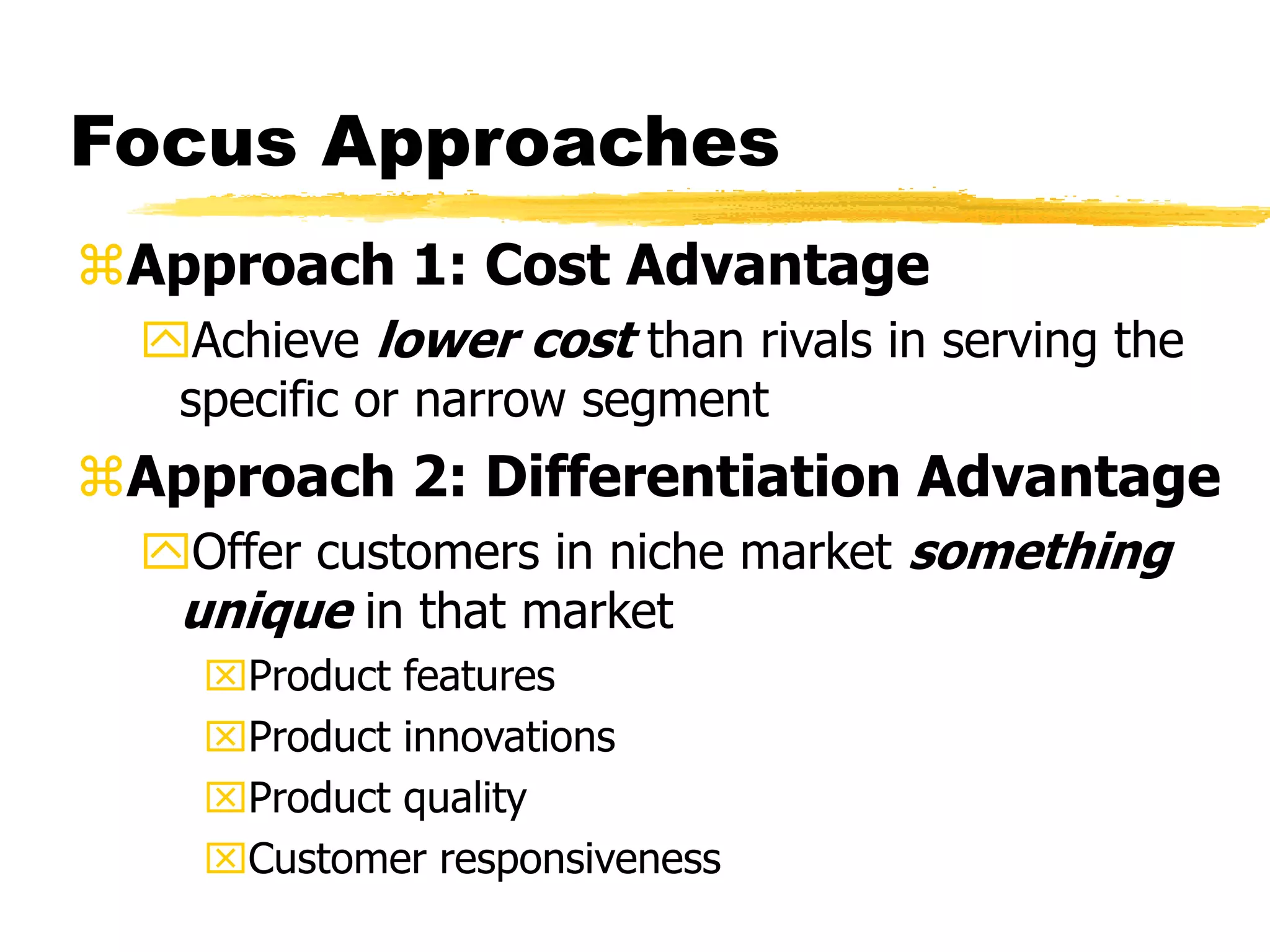
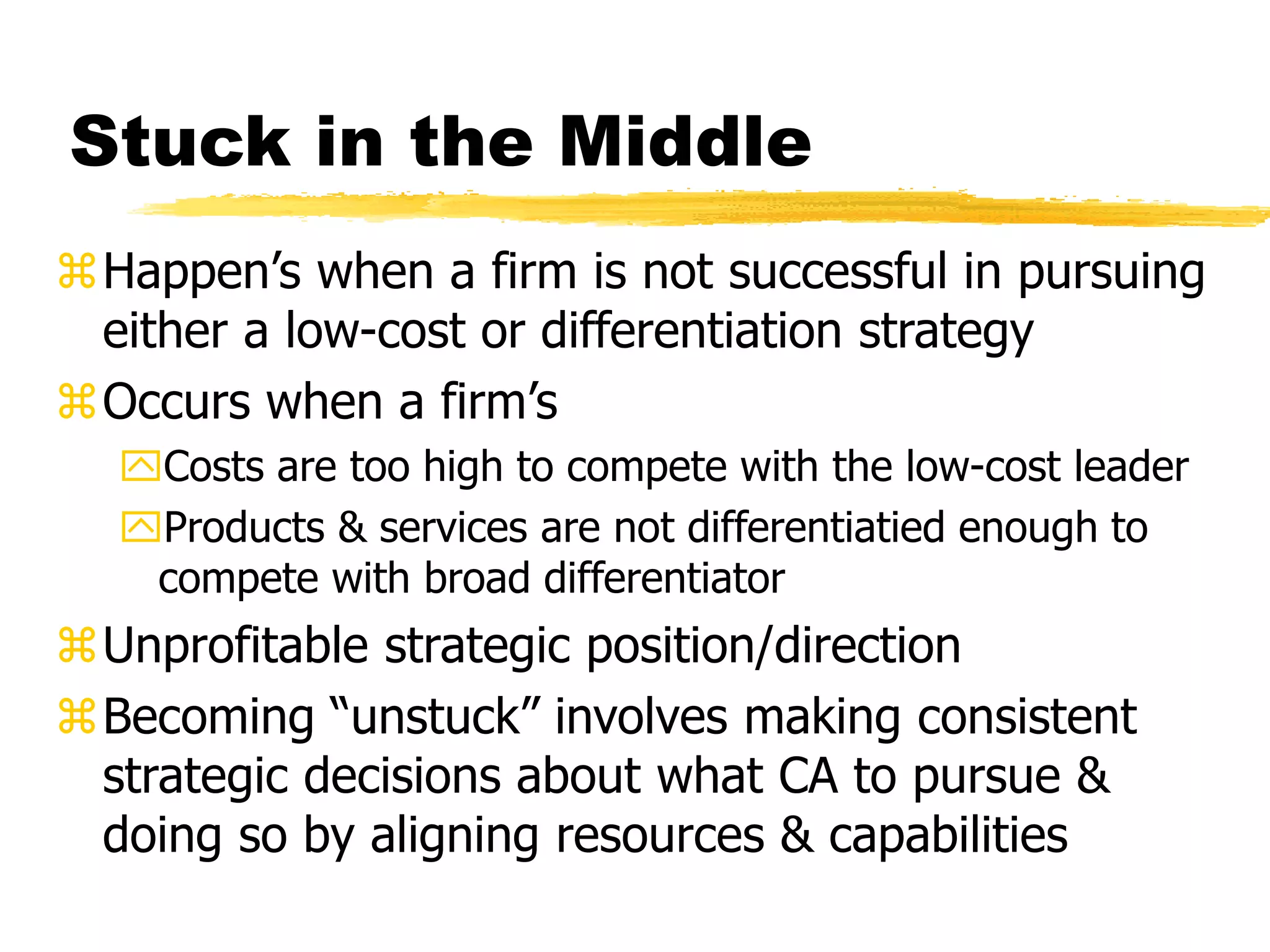
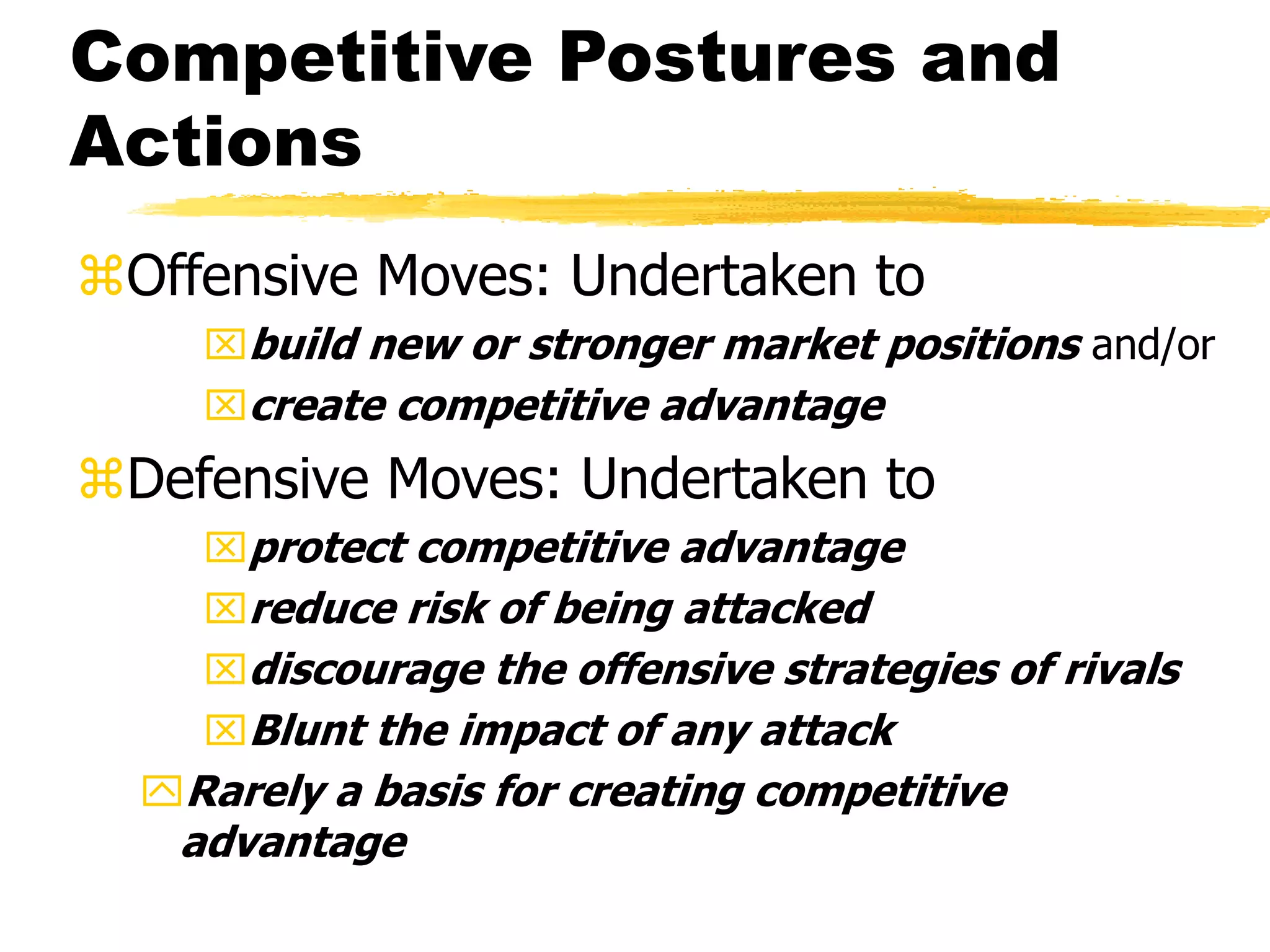
Competitive strategies aim to attract customers, withstand competition, and strengthen market position by exploiting competitive advantages. There are three generic competitive strategies: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. Cost leadership involves having the lowest costs in the industry while differentiation involves offering unique products/services. Focus strategy pursues either approach but in a narrow customer segment. Functional strategies play a key role in determining and implementing the overall competitive strategy.