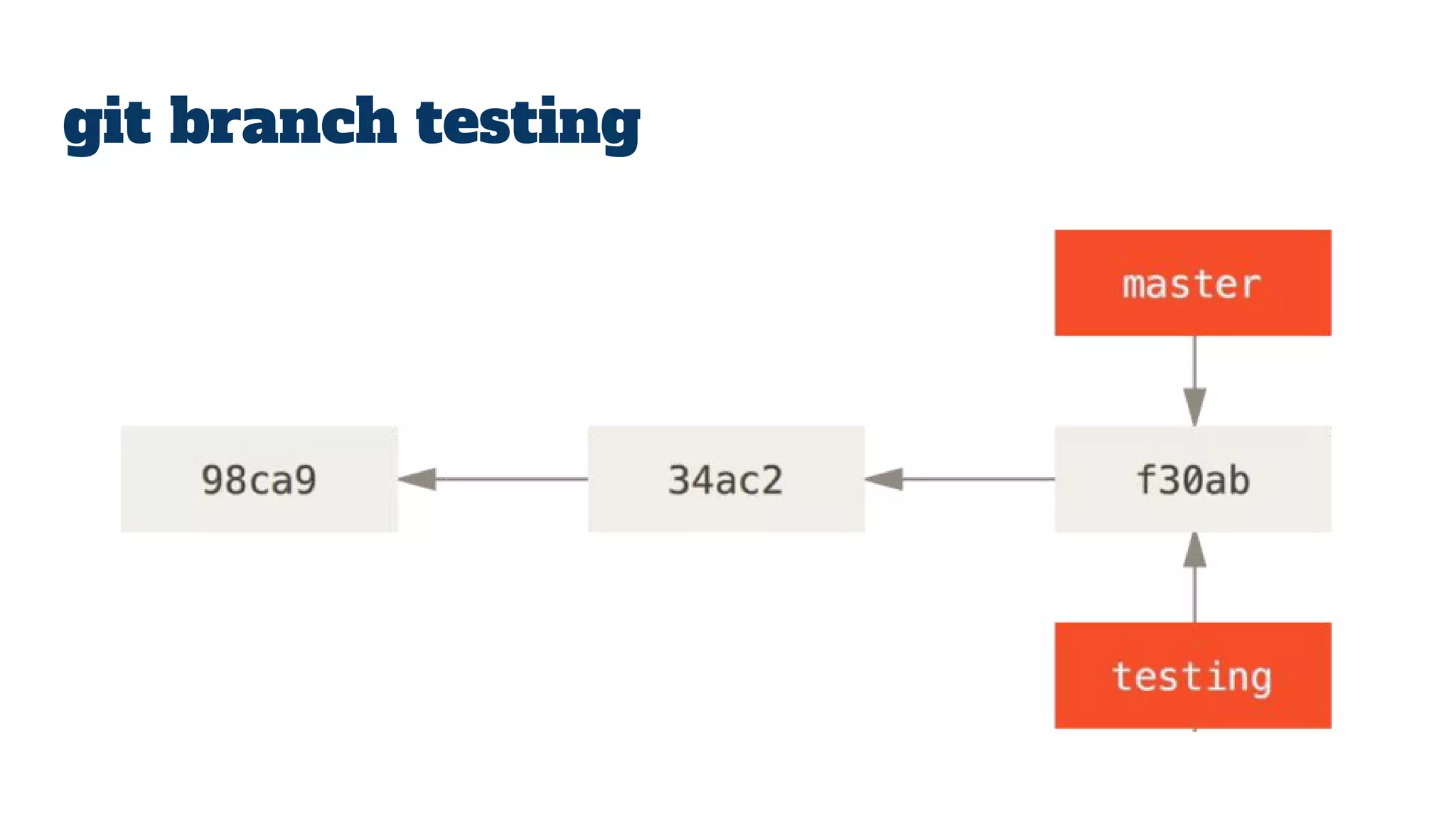
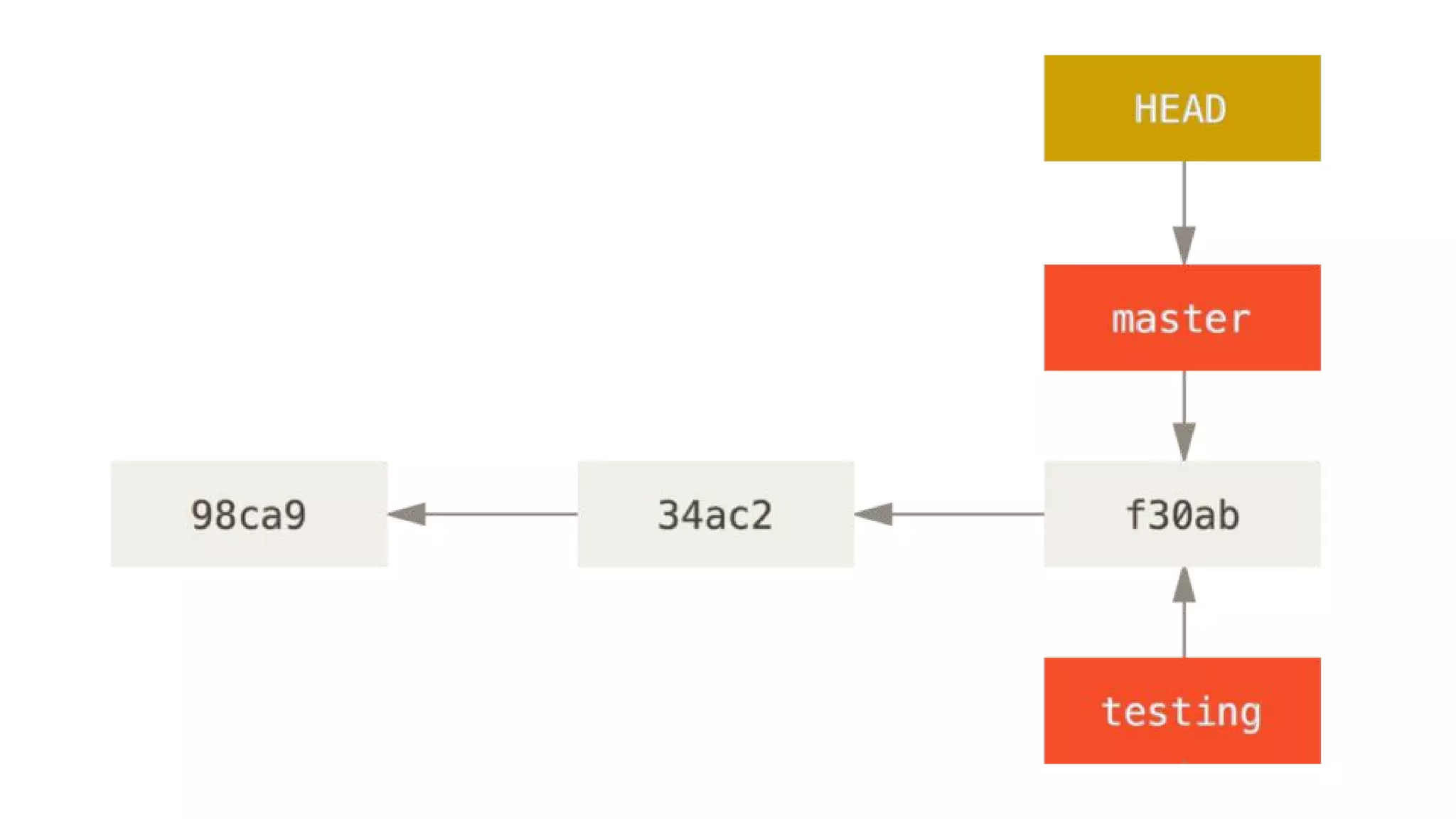
