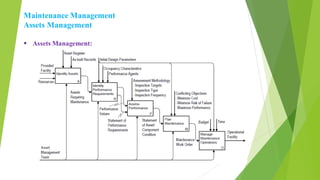
The document outlines a comprehensive 40-hour facilities maintenance course covering various topics such as mechanical and electrical systems, plumbing, water treatment, fire fighting, and maintenance management. It details course content divided into chapters focusing on practical engineering fundamentals and maintenance practices. The course aims to equip participants with essential skills and knowledge for managing and maintaining facility operations effectively.