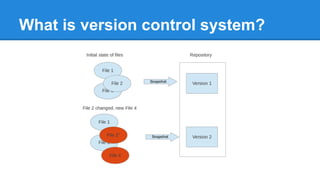
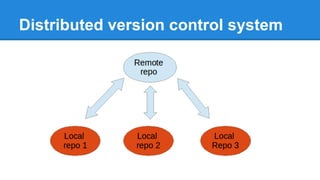
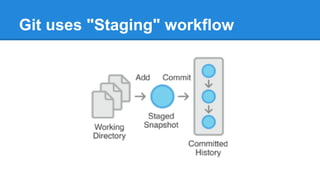
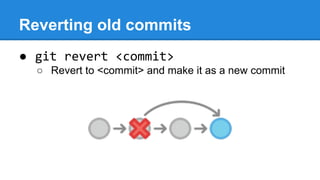
This document provides a simple introduction to Git, a distributed version control system. It explains what version control and distributed version control are. It then covers the basic Git concepts and commands for initializing and cloning repositories, staging and committing files, checking statuses and diffs, and working with remote repositories on GitHub. Key commands discussed include git init, git add, git commit, git status, git diff, git log, git remote add, git push, and git pull. The document encourages hands-on practice on the Try Git tutorial.