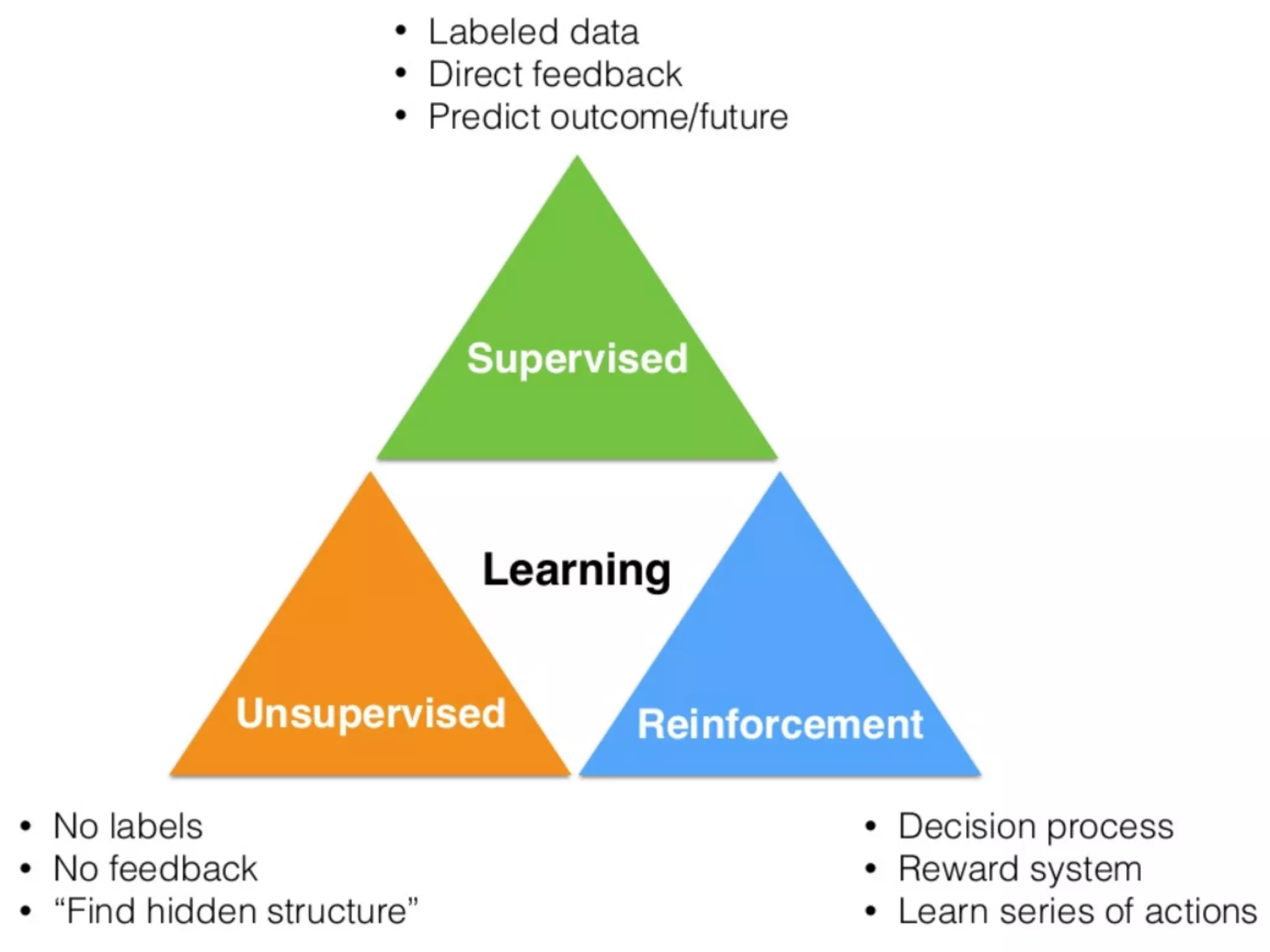
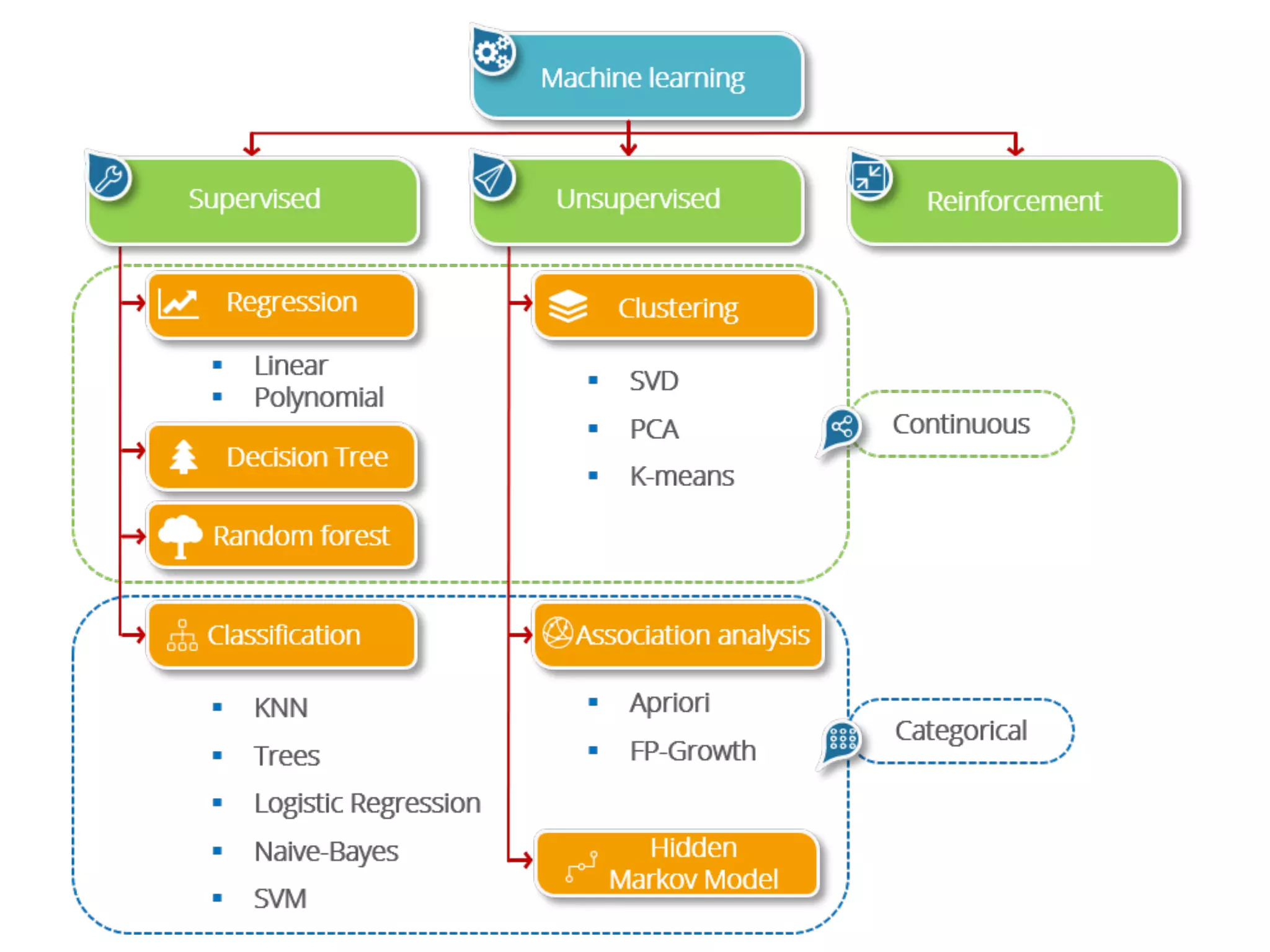
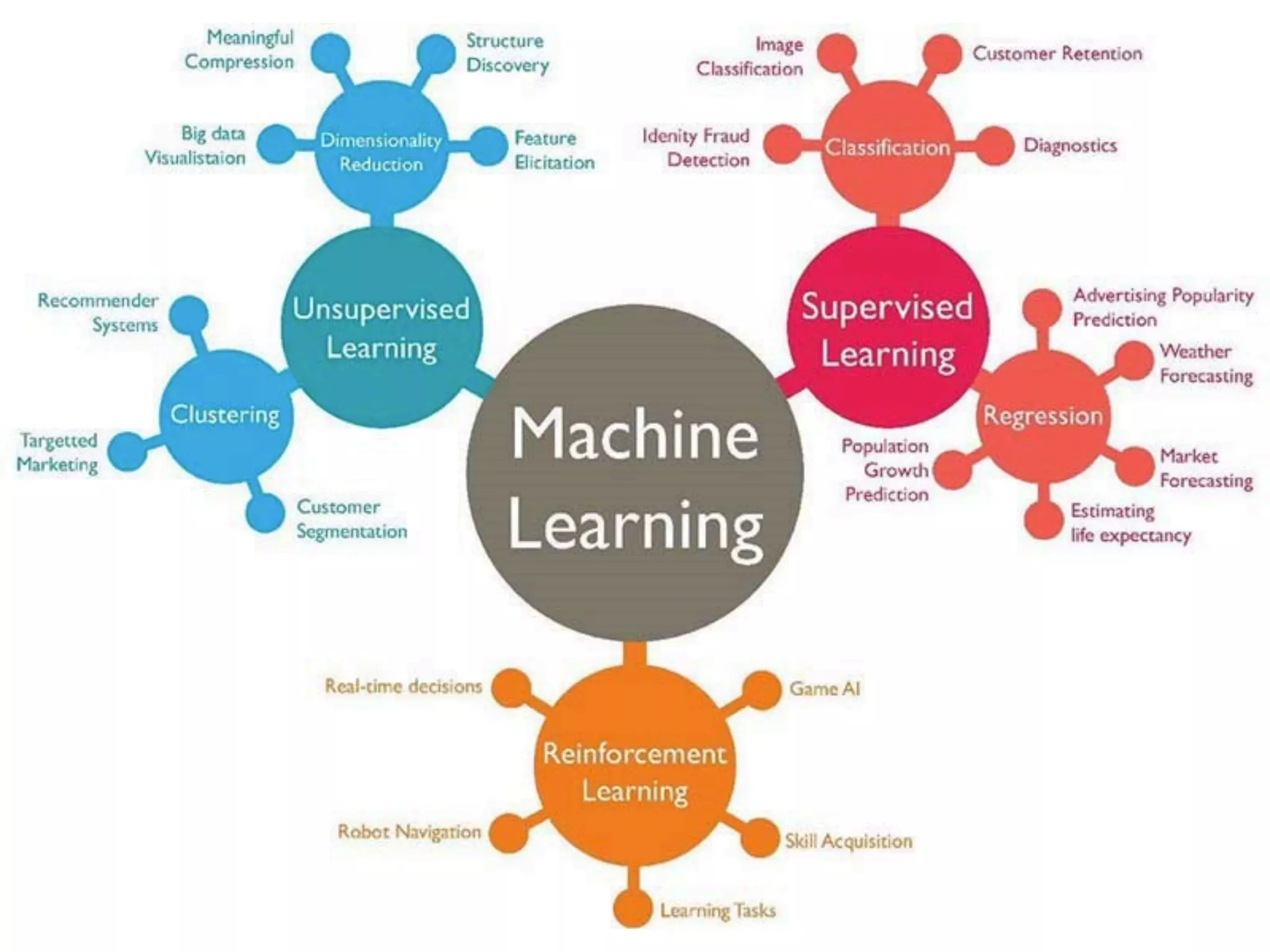
