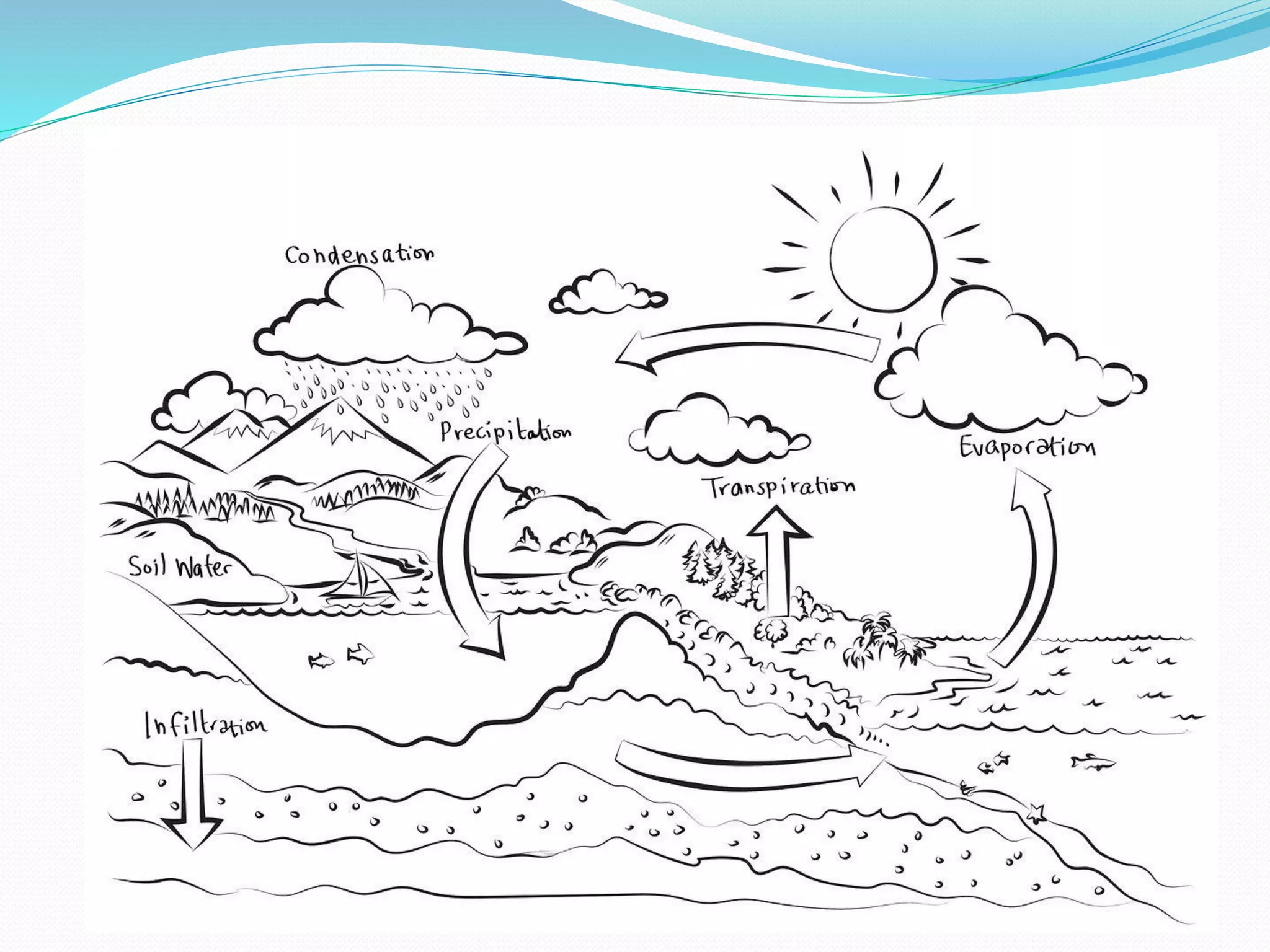
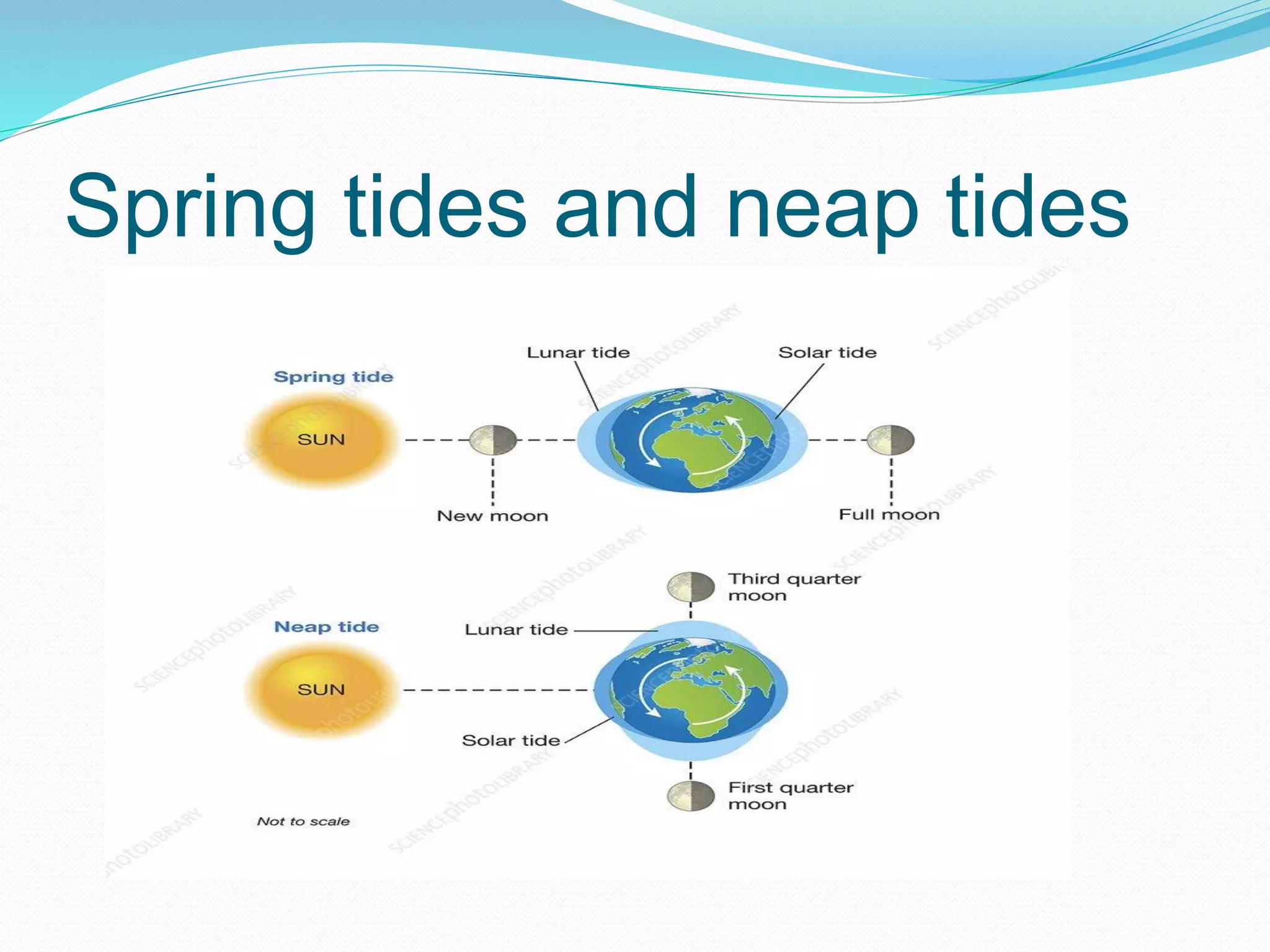
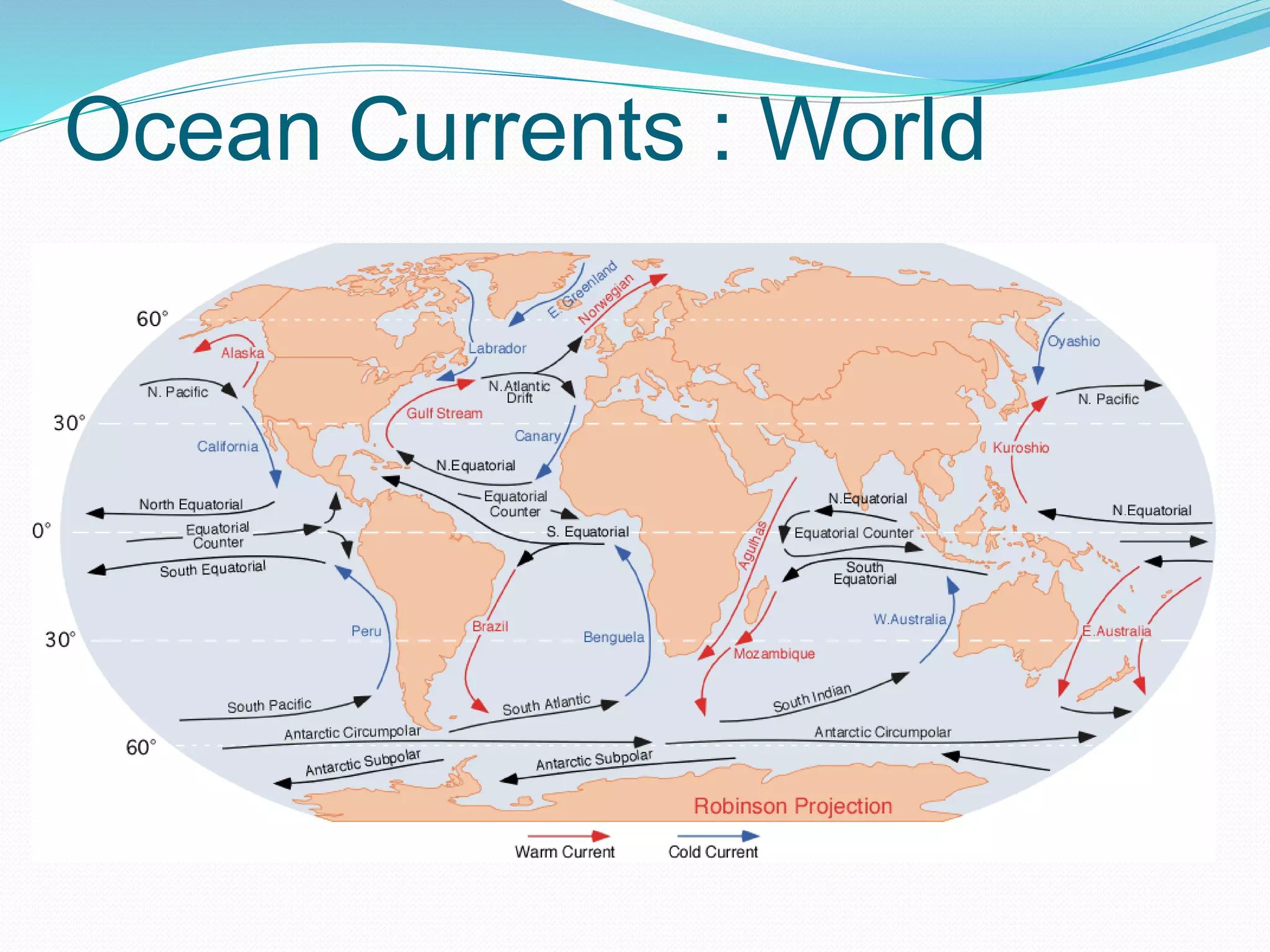
The document discusses the water cycle, highlighting evaporation, condensation, and precipitation as key processes. It details the distribution of water on Earth, noting that despite the abundance of water, many regions suffer from scarcity. Additionally, it explains ocean circulation phenomena such as waves, tides, and currents, emphasizing their importance for navigation, fishing, and climate influence.