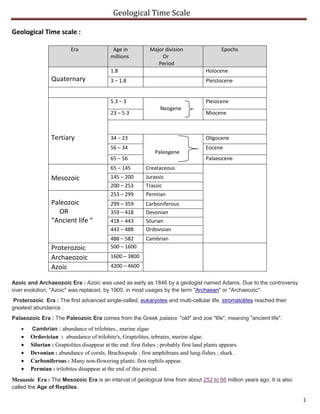
The geological time scale outlines Earth's history divided into eras, including the Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic, each containing various periods and epochs characterized by significant biological developments. Key highlights include the rise of trilobites and early aquatic life in the Paleozoic, the dominance of reptiles in the Mesozoic, and the emergence of mammals and flowering plants in the Cenozoic. The Quaternary era, the most recent, features two epochs marked by glaciation and the rise of modern humans.