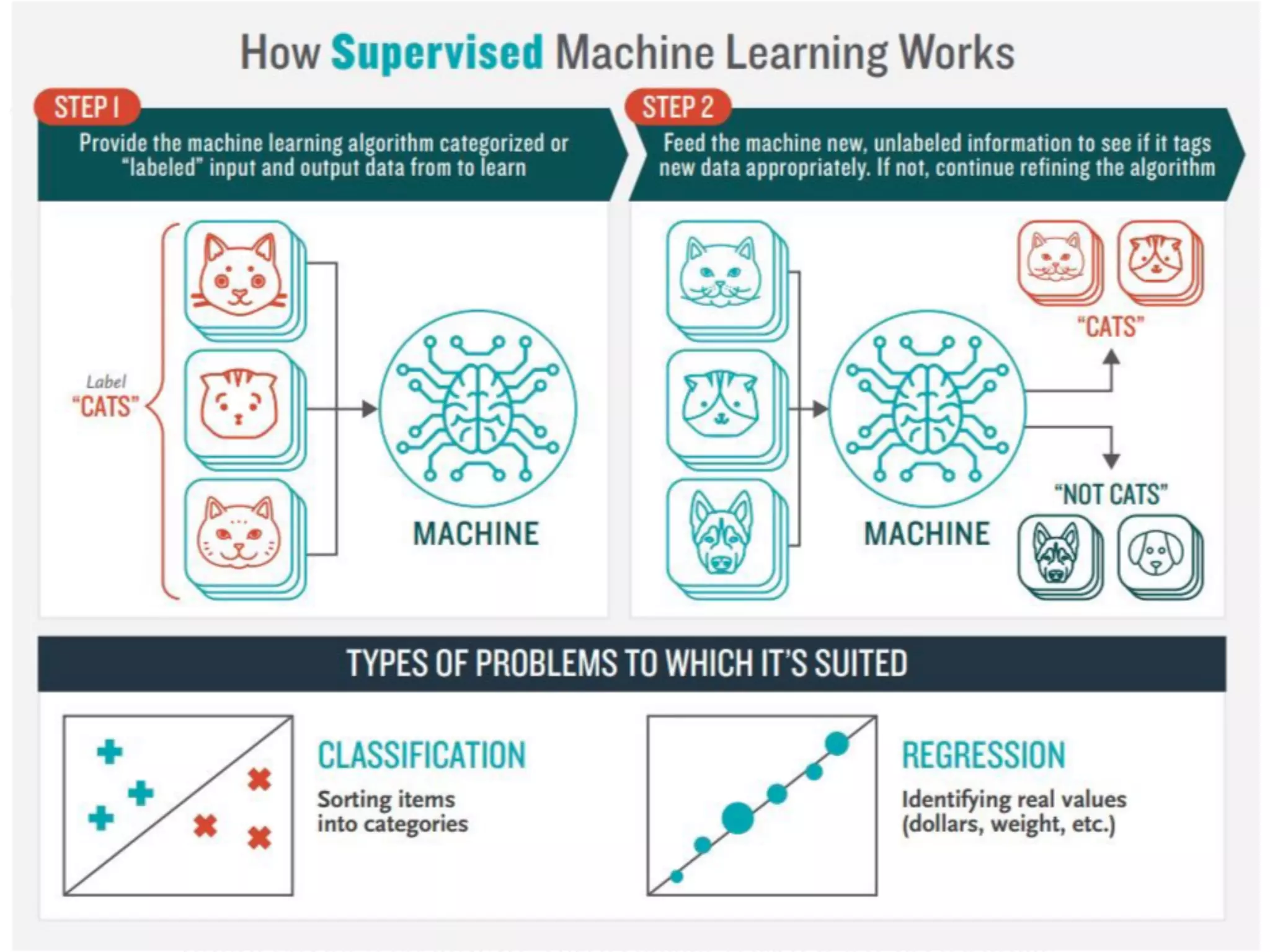
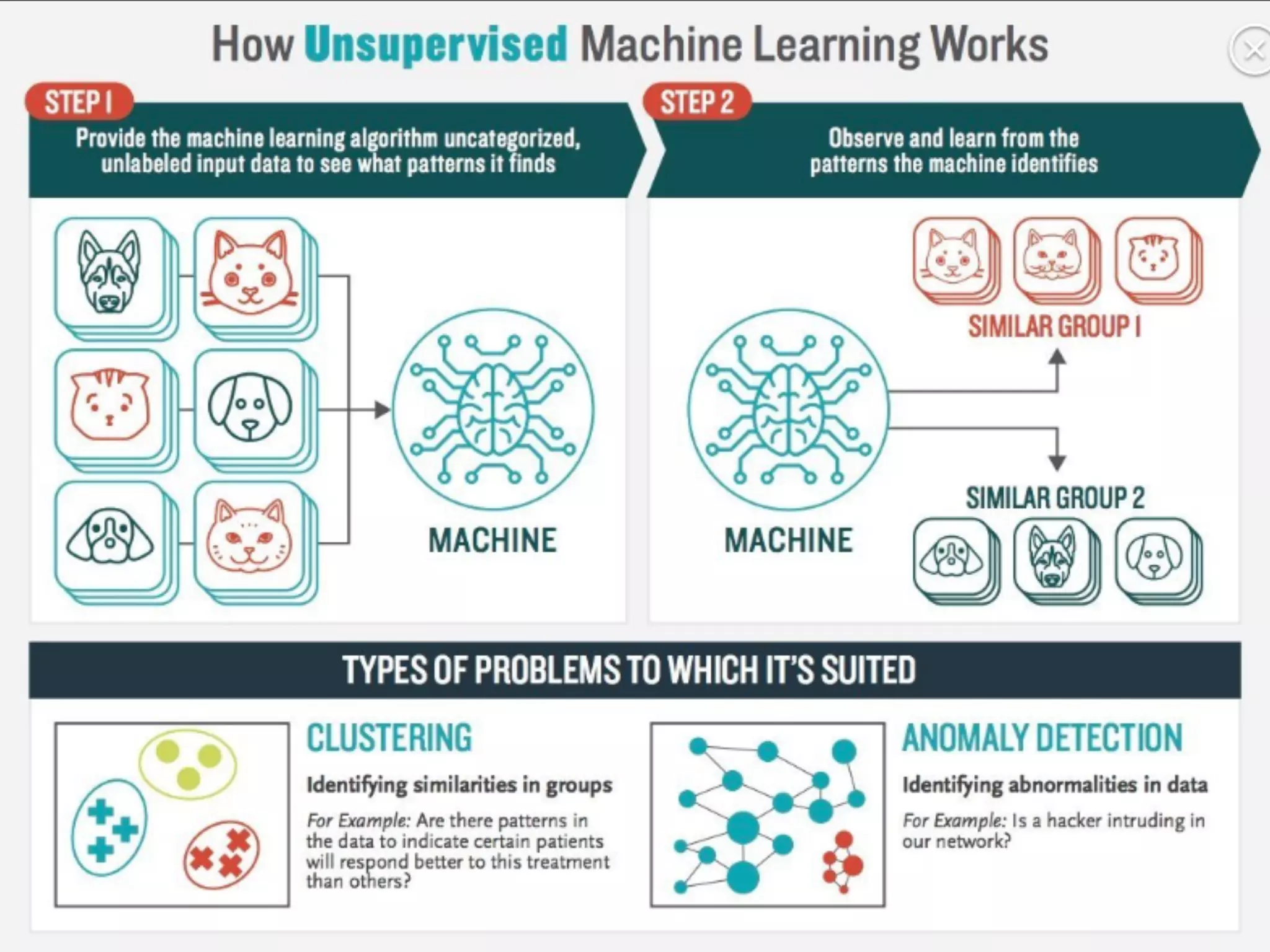
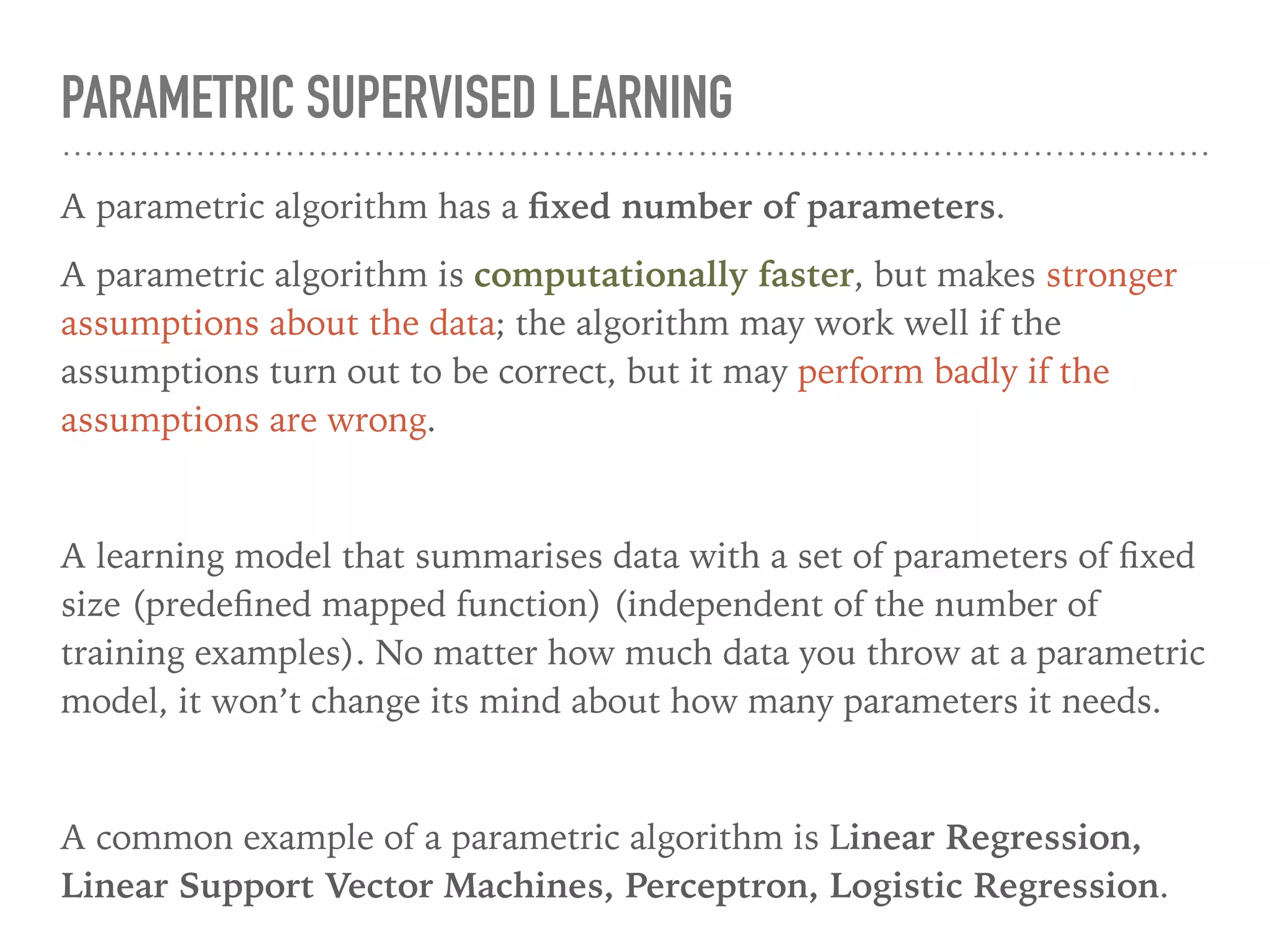
