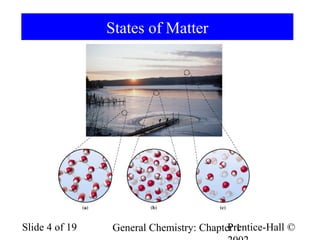
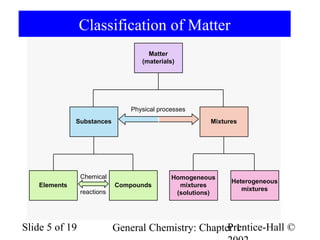
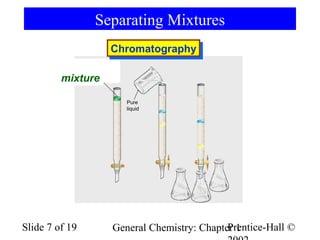
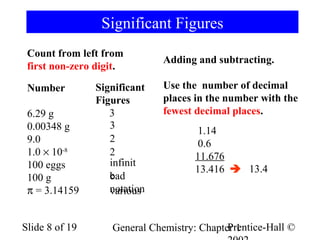
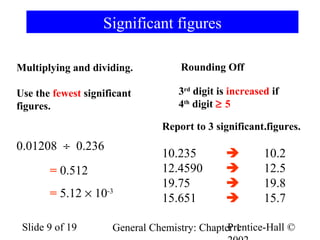
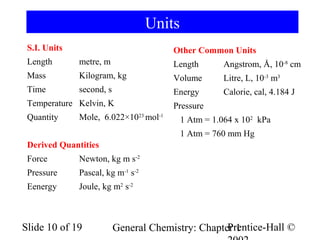
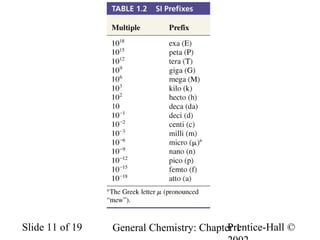
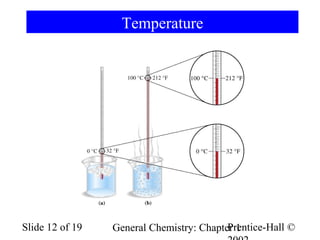
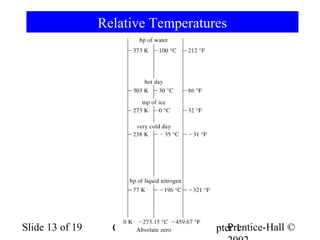
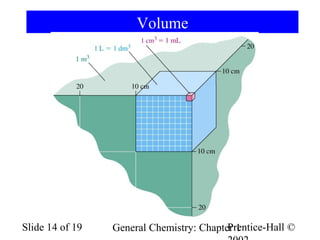
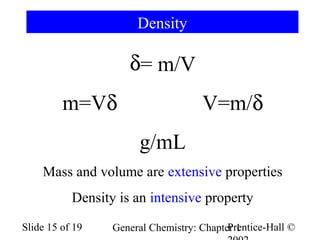
The document is a slide presentation on chapter 1 of a general chemistry textbook. Chapter 1 covers fundamental topics like the properties and states of matter, measurement units, and dimensional analysis. It defines physical and chemical properties, classifies matter as elements, compounds, and mixtures, and discusses techniques for separating mixtures. Key concepts explained include significant figures, temperature scales, volume, density, and unit conversions. The presentation concludes with sample end-of-chapter questions.