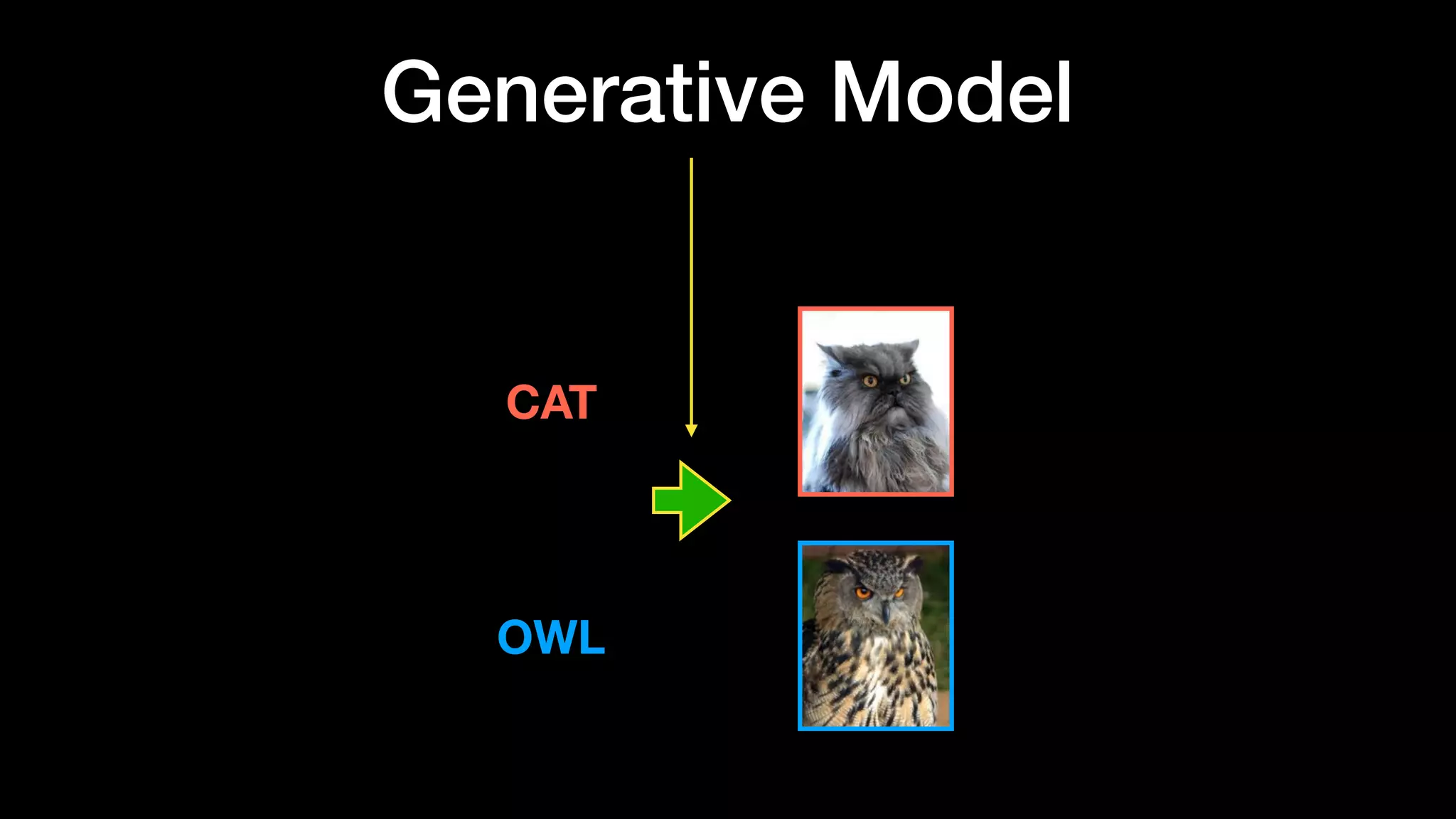
