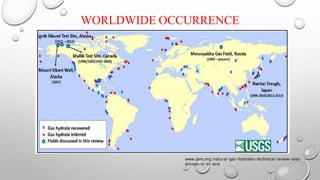
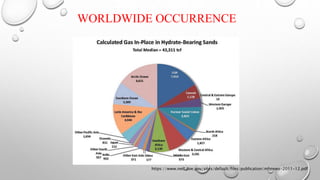
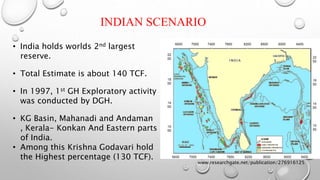
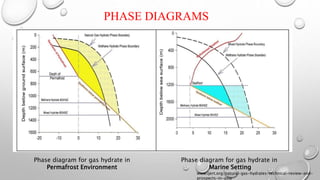
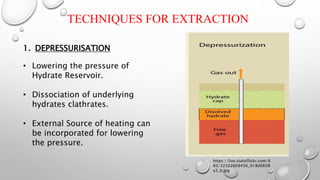
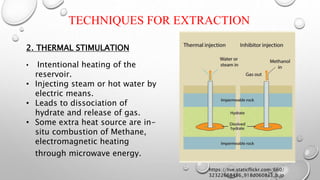
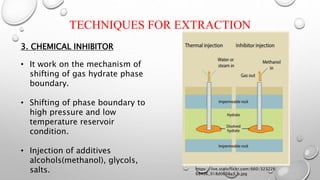
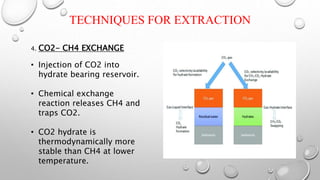
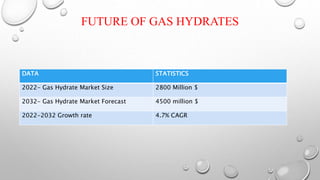
The document discusses gas hydrates, crystalline solids containing gas molecules surrounded by water, and their worldwide occurrence, particularly emphasizing India's significant reserves. It outlines extraction techniques, challenges in production, major industry players, and relevant policies impacting the gas hydrate sector. Additionally, it provides forecasts for market growth, indicating a projected increase in market size from $2.8 billion in 2022 to $4.5 billion by 2032.