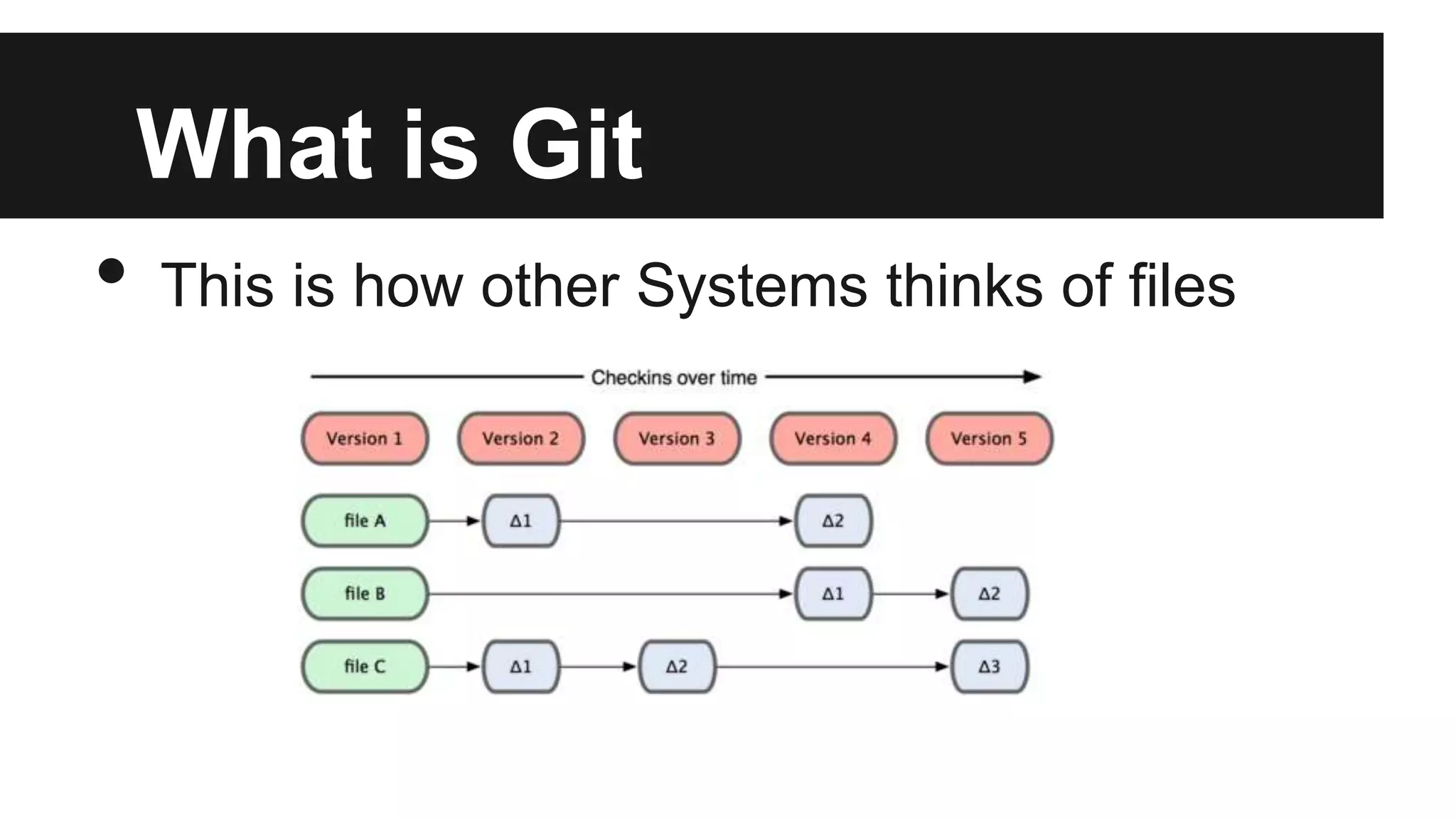
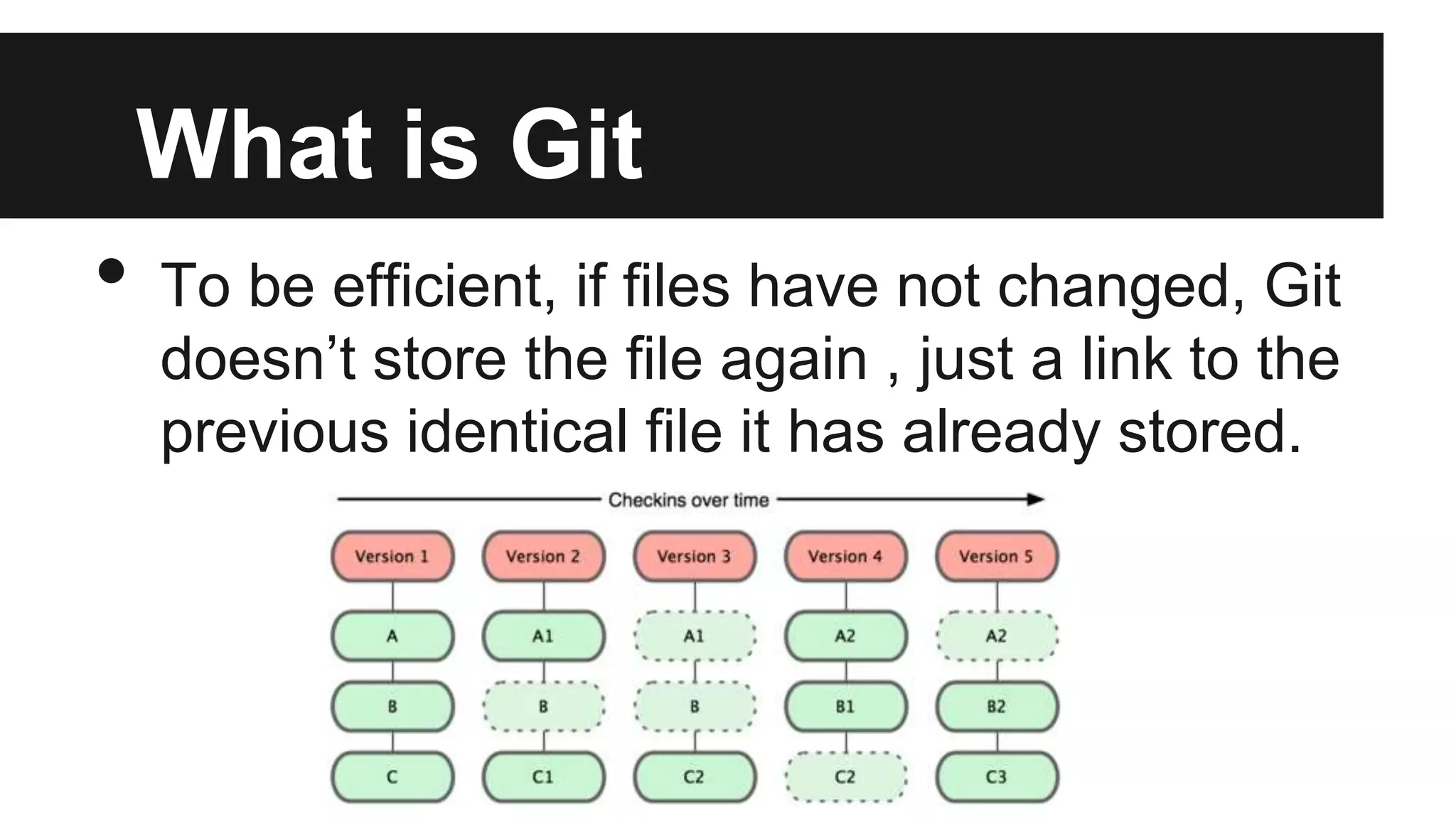
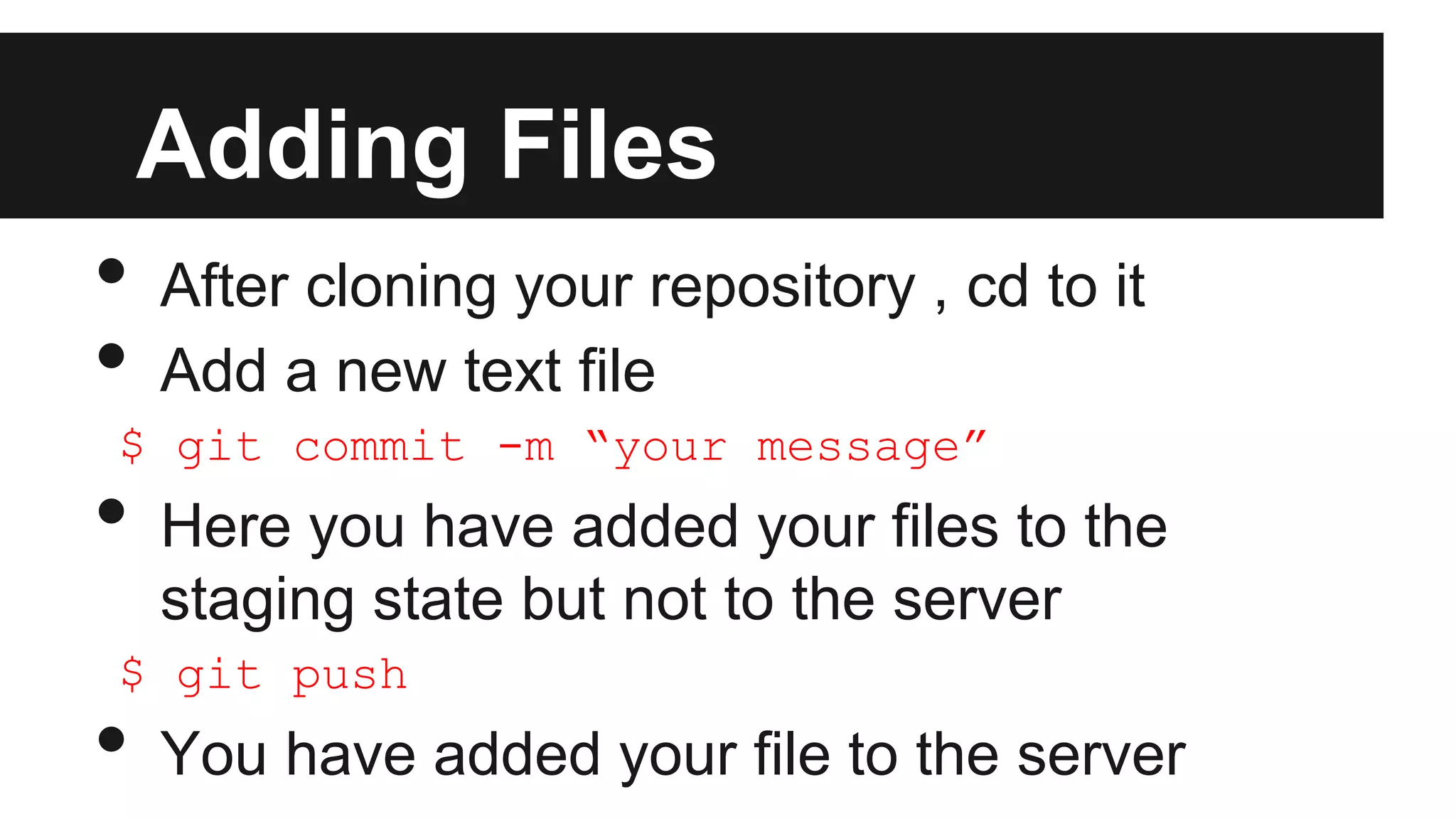
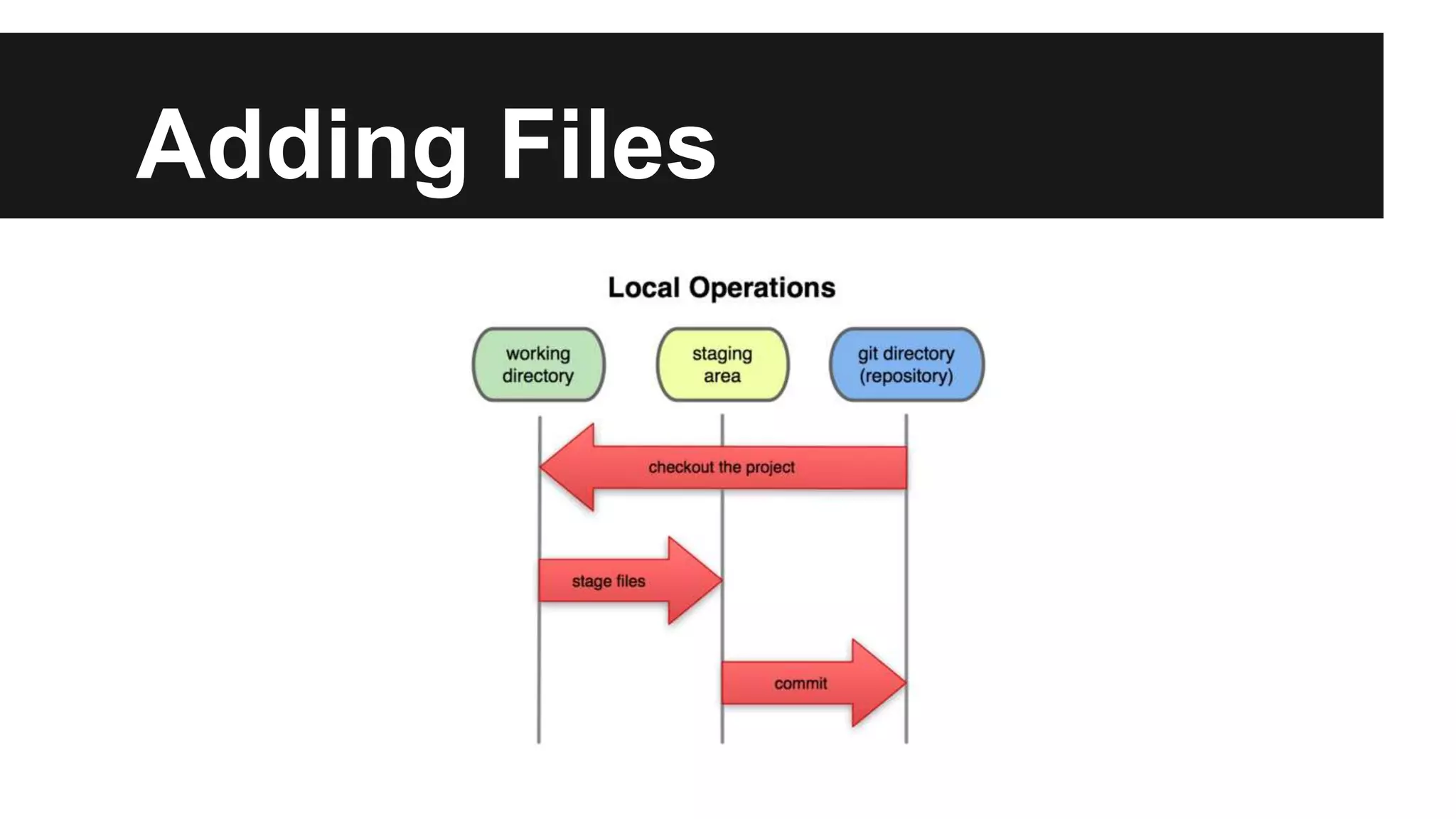
Git is a version control system that records changes to files over time by taking snapshots of the file system. It works by storing file changes as a set of snapshots rather than tracking file differences. This allows it to efficiently store unchanged files as links instead of re-storing the file. Some key Git concepts include cloning repositories, staging files, committing snapshots, pushing changes to remote repositories, branching to work on different versions, and stashing uncommitted changes. Submodules allow including other repositories within a repository.