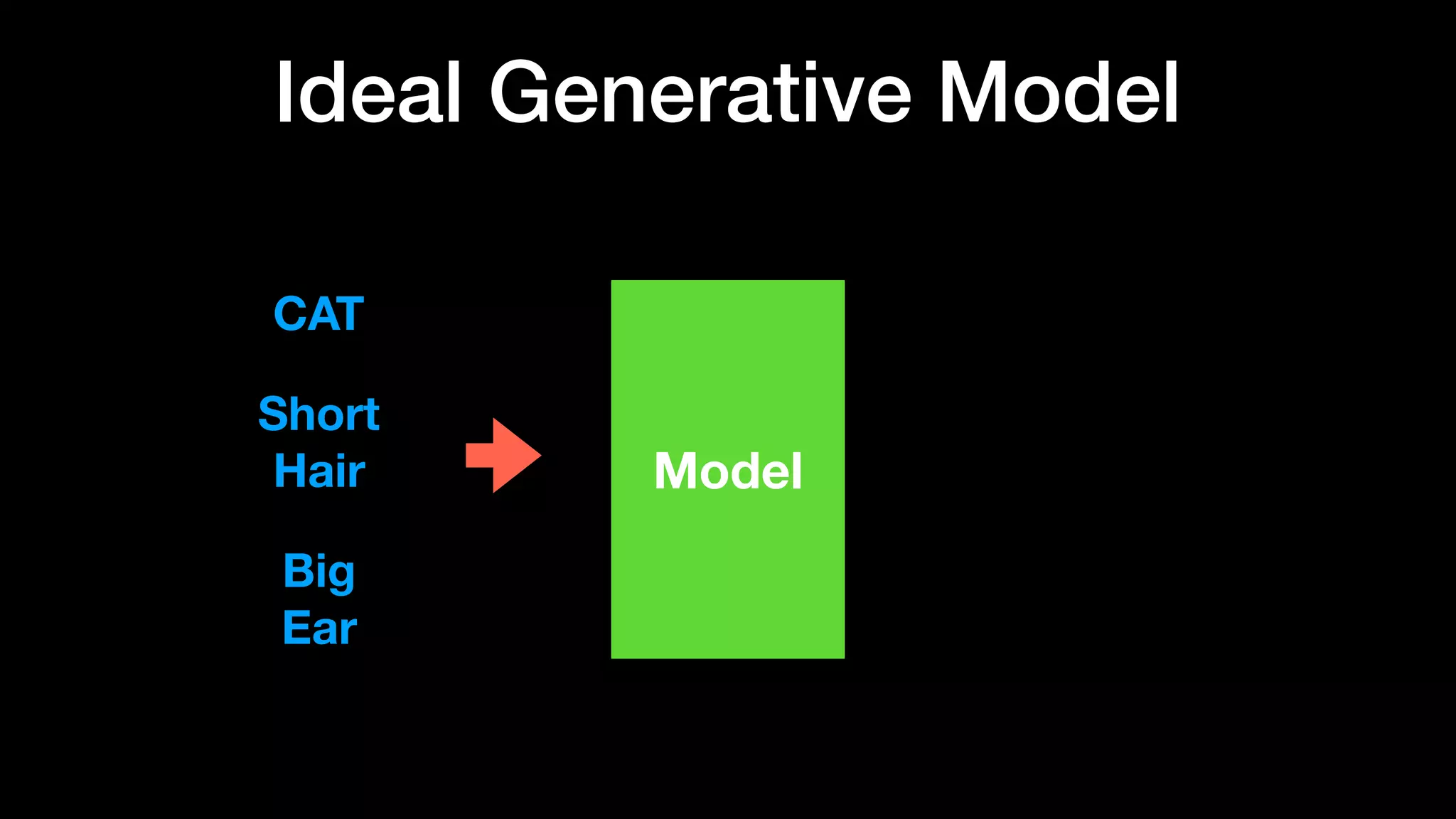
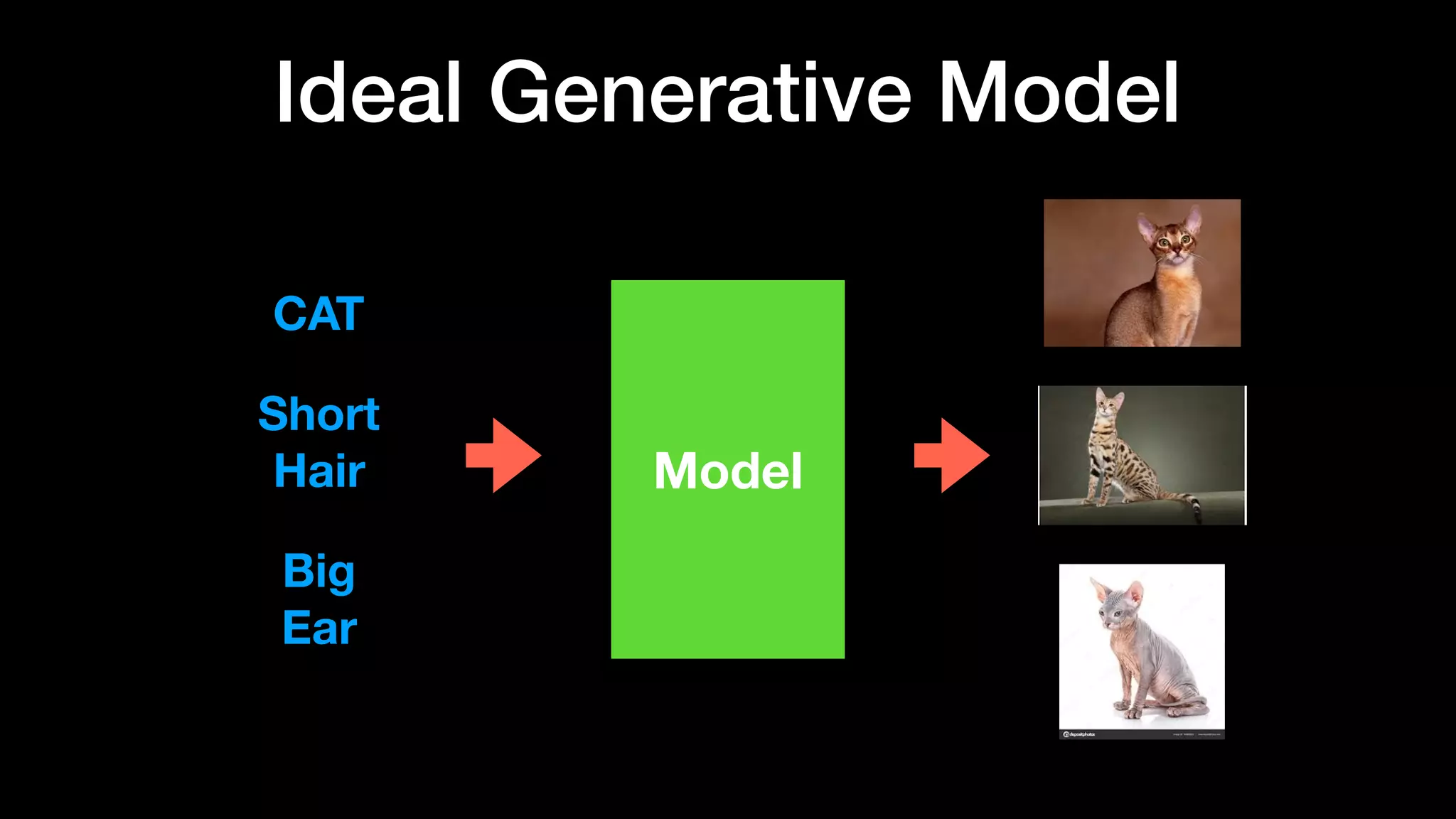