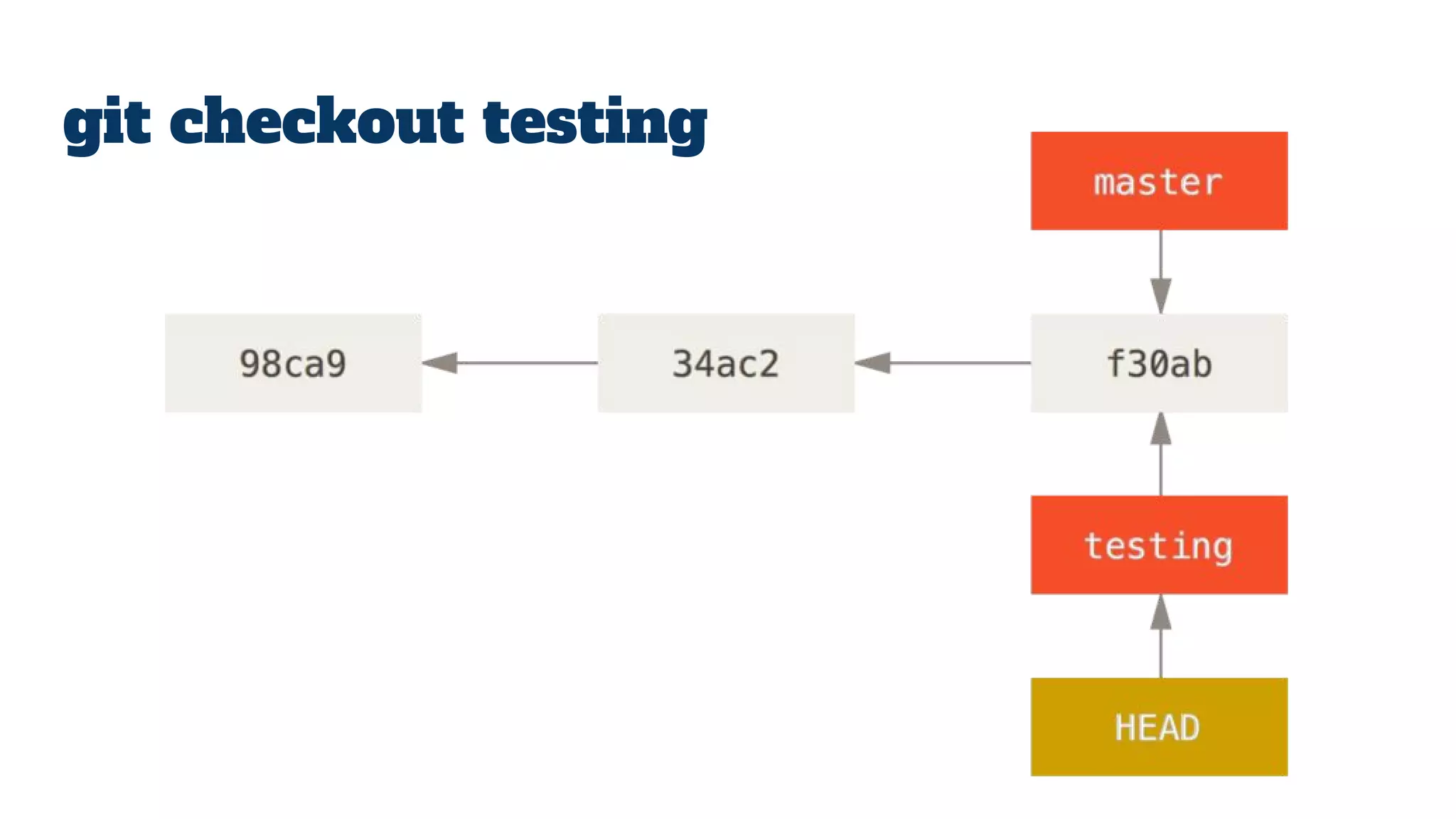
