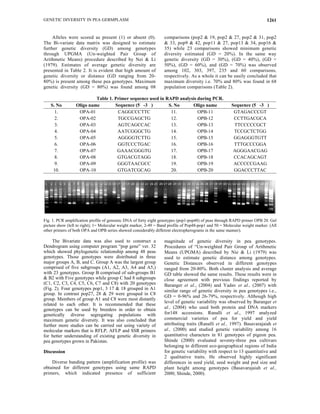
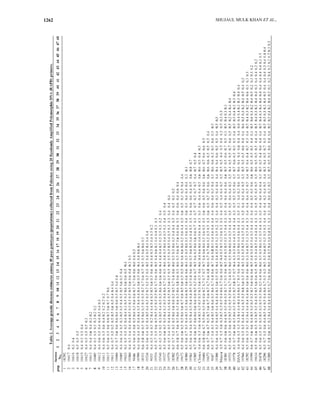
This study assessed genetic diversity in 48 pea genotypes from Pakistan using 20 RAPD DNA markers, revealing significant variations in genetic distance, ranging from 20% to 80%. Phylogenetic analysis grouped the genotypes into three major clusters, suggesting that genetically distinct populations can be identified for breeding purposes. The results emphasize the potential of utilizing molecular markers for enhancing crop breeding and conservation efforts in legumes.