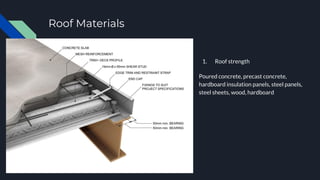
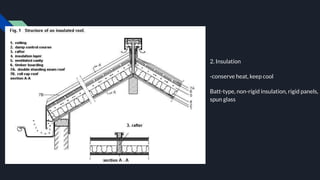
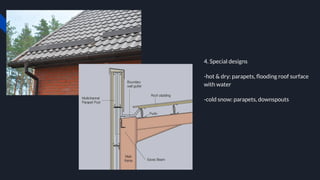
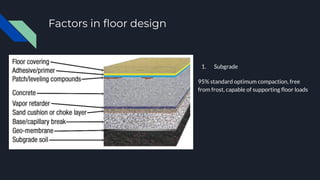
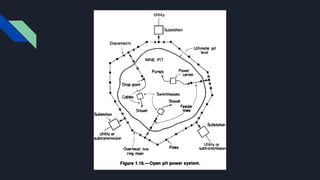
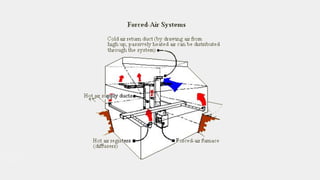
1. The document discusses various factors to consider when designing and constructing a general shop, including site location, building construction type, roof design, floors, electrical systems, heating/cooling, ventilation, cranes/monorails, water/sewage, storage, offices, and fire protection.
2. Key considerations include convenience to operations, drainage, expansion needs, insulation, durability, load capacity, and distributing utilities efficiently.
3. The document provides pros and cons of different construction materials and methods to help guide design decisions.
![GENERAL SHOP
DESIGN &
CONSTRUCTION
[JoCh]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/generalshopdesignconstruction-210819141527/85/General-shop-design-amp-construction-1-320.jpg)