3 -geologic time scale
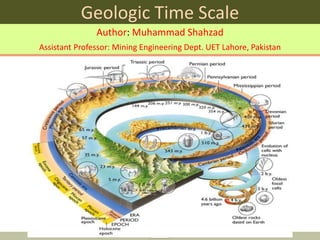
- 1. ENTER Geologic Time Scale Author: Muhammad Shahzad Assistant Professor: Mining Engineering Dept. UET Lahore, Pakistan
- 2. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN HADEAN Cryptic (4570 – 4150) Formation of Earth (4567.17 to 4570 Ma)
- 3. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN HADEAN Cryptic (4570 – 4150) Formation of Moon (4533 Ma) Oldest known mineral, Zircon (4406 ± 8 Ma) [Metamorphosed sandstone conglomerate of Jack Hills, Western Australia]
- 4. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN HADEAN Basin Group (4150 – 3920) Oldest known rock (4030 Ma) [The oldest known rock on Earth is found along the northeast coast of Hudson Bay, Canada.] First lifeforms, RNA (4000 Ma) Napier Orogeny in Antarctica (4000 ± 200 Ma)
- 5. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN HADEAN Basin Group (4150 – 3920) Oldest known rock (4030 Ma) [The oldest known rock on Earth is found along the northeast coast of Hudson Bay, Canada.] First lifeforms, RNA (4000 Ma) Napier Orogeny in Antarctica (4000 ± 200 Ma)
- 6. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN HADEAN Nectarian (3920 – 3850) Formation of Nectaris Basin and other major lunar basins by large impact events.
- 7. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN HADEAN Early Imbrian (3850 – 3800) End of the Late Heavy Bombardment of the inner solar system.
- 8. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN HADEAN Early Imbrian (3850 – 3800) Indirect photosynthetic evidence (e.g., kerogen) of primordial life
- 9. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN ARCHEAN Eoarchean (3800 – 3600) Simple single celled life (probably bacteria and perhaps archaea)
- 10. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN ARCHEAN Paleoarchean (3600 – 3200) First known oxygen-producing bacteria Oldest cratons on the earth (Canadian Shield & Pilbera Craton) Rayner Orogeny in Antarctica
- 11. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN ARCHEAN Paleoarchean (3600 – 3200) First known oxygen-producing bacteria Oldest cratons on the earth (Canadian Shield & Pilbera Craton) Rayner Orogeny in Antarctica
- 12. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN ARCHEAN Paleoarchean (3600 – 3200) First known oxygen-producing bacteria Oldest cratons on the earth (Canadian Shield & Pilbera Craton) Rayner Orogeny in Antarctica
- 13. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN ARCHEAN Mesoarchean (3200 – 2800) First stromatolites (colonial cyanobacteria) Humboldt Orogeny in Antarctica, Blake River Megacaldera Complex begins to form (present Ontario & Quebec)
- 14. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN ARCHEAN Mesoarchean (3200 – 2800) First stromatolites (colonial cyanobacteria) Humboldt Orogeny in Antarctica, Blake River Megacaldera Complex begins to form (present Ontario & Quebec)
- 15. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN ARCHEAN Mesoarchean (3200 – 2800) First stromatolites (colonial cyanobacteria) Humboldt Orogeny in Antarctica, Blake River Megacaldera Complex begins to form (present Ontario & Quebec)
- 16. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN ARCHEAN Neoarchean (2800 – 2500) Mantle overturn event Abitibi greenstone belt (present Ontario & Quebec)
- 17. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN ARCHEAN Neoarchean (2800 – 2500) Mantle overturn event Abitibi greenstone belt (present Ontario & Quebec)
- 19. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Paleoproterozoic Siderian (2500 – 2300) Oxygen catastrophe
- 20. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Paleoproterozoic Siderian (2500 – 2300) Banded iron formations
- 21. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Paleoproterozoic Siderian (2500 – 2300) Gawler Craton
- 22. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Paleoproterozoic Rhyacian (2300 – 2050) Huronian Glaciation Bushveld Formation
- 23. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Paleoproterozoic Orosirian (2050 – 1800) Oxygenic atmosphere Vredford & Sudbury Basin asteroids impacts
- 24. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Paleoproterozoic Orosirian (2050 – 1800) Oxygenic atmosphere Vredford & Sudbury Basin asteroids impacts Glenburgh (Capricorn) Orogeny in Australia
