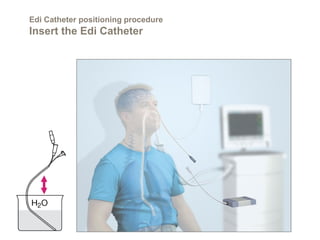
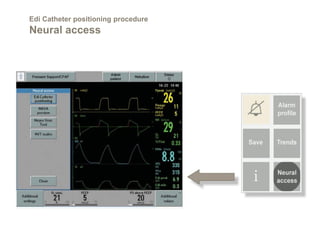
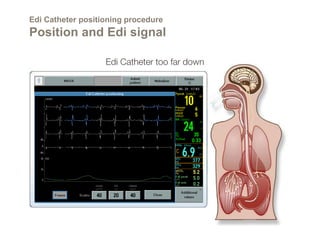
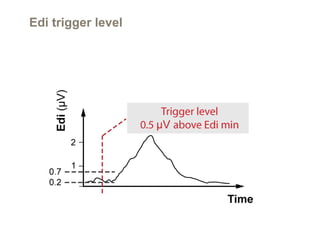
This document discusses Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist (NAVA), a mode of ventilation that uses diaphragm electrical activity (Edi) to trigger and cycle breaths. It describes the Edi catheter used to measure diaphragm activity, and the procedure for positioning the catheter. Settings for the NAVA mode include the NAVA level, trigger threshold, and cycling-off point. NAVA aims to improve patient-ventilator synchrony compared to other modes and allow proportional support based on patient effort.