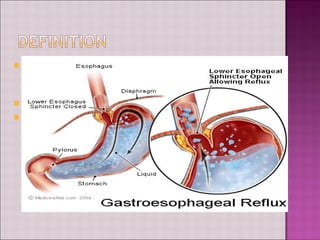
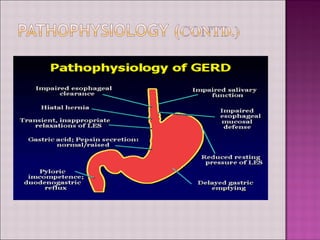
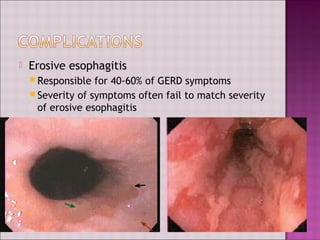
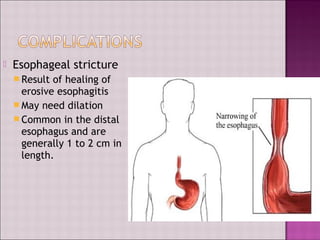
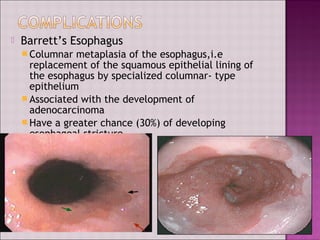
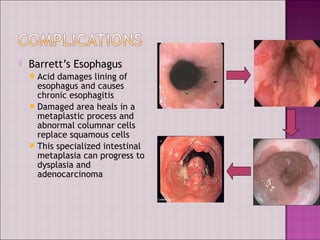
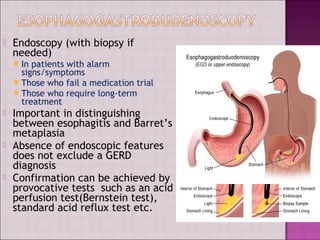
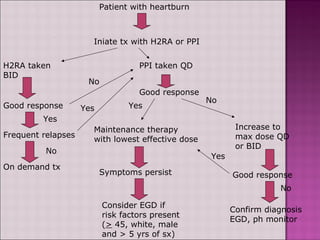
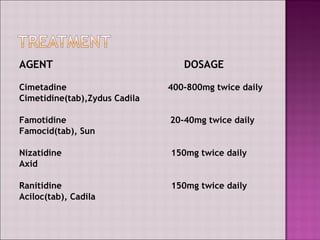
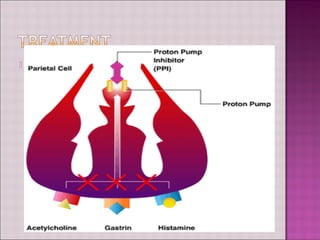
This document discusses gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It defines GERD as symptoms or mucosal damage caused by abnormal reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus. The main causes of GERD are disruption of the lower esophageal sphincter and other anatomical barriers. Clinical manifestations can include heartburn, regurgitation, or complications like erosive esophagitis or Barrett's esophagus. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications and medications like antacids, H2 receptor antagonists, or proton pump inhibitors. Surgery may be considered for severe cases that do not respond to medical management.