- 25. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Paleoproterozoic Orosirian (2050 – 1800) Oxygenic atmosphere Vredford & Sudbury Basin asteroids impacts Glenburgh Orogeny in Australia Kimban Orogeny in South Africa Ruker Orogeny in Antarctica
- 26. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Paleoproterozoic Statherian (1800 – 1600) First complex single celled life: protists with nuclei Mangaroon Orogeny in Western Australia Kararan Orogeny in South Australia
- 27. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Mesoproterozoic Calymmian (1600 – 1400) Barramundi Orogeny, MacArthur Basin, Northern Australia Isan Orogeny, Mount Isa Block, Queensland
- 28. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Mesoproterozoic Ectasian (1400 – 1200) Green algae in seas Grenville Orogeny in North America
- 29. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Mesoproterozoic Stenian (1200 – 1000) Formation of Rudinia Musgrave Orogeny, Musgrave Block, Central Australia
- 30. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Neooproterozoic Tonian (1000 – 850) Rodinia Supercontinent persists. Trace Fossils of multi celled eukaryotes
- 31. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Neooproterozoic Tonian (1000 – 850) Beginning of Adelaide Geosyncline in Australia
- 32. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Neooproterozoic Tonian (1000 – 850) Pan-African Orogeny
- 33. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Neooproterozoic Cryogenian (850 – 630) Snowball Earth period
- 34. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Neooproterozoic Cryogenian (850 – 630) Rodinia landmass begins to break up
- 35. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Neooproterozoic Cryogenian (850 – 630) Rodinia landmass begins to break up
- 36. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Neooproterozoic Cryogenian (850 – 630) Rodinia landmass begins to break up
- 37. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Neooproterozoic Ediacaran (630 – 542) Ediacaran biota flourish worldwide in seas Simple trace fossils of worm-like Trichophysus, etc.
- 38. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Neooproterozoic Ediacaran (630 – 542) First sponges and trilobitomorphs Soft-jellied creatures shaped like bags, discs, or quilts (like Dickinsonia)
- 39. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Neooproterozoic Ediacaran (630 – 542) Taconic Orogeny in North America
- 40. Geologic Time Scale PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC Neooproterozoic Ediacaran (630 – 542) Aravelli Range orogeny in Indian subcontinent
- 41. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Cambrian (542 – 488.3) Most modern phyla First chordates Trilobites, priapulid worms, sponges, inarticulate brachiopods etc.
- 42. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Cambrian (542 – 488.3) Anomalocarids
- 43. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Cambrian (542 – 488.3) Many Ediacaran fauna die out Prokaryotes, protists & fungi continue to present day Gondwana emerges Atmospheric CO2 content roughly 20-35 times present-day
- 44. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Ordovician (488.3 – 443.7) Invertebrates diversify into many types long straight-shelled cephalopods. Early corals, articulate brachiopods, bivalves, ostracods, many types of echinoderms (crinoids, cystoids, starfish, etc.) branched graptolites, and other taxa all common.
- 45. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Ordovician (488.3 – 443.7) Invertebrates diversify into many types long straight-shelled cephalopods. Early corals, articulate brachiopods, bivalves, ostracods, many types of echinoderms (crinoids, cystoids, starfish, etc.) branched graptolites, and other taxa all common.
- 46. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Ordovician (488.3 – 443.7) Condents appear First green plants and fungi on land Ice age at end of period
- 47. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Silurian (443.7 – 416.0) First vascular plants, first millipedes and arthropleurids on land First jawed fishes, armoured jawless fish populate the seas.
