This document provides an overview of getting started with Consul, including:
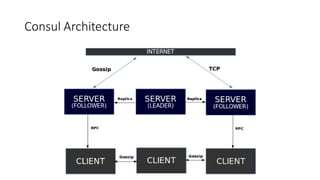
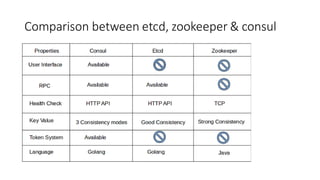
1. Consul is a tool for discovering and configuring services that is built on Golang and uses 3 basic ports for RPC, HTTP, and DNS.
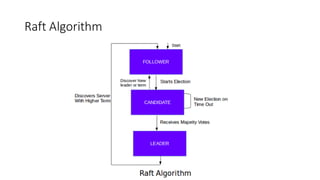
2. It features service discovery, health checking, key/value storage, and multi-datacenter support.
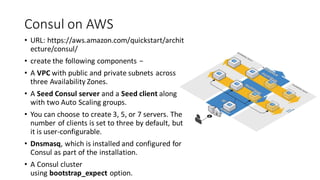
3. Setup involves downloading the Consul binary, running the agent, and using commands like "consul members" and "consul join" to manage nodes.