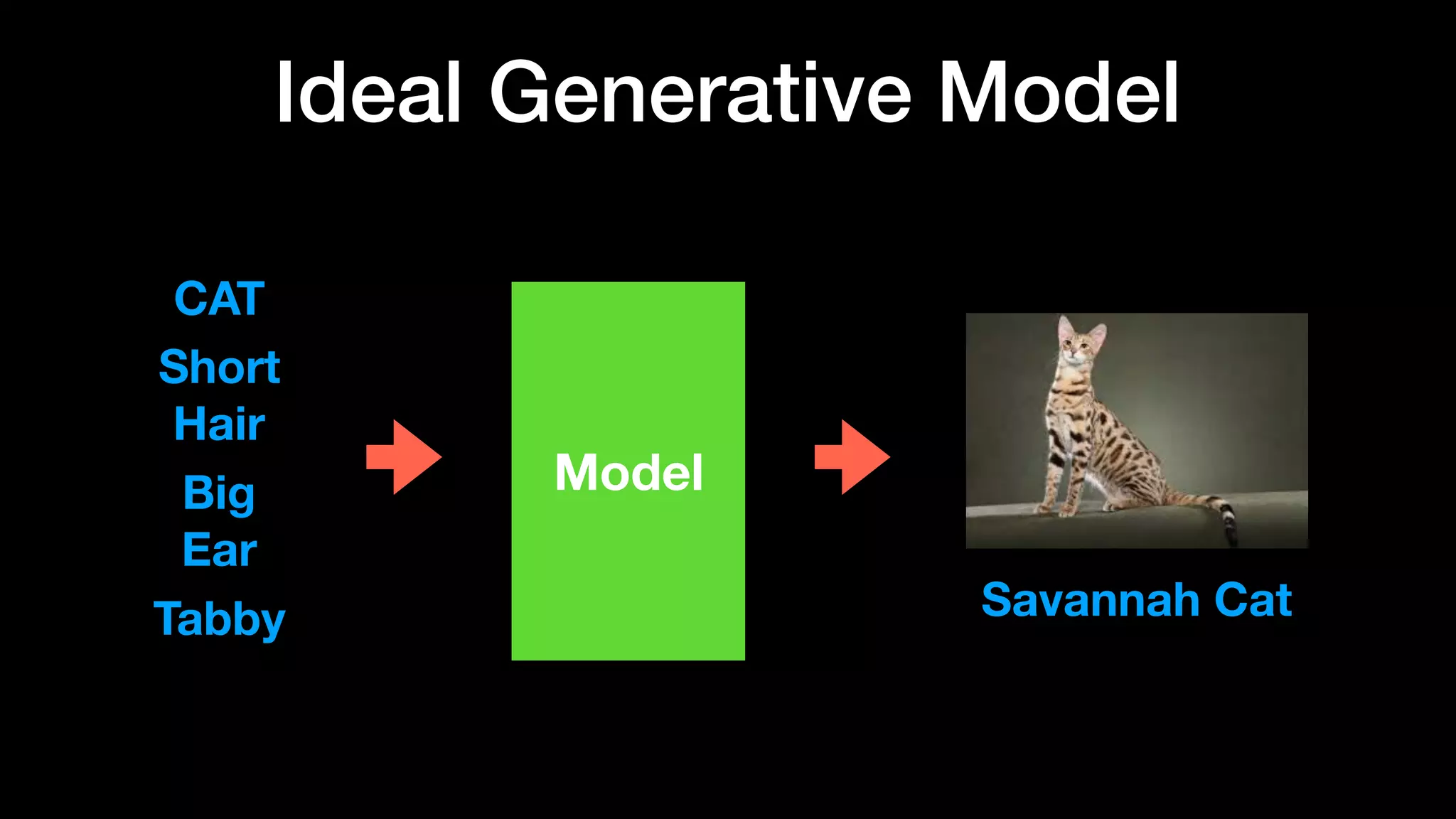
