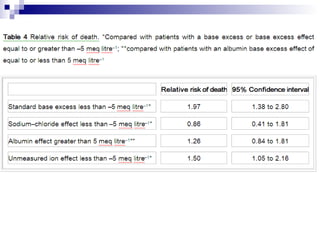
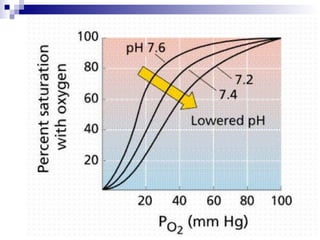
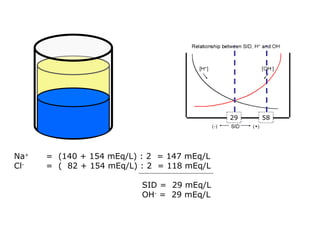
This document summarizes a case study of a child with metabolic acidosis following sepsis and 20% body surface area burns. It applies the Fencl-Stewart approach to analyze the acid-base disturbance. This involves measuring the standard base excess, sodium-chloride effect, albumin effect, and calculating the unmeasured ion effect. In this case, the unmeasured ion effect of -21.5 mEq/L suggests lactic acidosis as the cause. Bicarbonate therapy is not recommended due to risks of worsening tissue hypoxia and intracellular acidosis. The appropriate treatment is to correct hypoalbuminemia, hypernatremia, and the underlying cause of lactic acidosis through improving oxygen delivery and


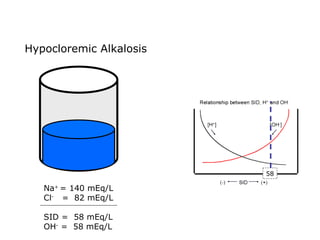


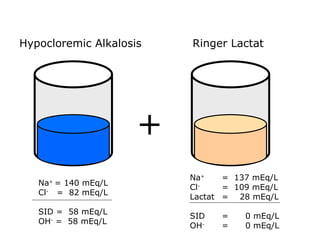
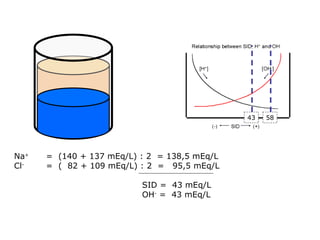
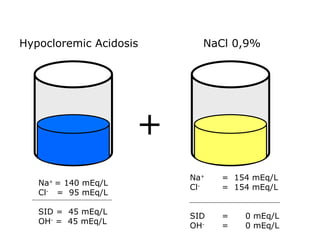



![Kasus 2 Stong Ion Difference =[Na + ]–[Cl – ] = 160-110 = 50 ALBUMIN EFFECT = albumin 1.2 g/dL = HIPOALBUMIN UNMEASURED ION EFFECT ???? As. Laktat akibat gangguan perfusi dan oksigenisasi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/telaaahkasusgangguanasambasa-090822051802-phpapp02/85/Gangguan-Asam-Basa-18-320.jpg)

![Four variables STANDARD BASE EXCESS (mmol /litre = meq / litre) from a blood gas machine SODIUM–CHLORIDE EFFECT (meq / litre) =[Na + ]–[Cl – ]–38 ALBUMIN EFFECT (meq/ litre) =0.25x[42–albumin (g/litre)] UNMEASURED ION EFFECT (meq / litre) = standard base excess–(sodium–chloride effect)– albumin effect](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/telaaahkasusgangguanasambasa-090822051802-phpapp02/85/Gangguan-Asam-Basa-20-320.jpg)
![Kasus 2 STANDARD BASE EXCESS from a blood gas machine = -2 mEq/L SODIUM–CHLORIDE EFFECT (meq / litre) =[Na + ]–[Cl – ]–38 = 160-110-38 = 12 mEq/L ALBUMIN EFFECT (meq/ litre) = 0.25 x [42–albumin (g/litre)] = 0.25 x [42-12 g/L] = 7.5 mEq/L UNMEASURED ION EFFECT (meq / litre) = standard base excess–(sodium–chloride effect)– albumin effect = -2 – 12 – 7.5 = -21.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/telaaahkasusgangguanasambasa-090822051802-phpapp02/85/Gangguan-Asam-Basa-21-320.jpg)