- 48. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Silurian (443.7 – 416.0) Sea-scorpians reach large size Beginning of Caledonian Orogeny, and the Scandinavian Mountains
- 49. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Silurian (443.7 – 416.0) Beginning of Caledonian Orogeny
- 50. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Silurian (443.7 – 416.0) Beginning of Scandinavian Mountains
- 51. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Silurian (443.7 – 416.0) Beginning of Caledonian Orogeny, and the Scandinavian Mountains
- 52. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Devonian (416 – 359.2) First clubmosses, horsetails and ferns appear
- 53. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Devonian (416 – 359.2) First seed-bearing plants, first trees and first insects Early sharks, jawed fishes and lobe-finned fishes rule the sea
- 54. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Devonian (416 – 359.2) First amphibions still aquatic Old Red Continent of Euroamerica
- 55. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Devonian (416 – 359.2) Acadian Orogeny for Anti-atlas Mountains of North Africa and Applachian Mountains of North America
- 56. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Mississippian (359.2 – 318.1) Large primitive trees First land vertebrates and amphibious sea- scorpians
- 57. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Mississippian (359.2 – 318.1) Lobe-finned Rhizodonts dominant water predators Early sharks common in oceans Corals, bryozoa, goniatites and brachiopods very common Trilobites and nautiloids decline Glaciation in East Gonwana
- 58. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Pennsylvanian (318.1 – 299) Winged insects radiate suddenly Amphians common and diverse First reptiles and coal forests Highest ever atmospheric oxygen levels
- 59. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Pennsylvanian (318.1 – 299) Uralian Orogeny
- 60. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Permian (299 – 251) Landmasses unite into supercontinent Pangea End of Permo-Carboniferous
- 61. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Permian (299 – 251) Synapsid reptiles become plentiful Cone-bearing gymnosperms (first true seed bearing plants)
- 62. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Permian (299 – 251) Beetles and flies evolve Permian-Triassic event occur on 251 Ma, 95% life on earth become extinct Altaid Orogeny in Asia
- 63. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Paleozoic Permian (299 – 251)
- 64. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Mesozoic Triassic (251 – 199.6) Archosaurs dominant on land as dinosaurs, and as Ichthyosaurs and nothosaurs in oceans, and in air as pterosaurs First mammels Crocodilia appear
- 65. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Mesozoic Triassic (251 – 199.6) Cimmerian Orogeny
- 66. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Mesozoic Jurrasic (199.6 – 145.5) Gymnosperms & ferns common Many types of dinosaurs such as sauropods, carnosaurs and stegosuars Mammels common but small First birds and lizards Sea urchins very common alongwith starfish and sponges CO2 levels 4-5 times the present-day level.
- 68. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Mesozoic Jurrasic (199.6 – 145.5) Breakup of Pangea into Gondwanaland & Laurasia
- 69. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Mesozoic Cretaceous (145.5 – 65.5) Flowering plants with new types of insects. Many new types of dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurs, Titanosaurs, duck bills and horned dinosaurs Modern sharks Breakup of Gondwana Atmospheric CO2 close to present-day
- 70. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Cenozoic Paleogene Paleocene (65.5 – 55.8) Tropical climate Modern plants appear Extinction of dinosaurs First large mammels (up to bear or small hippo size) Alpine Orogeny in Europe & Asia Indian Subcontinent collides with Asia (55 Ma) Himalayan Orogeny
- 71. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Cenozoic Paleogene Eocene (55.8 – 33.9) Cooling climate Primitive whales First grasses Reglaciation of Antarctica and formation of its ice age
- 72. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Cenozoic Paleogene Oligocene (33.9 – 23.03) Warm but cooling climate moving towards Icehouse Rapid evolution and diversification of fauna, especially mammels Major evolution and dispersal of flowering plants
- 73. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Cenozoic Neogene Miocene (23.03 – 5.332) Moderate Icehouse climate Modern mammels & bird families Horses and mastodons diverse Kaikoura Orogeny, Carpathean orogeny, Hellenic orogeny begins and continuous today
- 74. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Cenozoic Neogene Pliocene (5.332 – 2.588) Intensification of present Icehouse conditions, Present ice age begins roughly 2.58 Ma; cool and dry climate Many of the existing genera of mammels and recent mollusks Homo habilis appear
- 75. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Cenozoic Quaternary Pleistocene (2.588 – 0.01143) Flourishing and then extinction of many large mammels Evolution of anatomically modern humans Quaternary Ice Age continues with glaciations Further intensification of Icehouse conditions, roughly 1.6 Ma Last glacial period (18000 – 15000)
- 76. Geologic Time Scale CAMBRIAN PHANEROZOIC Cenozoic Quaternary Holocene (0.01143 – recent) Last glacial period ends Rise of human civilization Sahara forms from savannah Agriculture begins Stone age begin around 10000 BC, giving away to Copper age (3500 BC) and Bronze Age (2500 BC). Cultural growth and technical advancement through the Iron Age (1200 BC), giving rise to Classical antiquity such as Roman Empire and even to the Middle Ages and present day