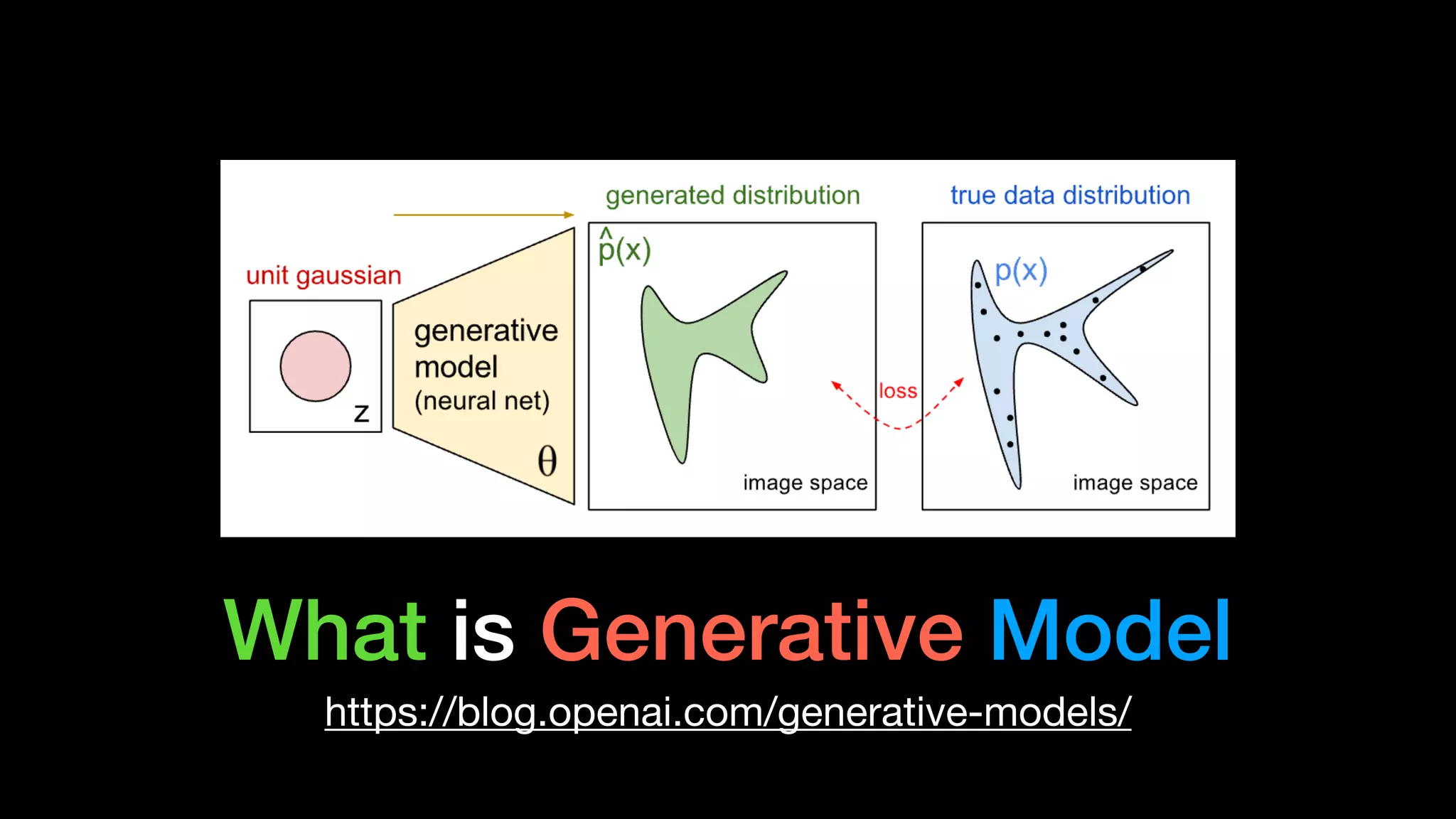
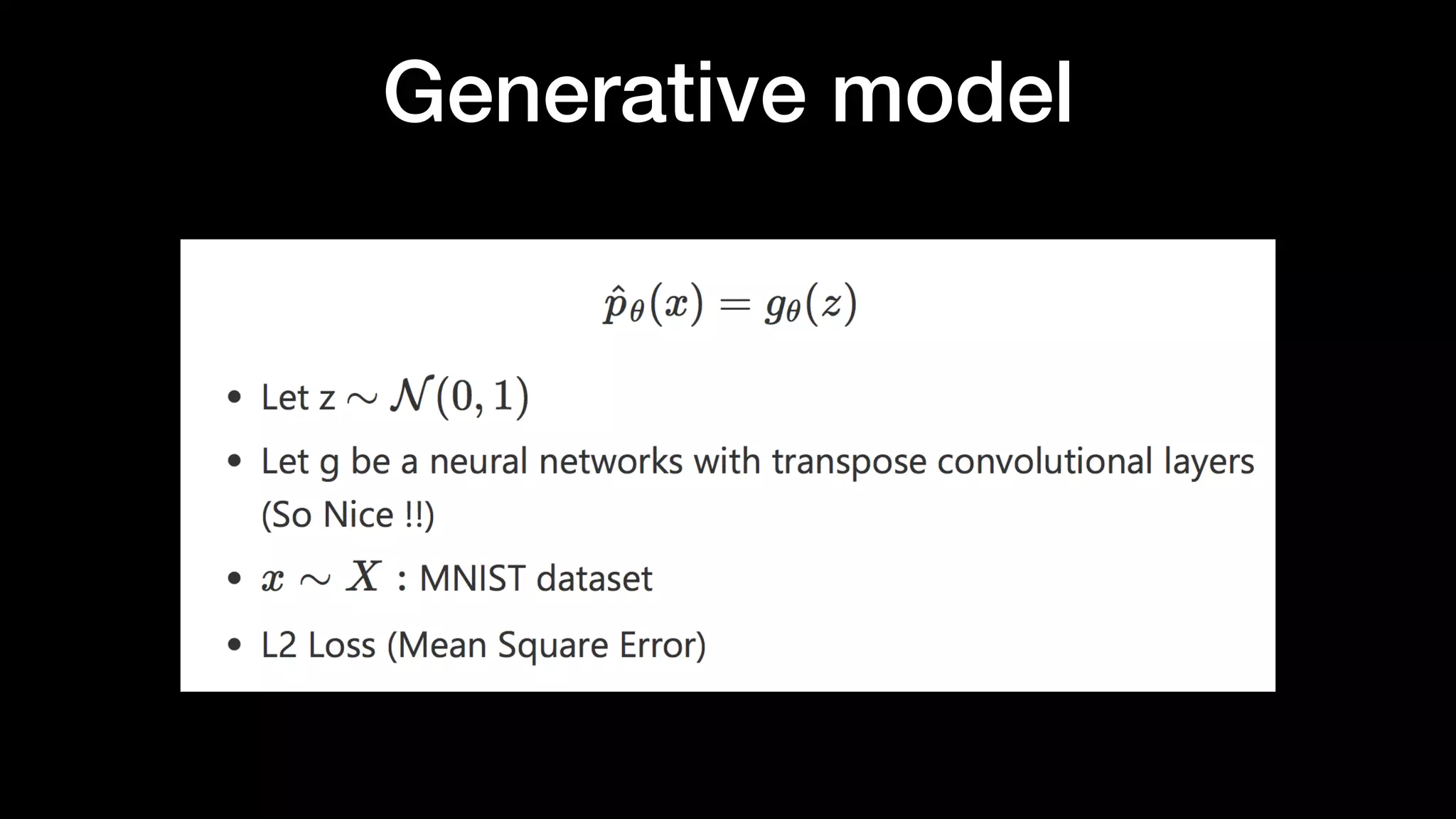
