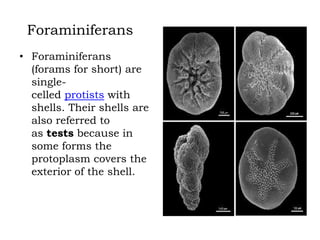
The document provides brief descriptions of various prehistoric lifeforms. It describes mammoths as large, hairy elephants with curved tusks. Mastodons are described as an extinct relative of elephants that inhabited North America until 11,000 years ago. Saber-toothed cats are defined as predatory mammals characterized by long, curved canine teeth. Ground sloths are introduced as a diverse group of extinct sloths that were larger than modern tree sloths.


























![Bryozoans
The Bryozoa, also known as
Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or
commonly as moss animals,[5]
are a phylum of aquatic
invertebrate animals. Typically
about 0.5 millimetres
(0.020 in) long, they are filter
feeders that sieve food
particles out of the water using
a retractable lophophore, a
"crown" of tentacles lined with
cilia.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biomain22-140129020129-phpapp02/85/geologic-time-table-in-biology-31-320.jpg)














