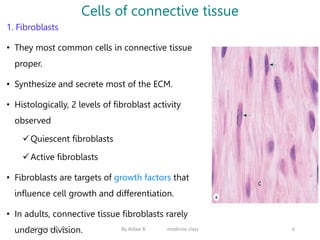
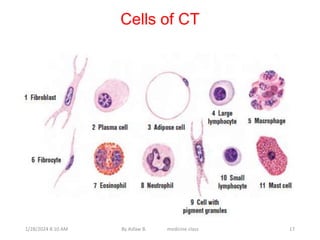
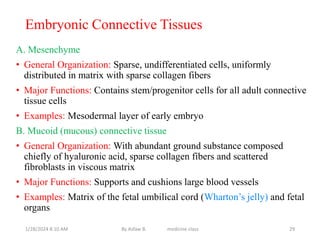
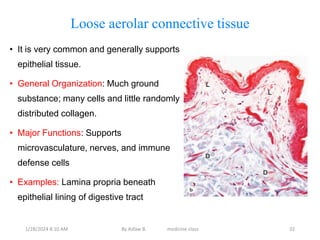
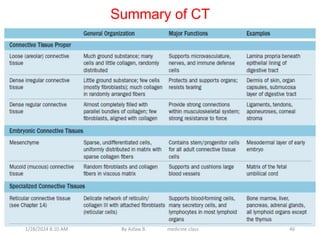
Connective tissue is one of the most abundant tissues in the body. It consists of cells such as fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells, and plasma cells embedded in an extracellular matrix containing collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and ground substance. There are several types of connective tissue including loose connective tissue, dense irregular connective tissue, dense regular connective tissue, and reticular connective tissue. Connective tissue performs important functions such as binding and supporting other tissues, protecting organs, enabling nutrient exchange, and participating in immune responses.