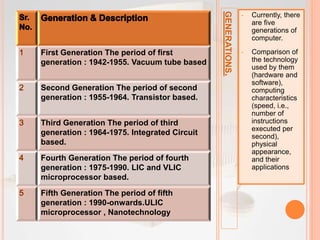
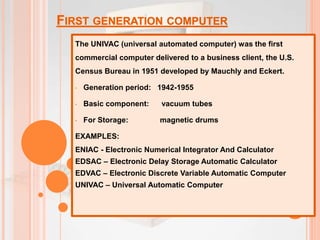
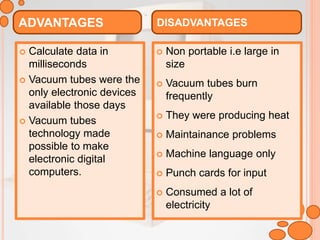
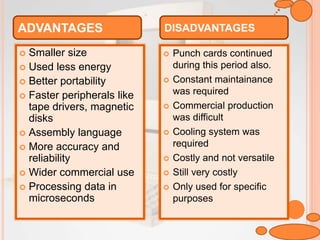
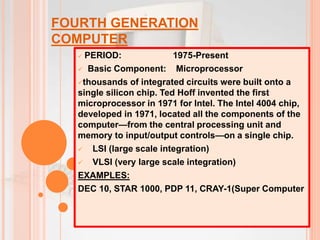
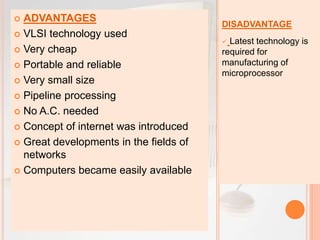
The document discusses the five generations of computers from the 1940s to present. The first generation used vacuum tubes and were very large. The second generation used transistors which made computers smaller and more efficient. The third generation used integrated circuits which further increased speed and reduced size. The fourth generation saw the development of microprocessors which placed all computer components on a single chip. The fifth generation focuses on artificial intelligence and technologies like quantum computing and nanotechnology. Each generation brought improvements in size, speed, cost and capabilities.