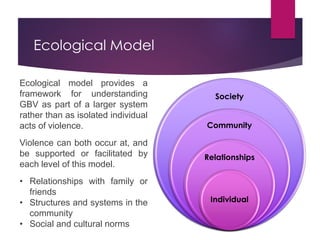
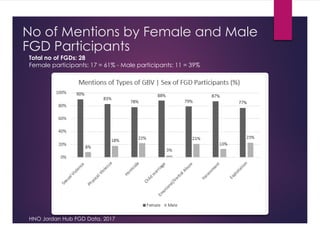
The document discusses gender-based violence (GBV) in the context of social work, migration, and refugees, highlighting the definitions of sex and gender, various forms of GBV, and the ecological model that places violence within a larger societal framework. It identifies the causes and consequences of GBV, the affected populations, and the crucial role social workers play in supporting survivors through advocacy, case management, and access to resources. The content emphasizes the importance of understanding the complexities of GBV and addressing the immediate needs of those impacted.