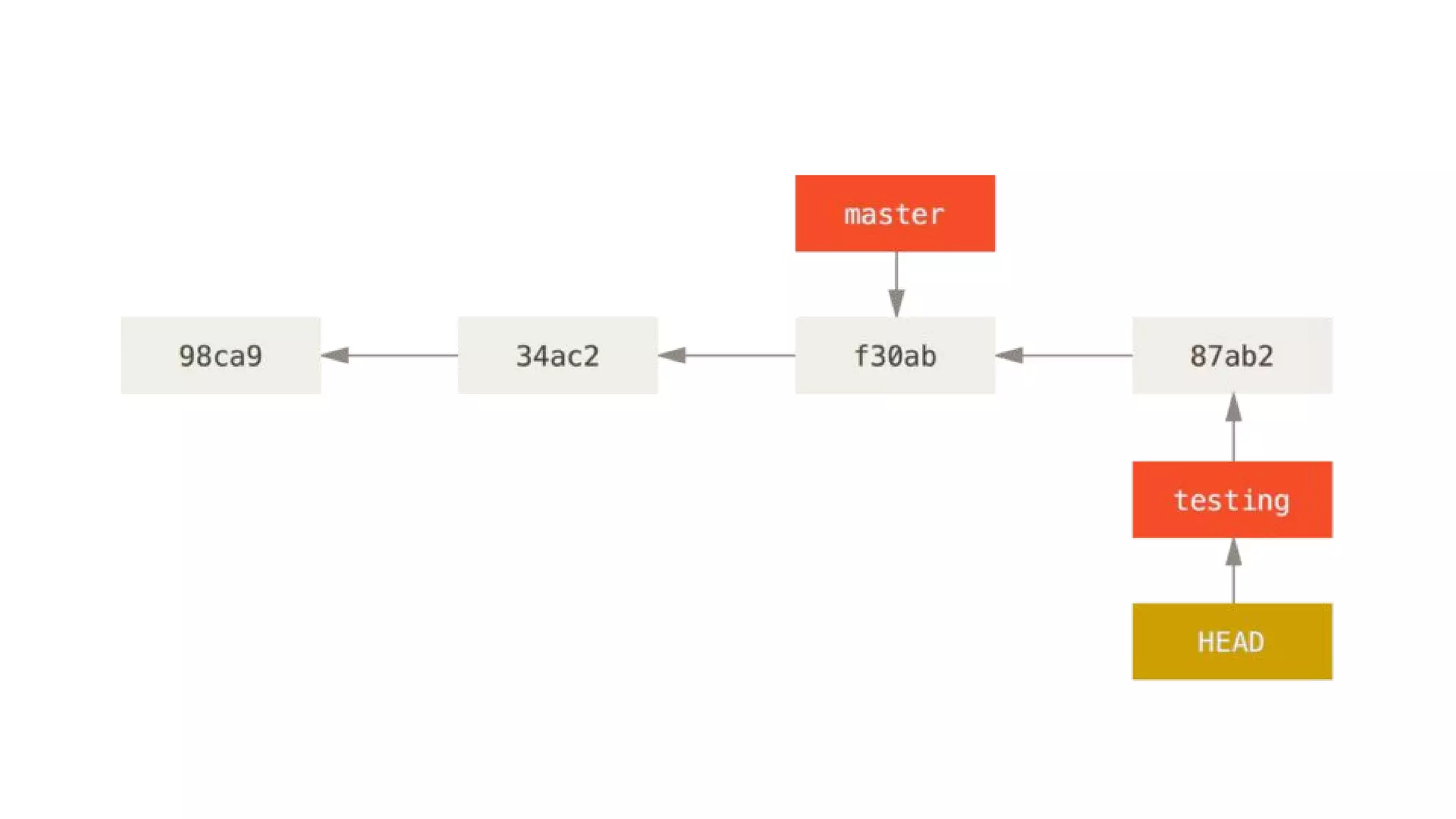
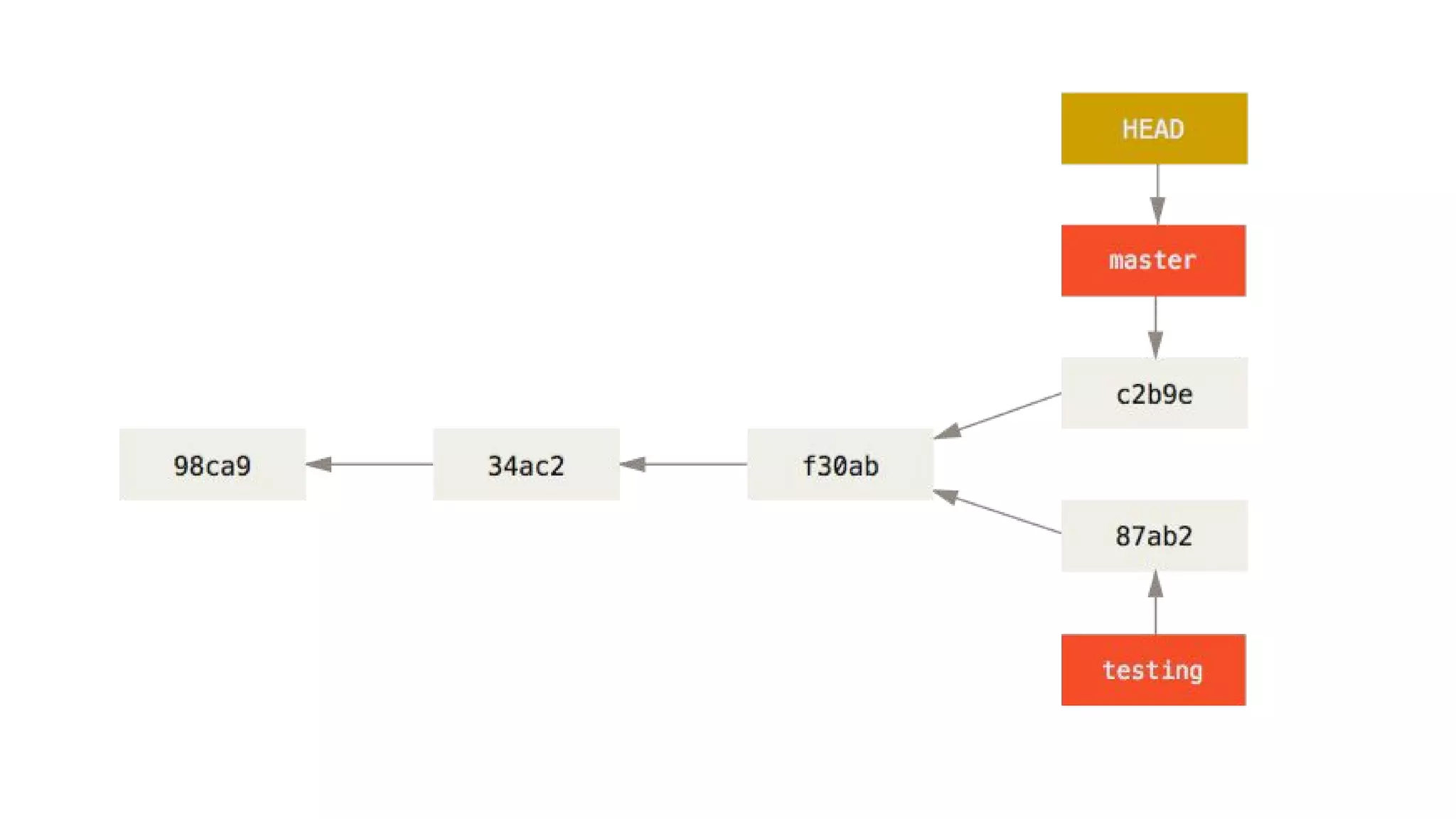