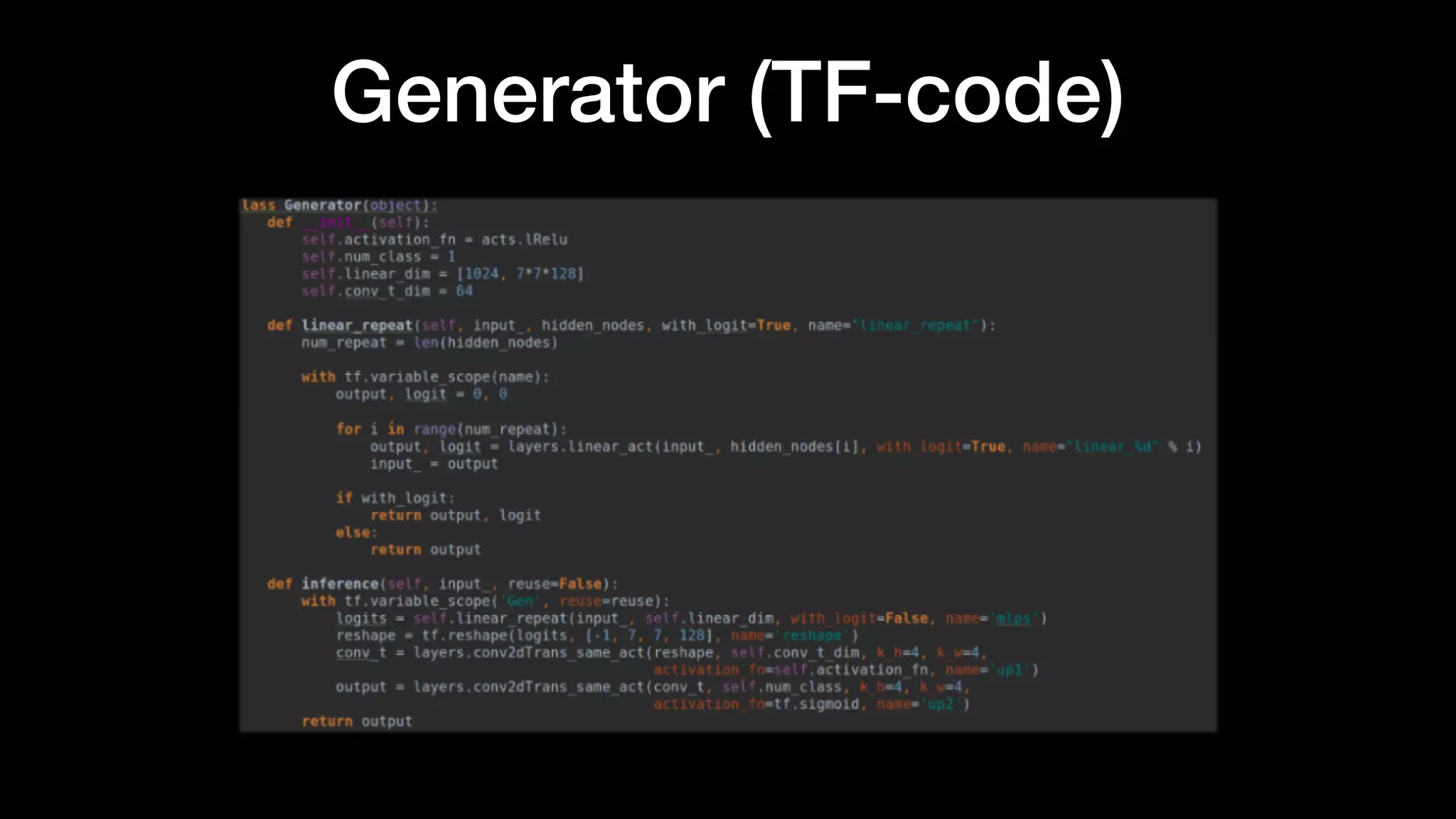
