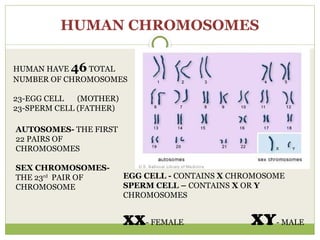
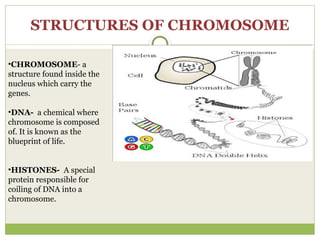
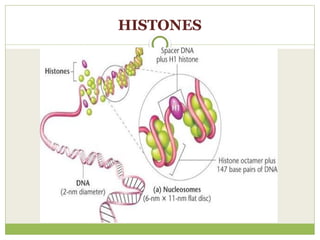
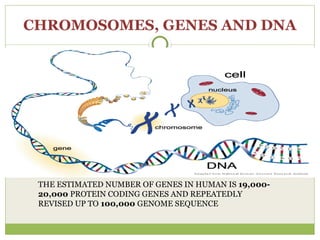
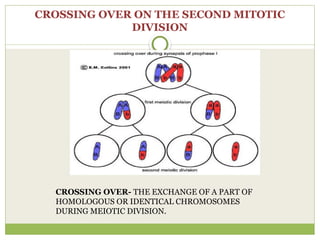
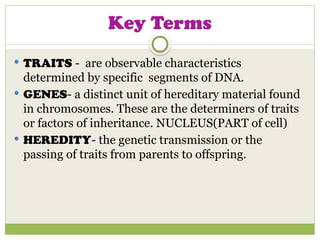
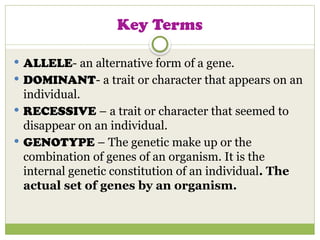
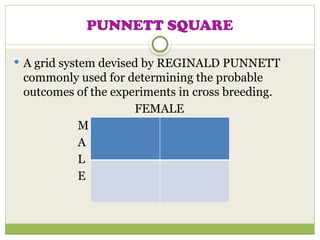
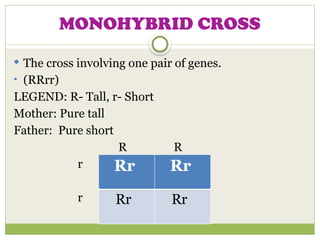
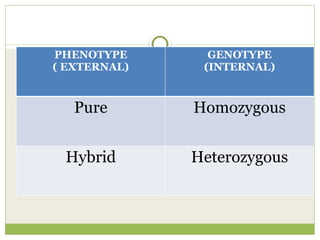
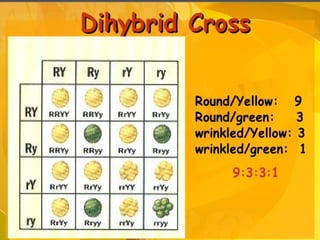
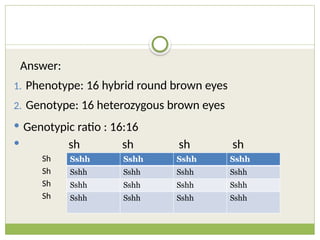
The document discusses human chromosomes, detailing the structure and function of chromosomes, DNA, and genes, and defining key genetics concepts such as heredity, traits, and genetic makeup. It explains meiosis, the formation of twins, Mendel's laws of inheritance, and provides examples of monohybrid and dihybrid crosses using Punnett squares. The text also touches on non-Mendelian inheritance patterns, including incomplete dominance and the difference between genotype and phenotype.