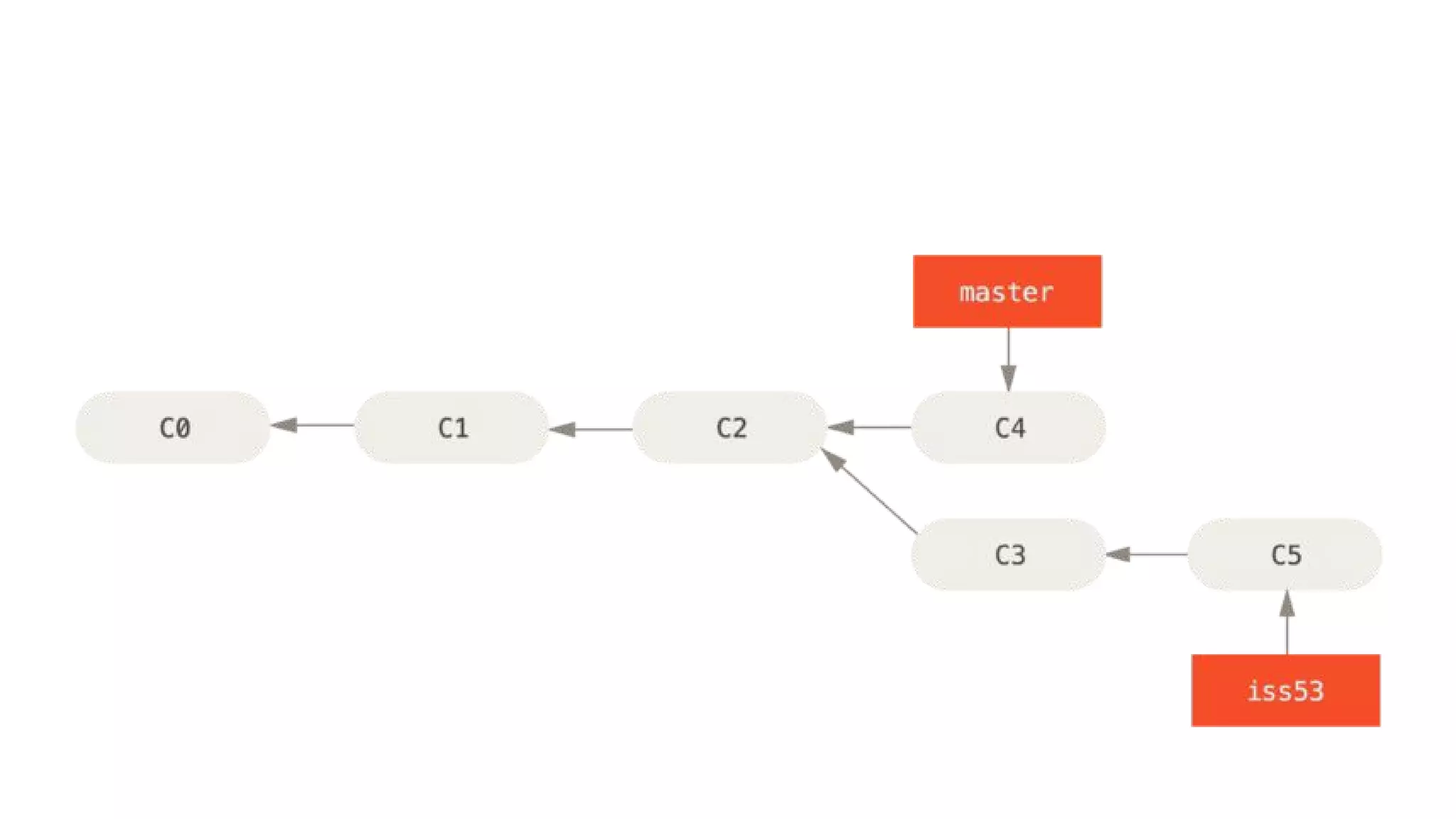
