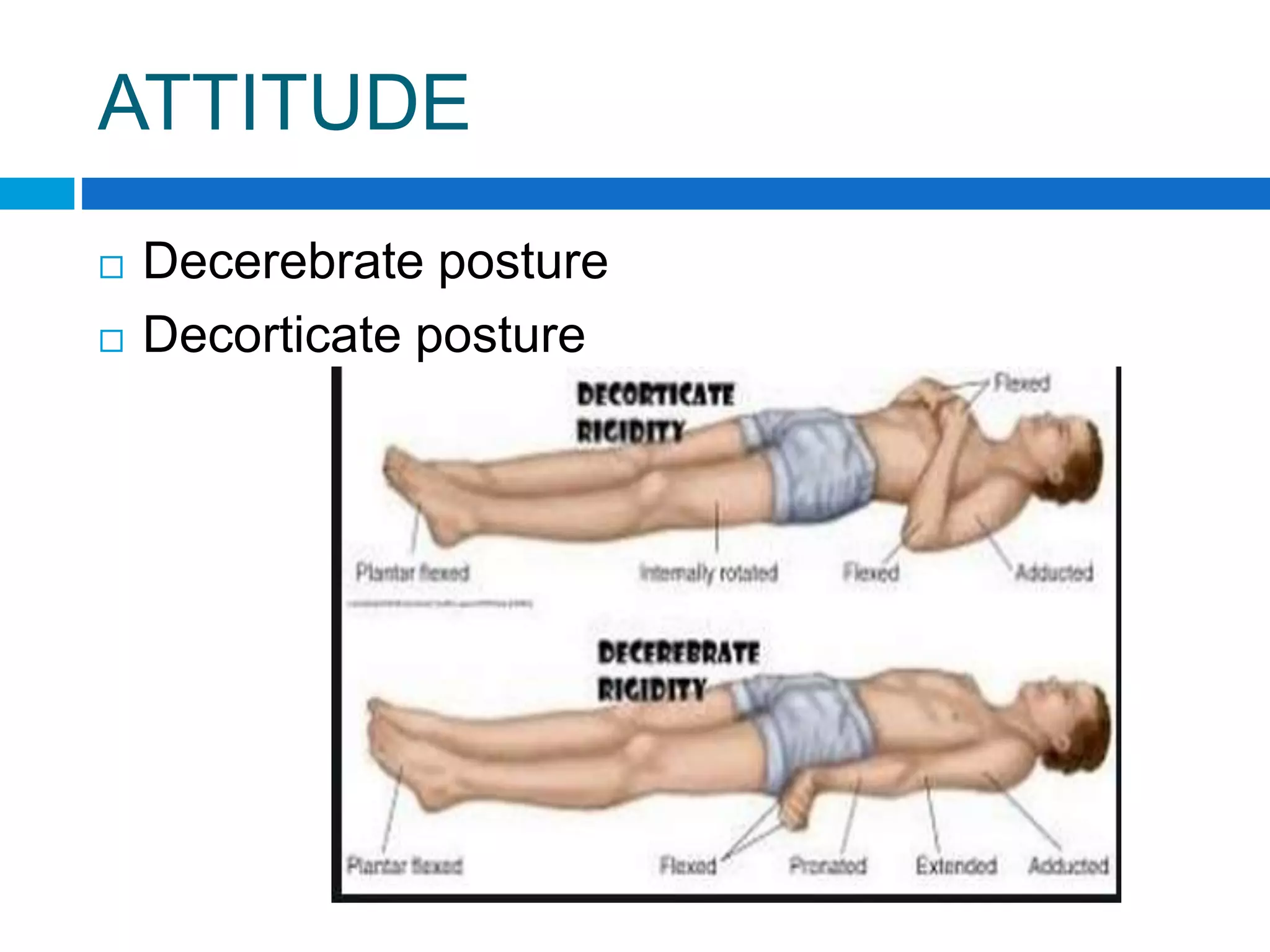
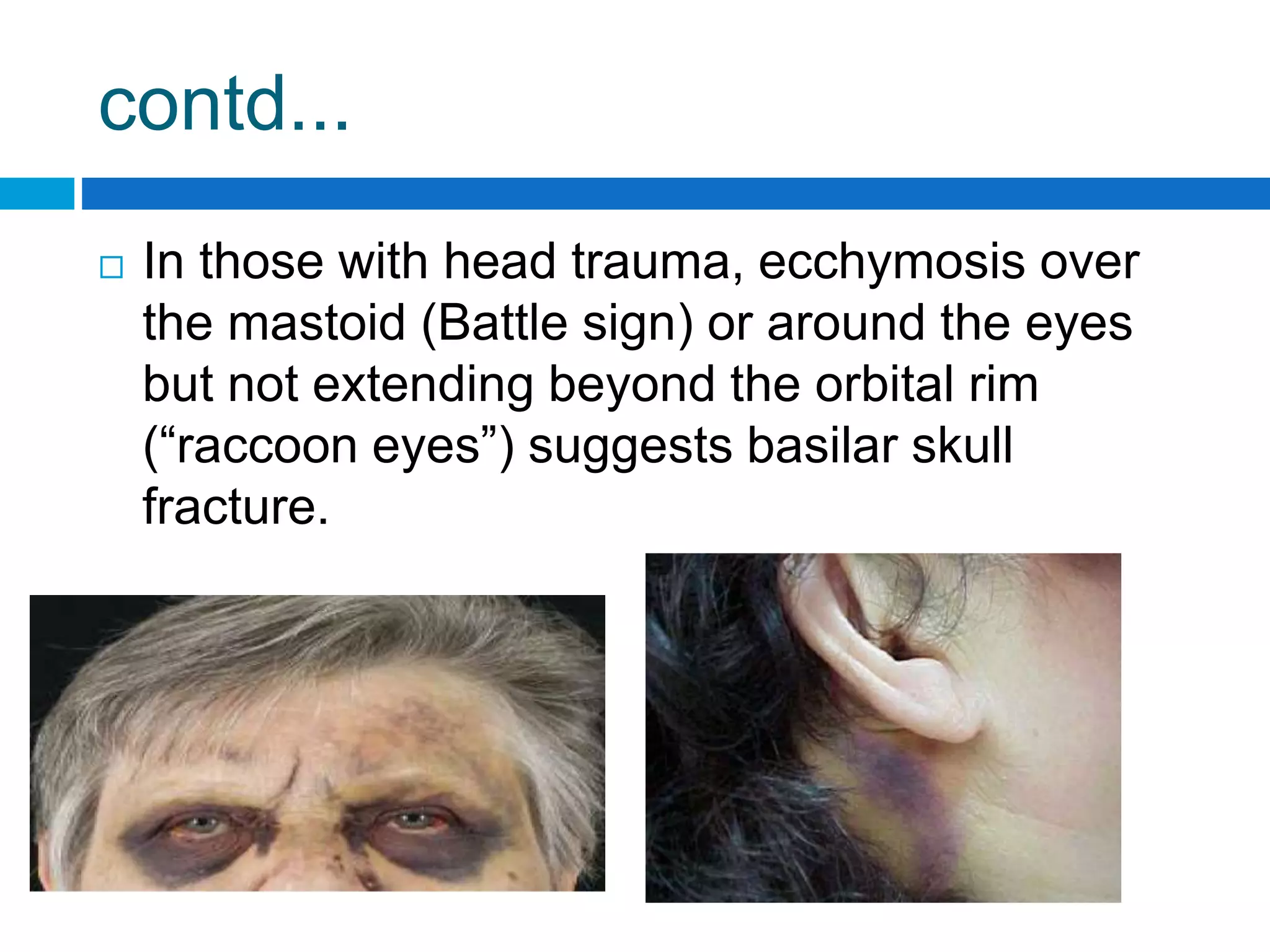
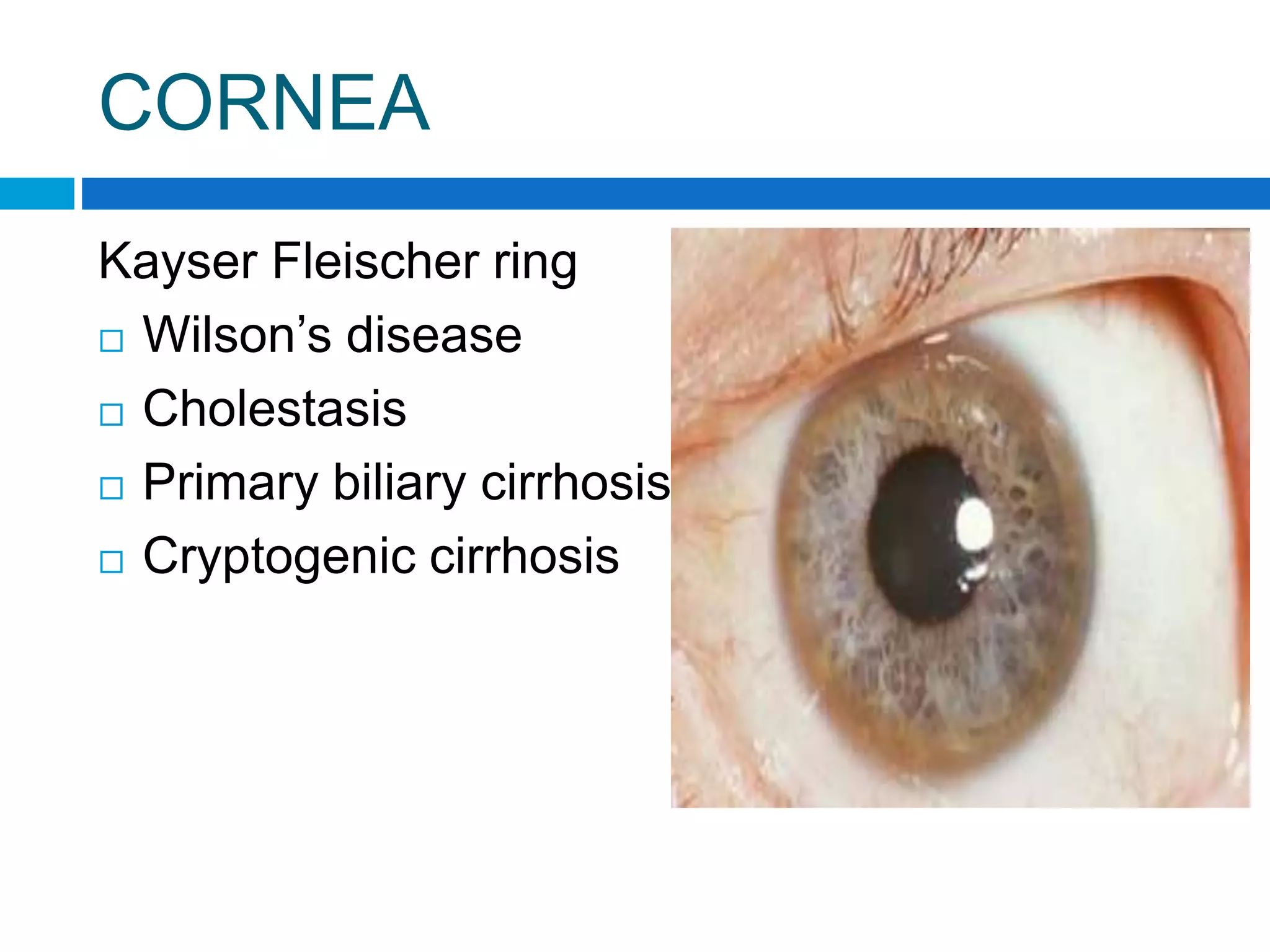
This document provides guidance on performing a physical examination of the central nervous system. It outlines examination of various body systems and signs, including attitude, level of consciousness, head, facies, eyes, ears, mouth, neck, skin, extremities, and spine. It describes abnormalities to examine for, such as craniosynostosis deformities of the head, facial palsies, ptosis, neurocutaneous lesions, clubbing, and peripheral nerve disorders. The examination aims to detect neurological deficits or systemic diseases that may involve the CNS.