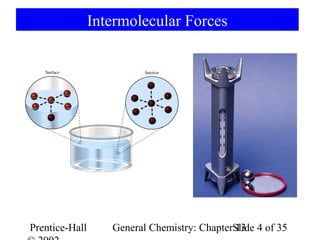
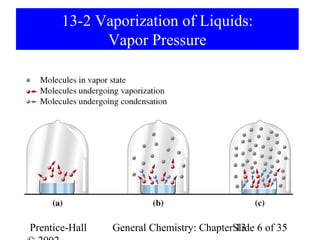
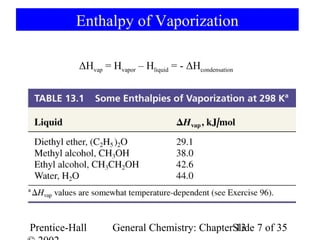
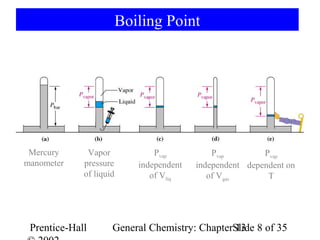
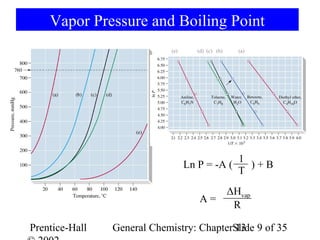
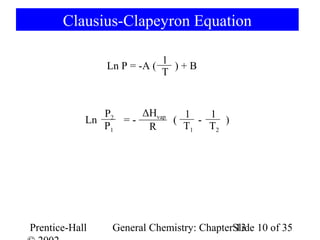
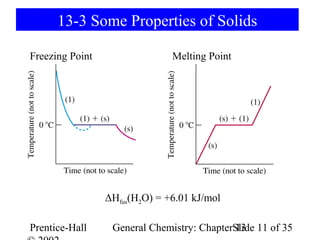
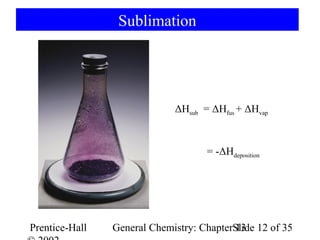
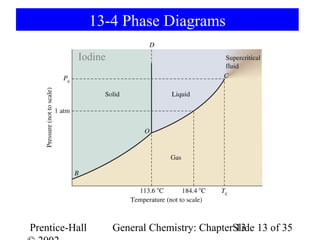
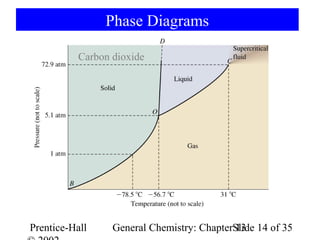
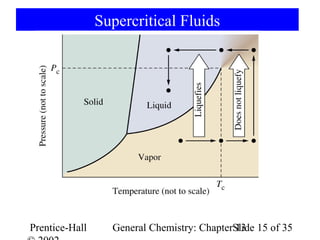
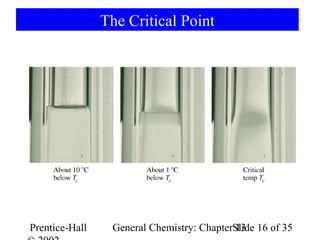
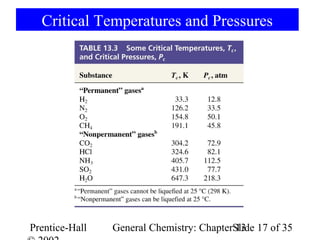
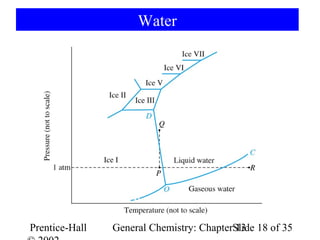
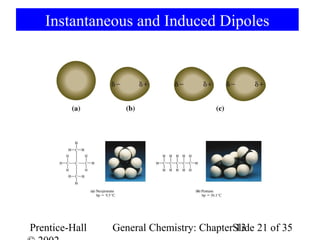
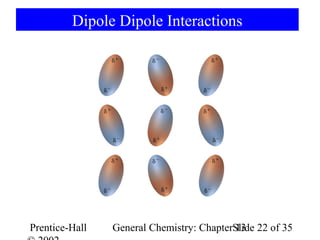
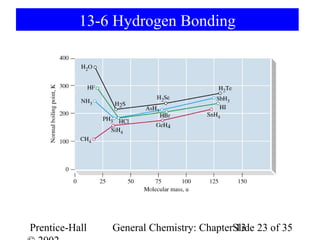
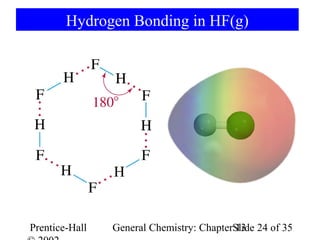
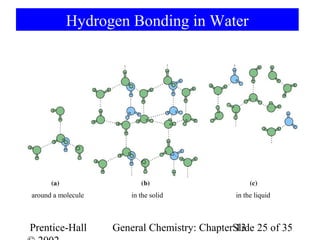
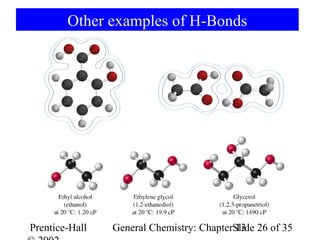
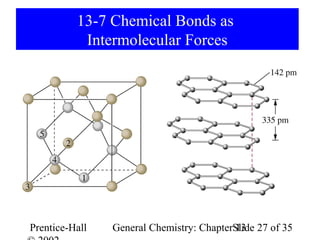
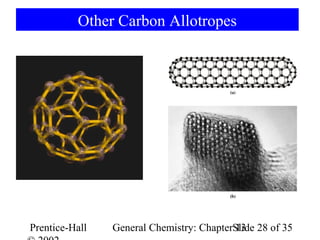
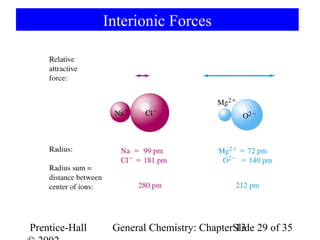
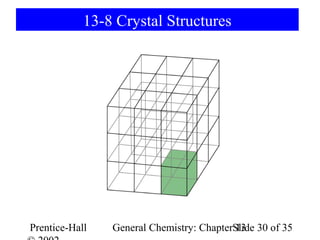
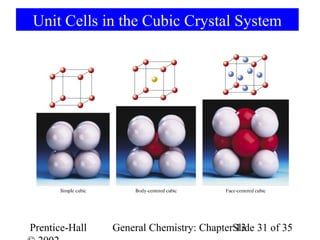