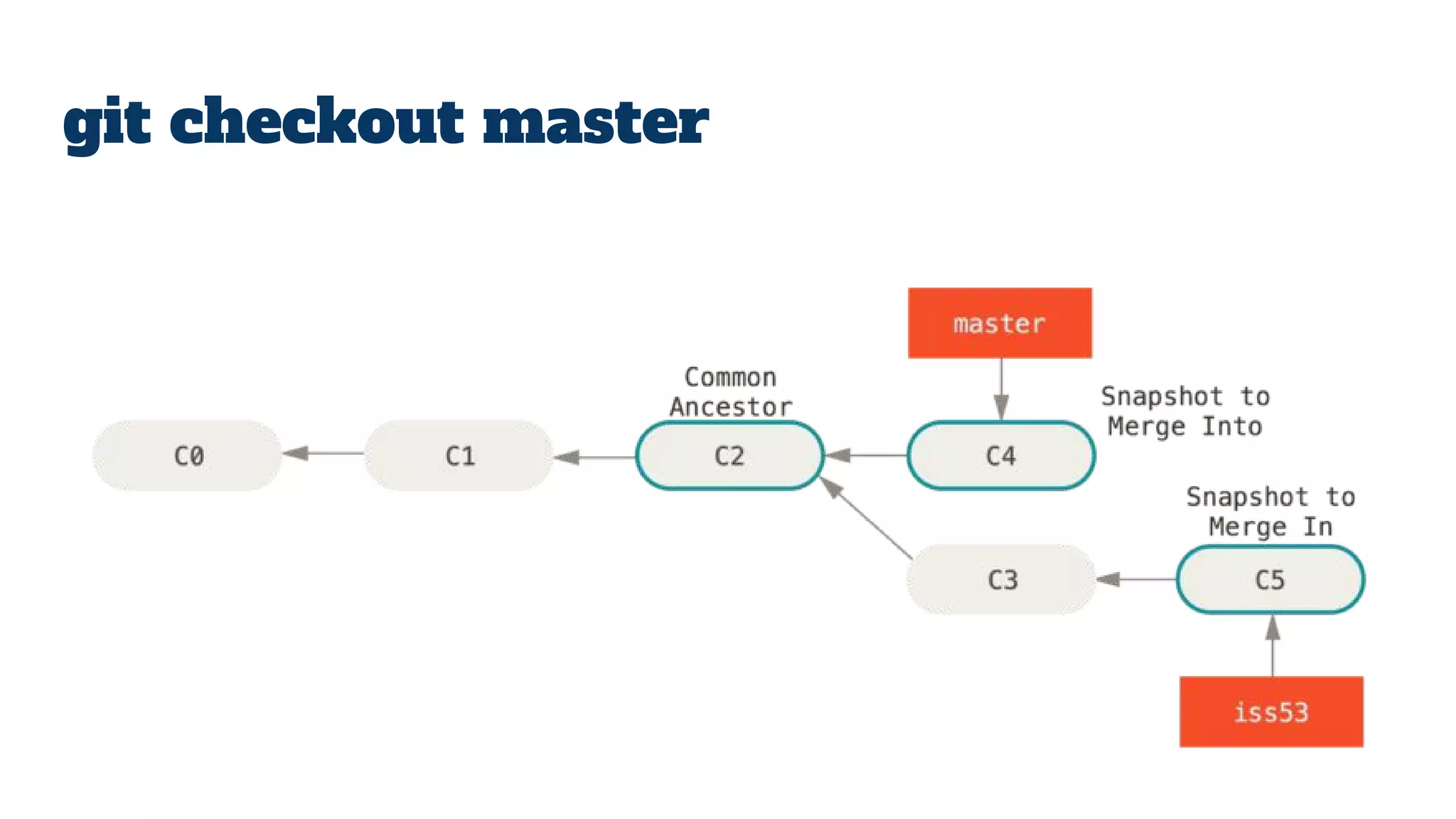
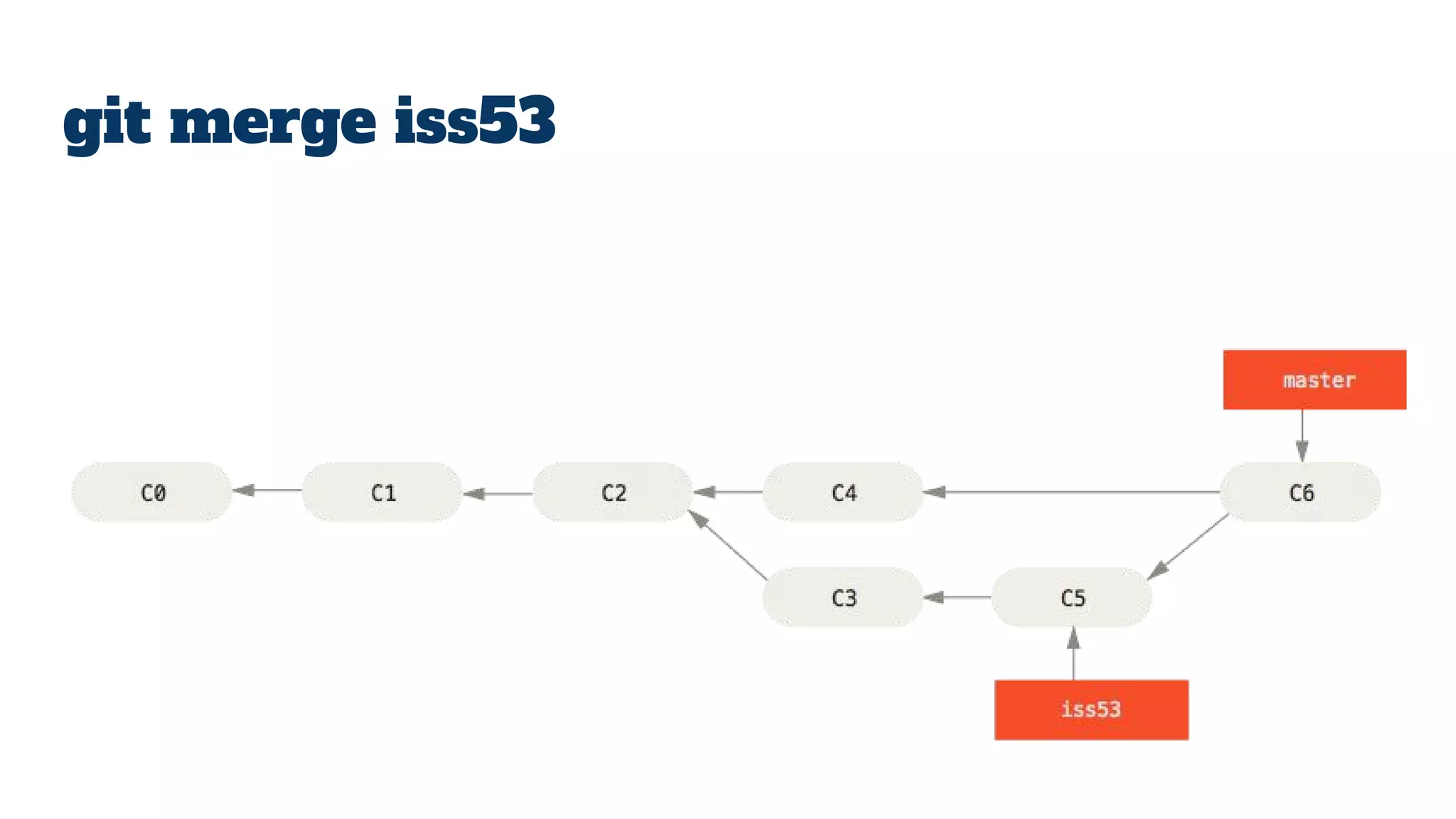
- Git repositories have branches to isolate different lines of development. The default branch is usually called master, but additional branches like testing can be created and merged back in.