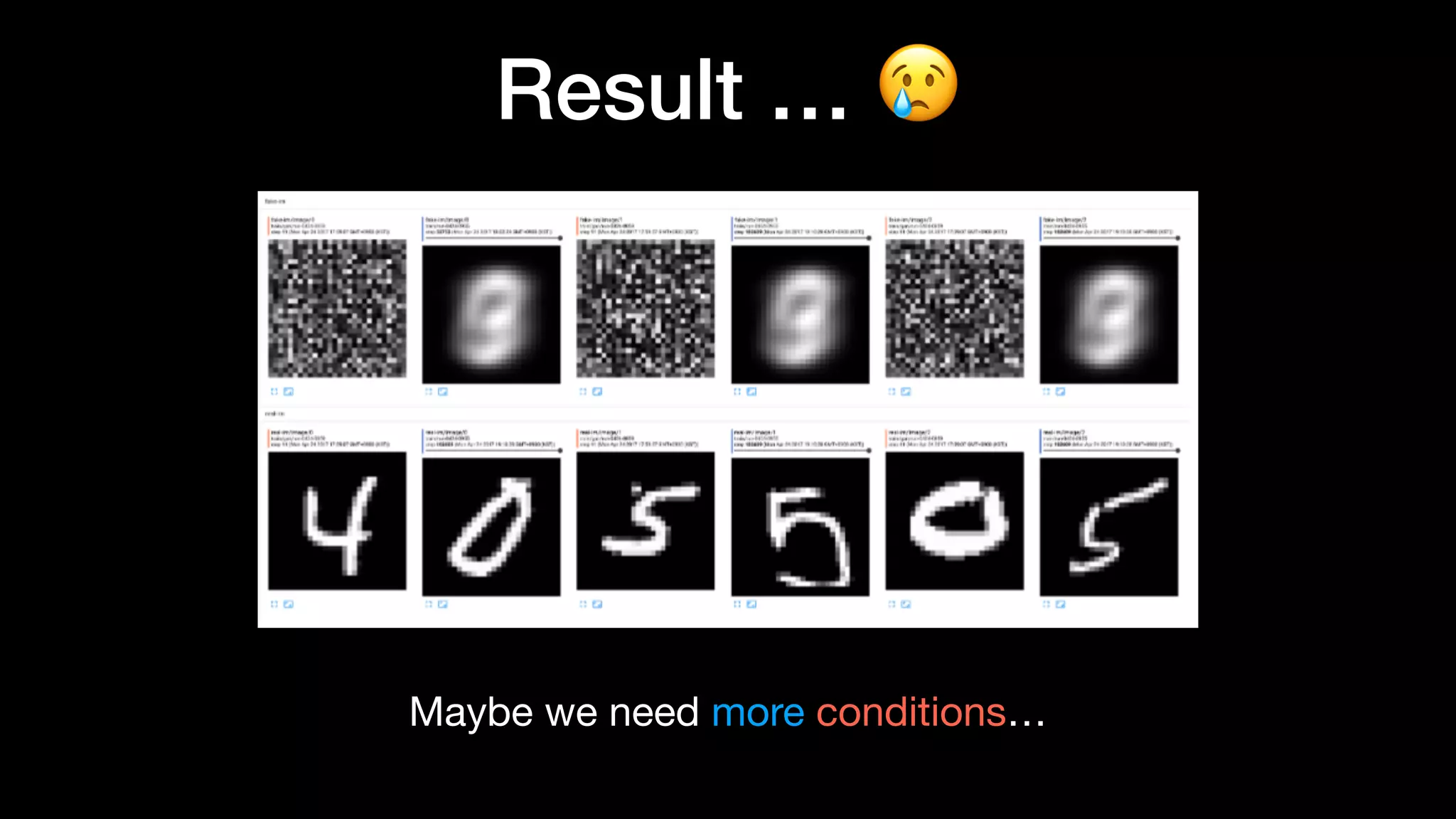
