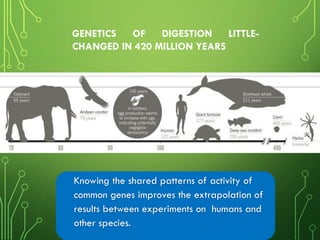
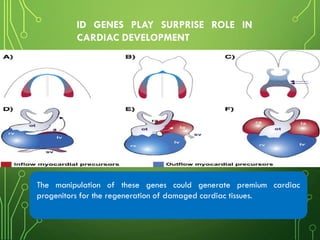
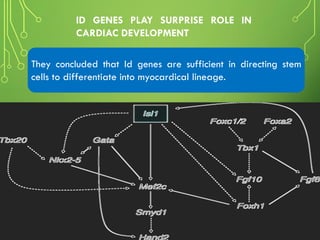
This document summarizes two scientific studies on gene mapping. The first study mapped the genomic atlas of the gut lining and found that genetics of digestion have remained largely unchanged over 420 million years, controlled by conserved regulatory elements. The second study identified four Id genes essential for heart development in mice through CRISPR gene editing. Manipulation of these genes may help regenerate damaged heart tissue. Together, the studies provide insights with potential applications in treating metabolic and heart diseases.