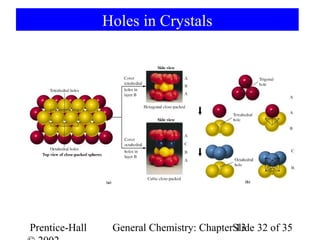
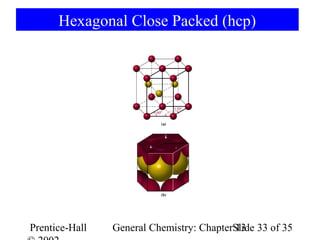
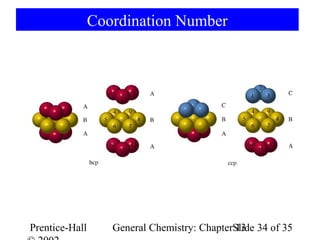
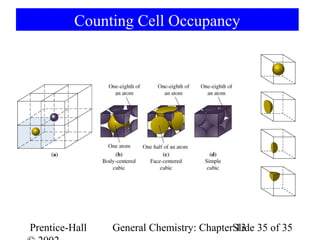
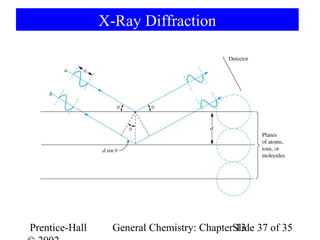
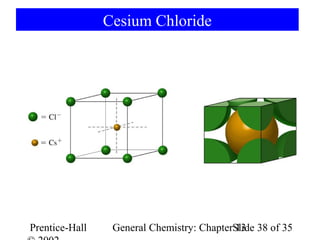
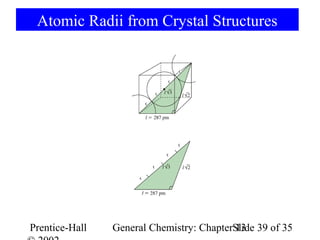
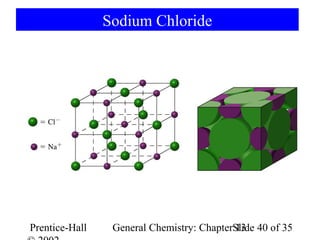
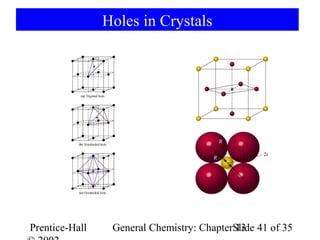
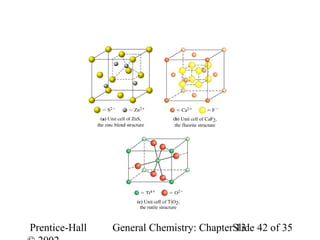
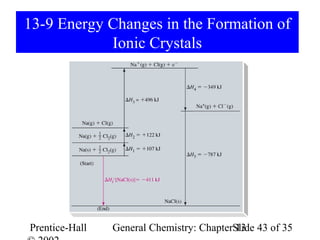
This document is a chapter from a general chemistry textbook titled "General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications" by Petrucci, Harwood, and Herring. The chapter is titled "Liquids, Solids and Intermolecular Forces" and covers topics such as the properties of liquids and solids, intermolecular forces like hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces, phase diagrams, crystal structures of solids, and energy changes during phase changes. It includes diagrams to illustrate concepts like vapor pressure curves, phase diagrams, and crystal unit cells.