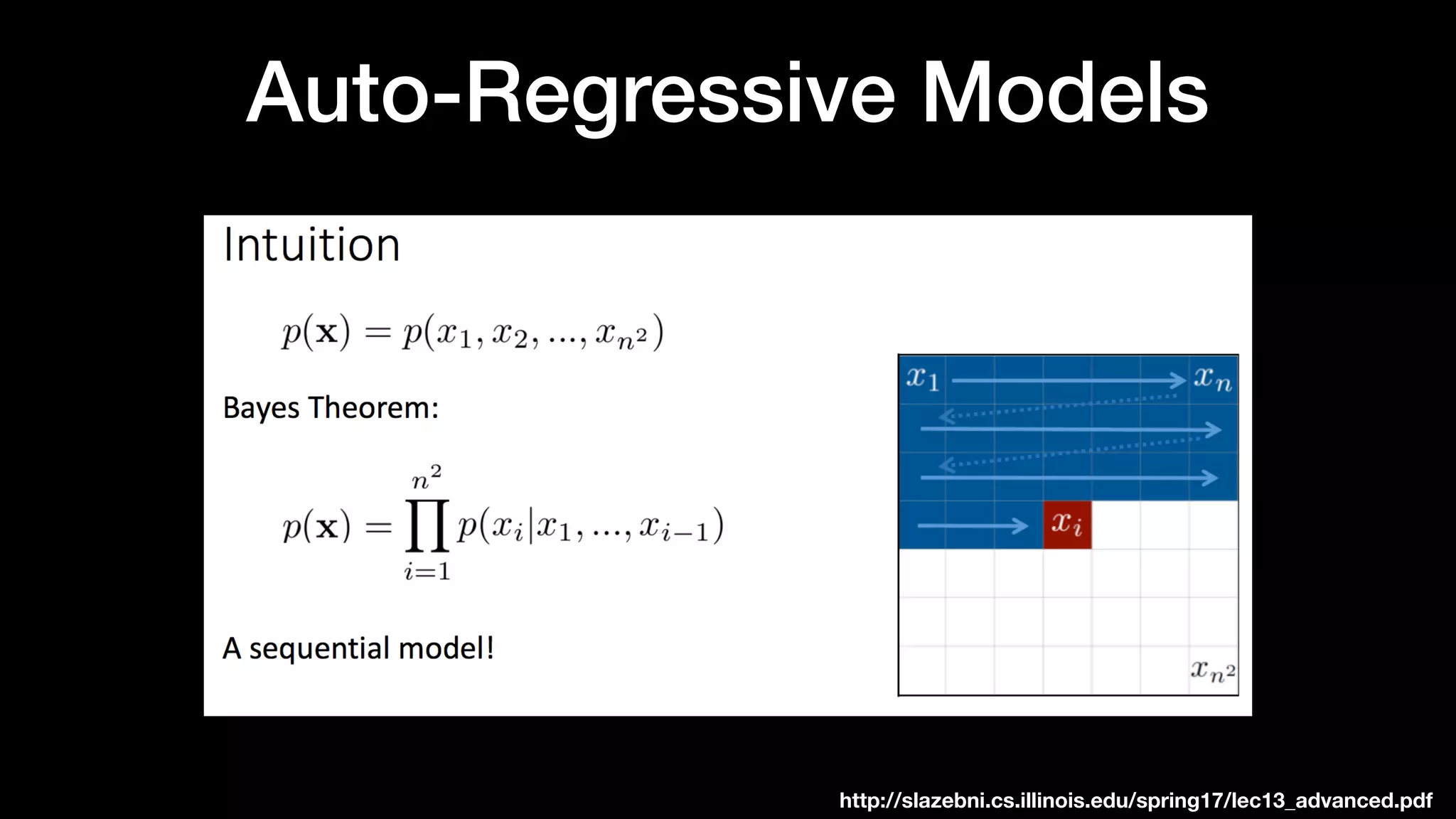
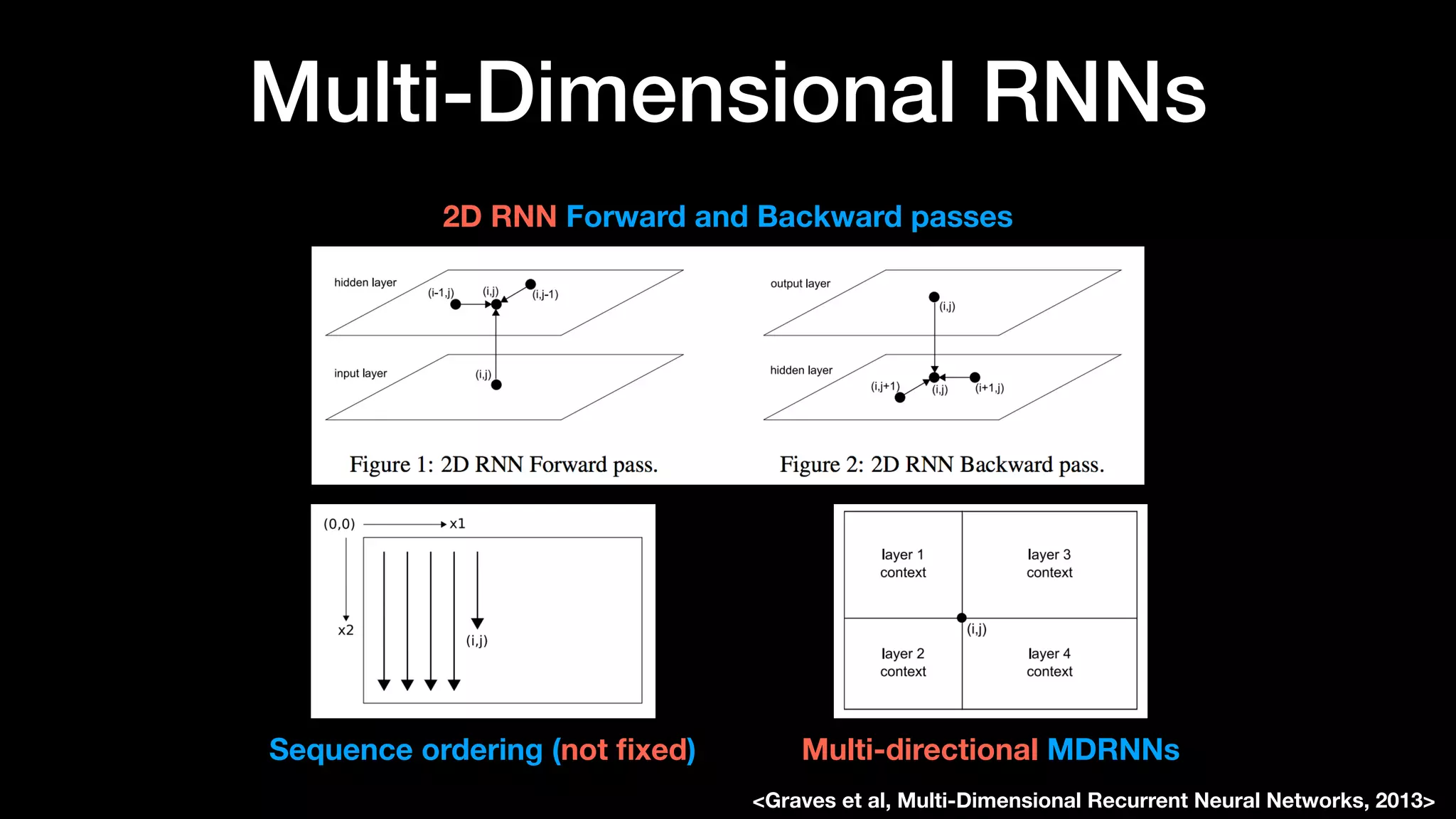