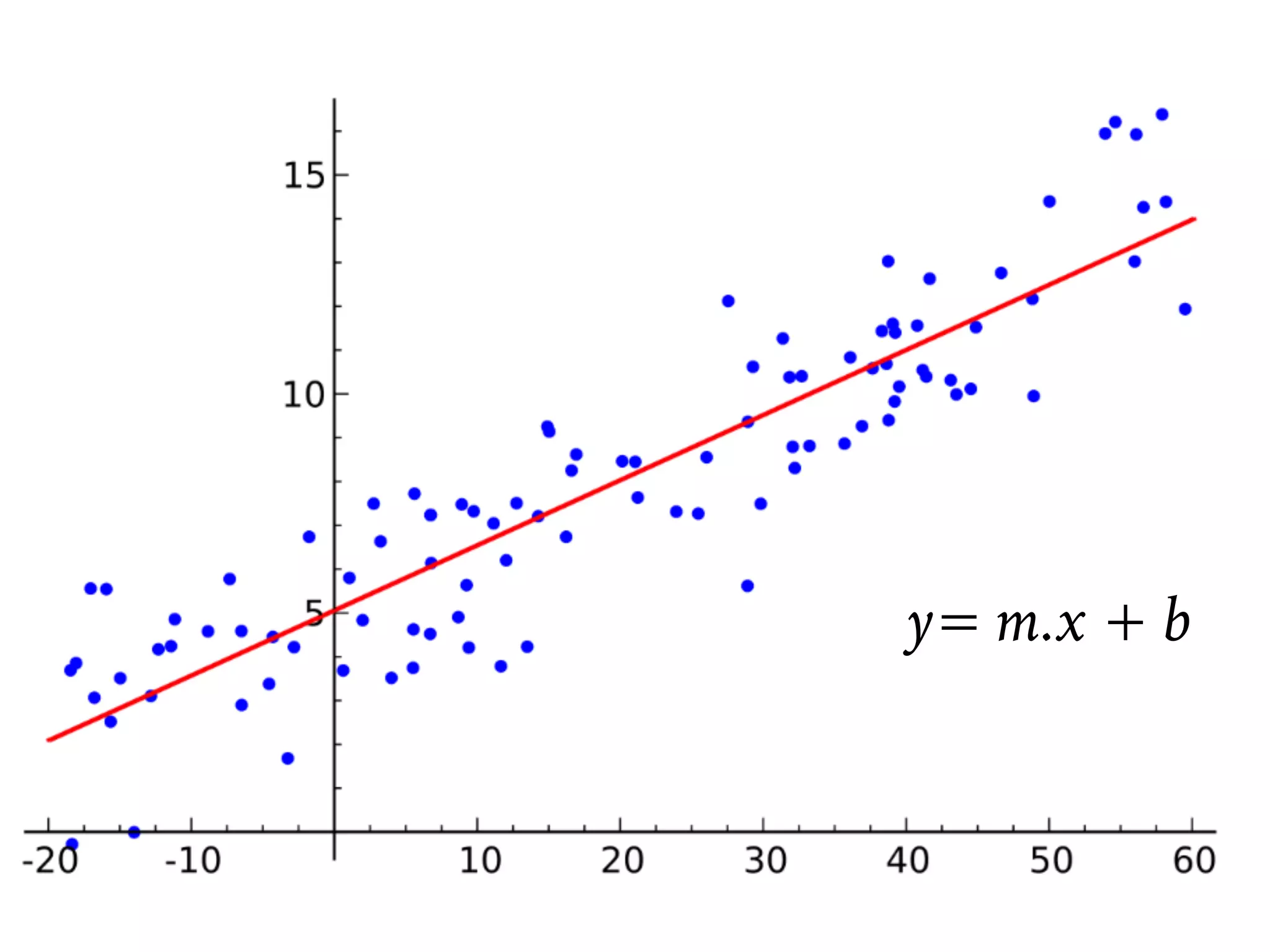
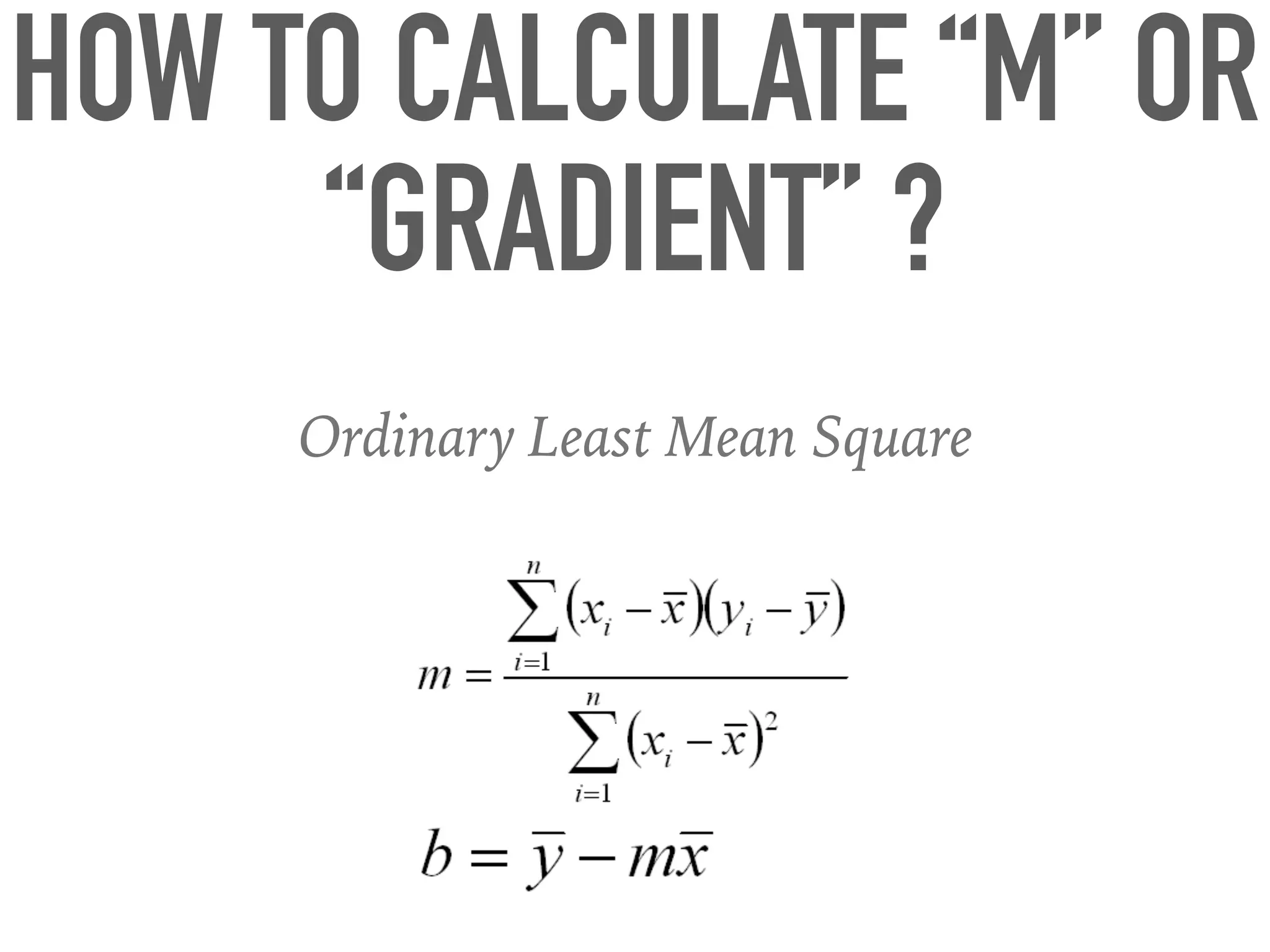
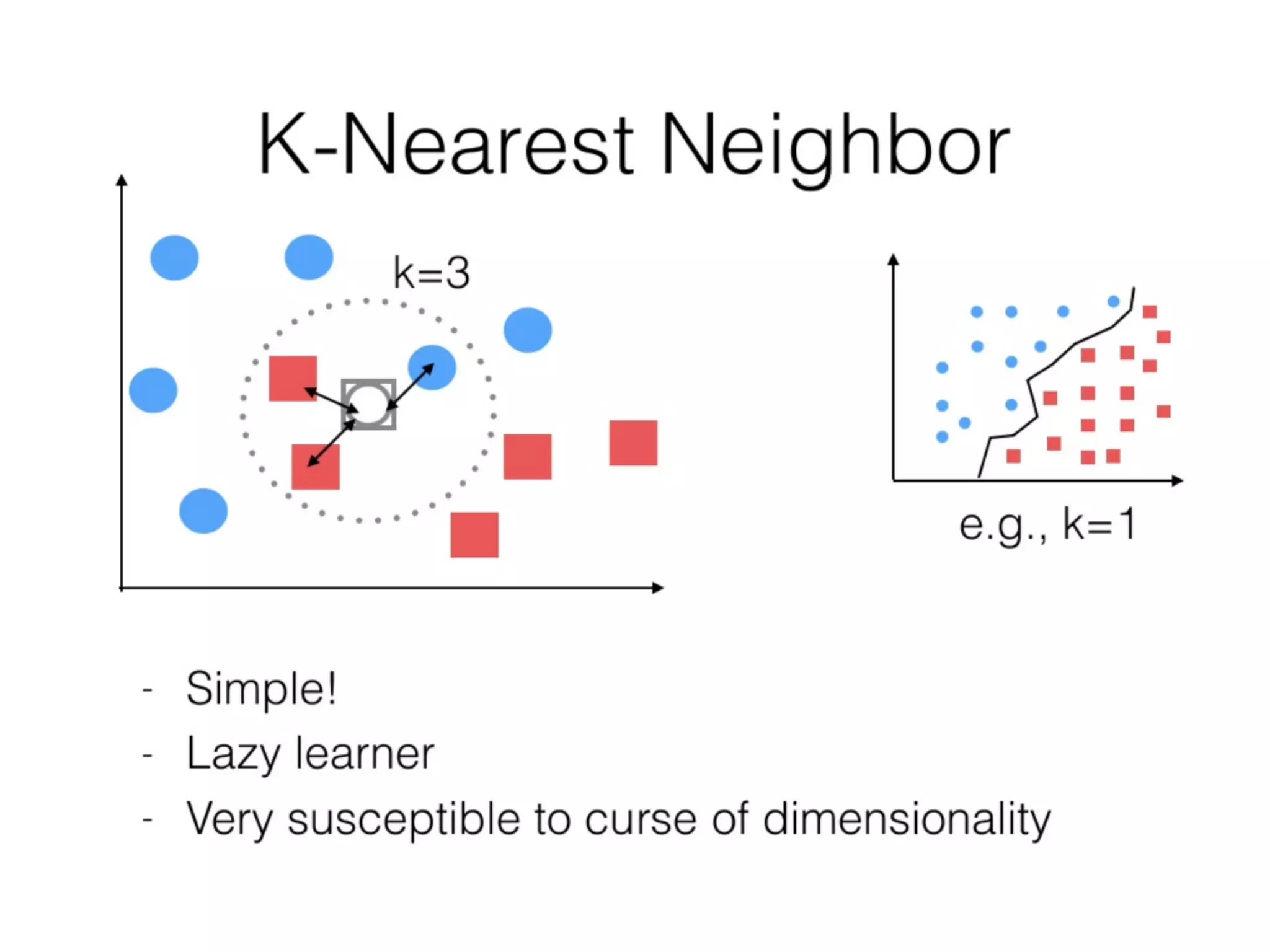
This document provides an overview of parametric and non-parametric supervised machine learning. Parametric learning uses a fixed number of parameters and makes strong assumptions about the data, while non-parametric learning uses a flexible number of parameters that grows with more data, making fewer assumptions. Common examples of parametric models include linear regression and logistic regression, while non-parametric examples include K-nearest neighbors, decision trees, and neural networks. The document also briefly discusses calculating parameters using ordinary least mean square for parametric models and the limitations when data does not follow predefined assumptions.