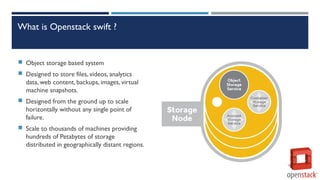
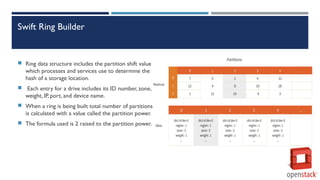
OpenStack Swift is an object storage system that can store large amounts of unstructured data and scale horizontally. It replicates data across multiple availability zones for redundancy. The Swift architecture uses rings, partitions, and replicas to determine where to store objects and find their locations. Clients can PUT, GET, and DELETE objects stored in containers within accounts via the Swift API and HTTP requests to the storage URLs.