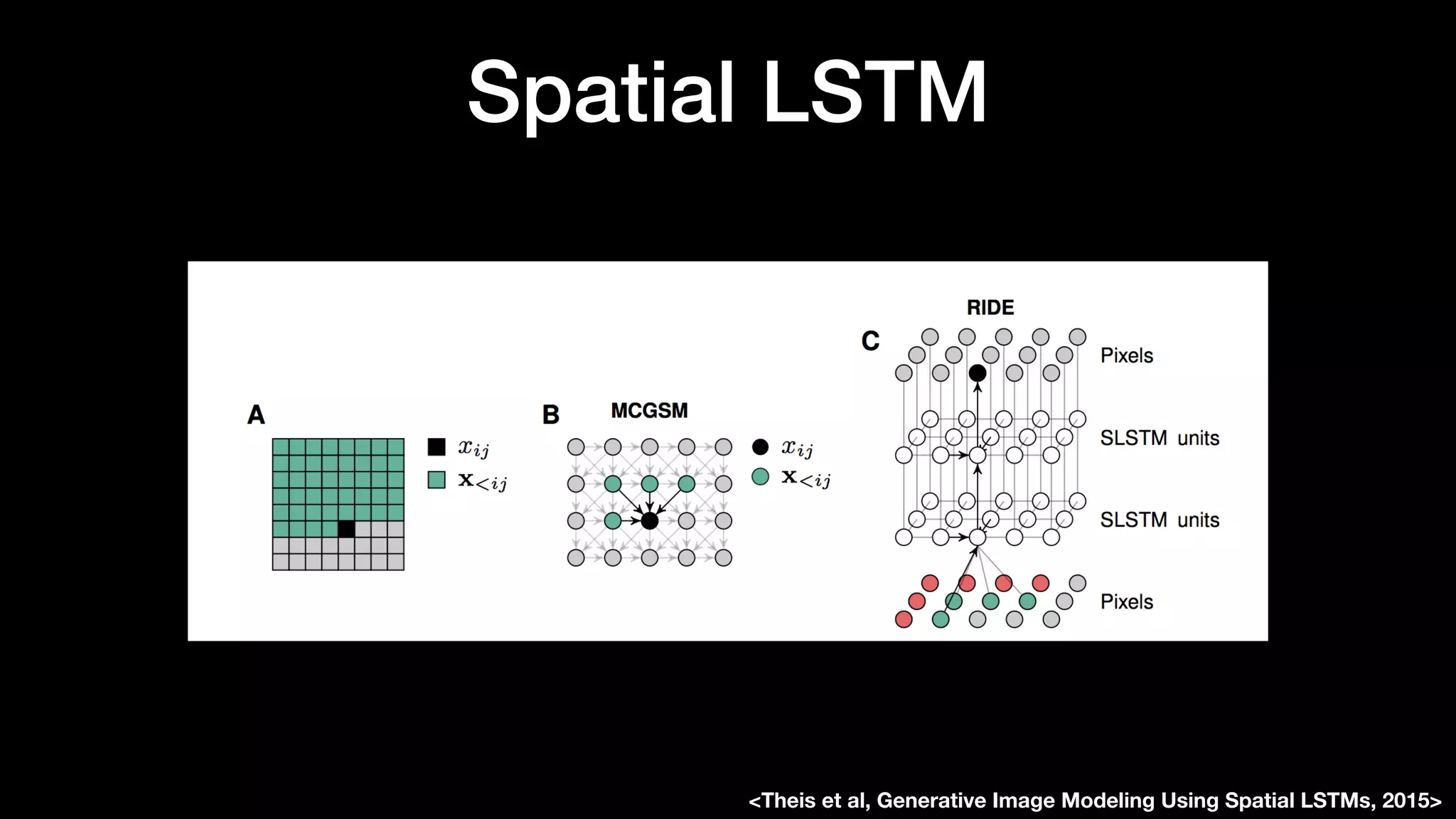
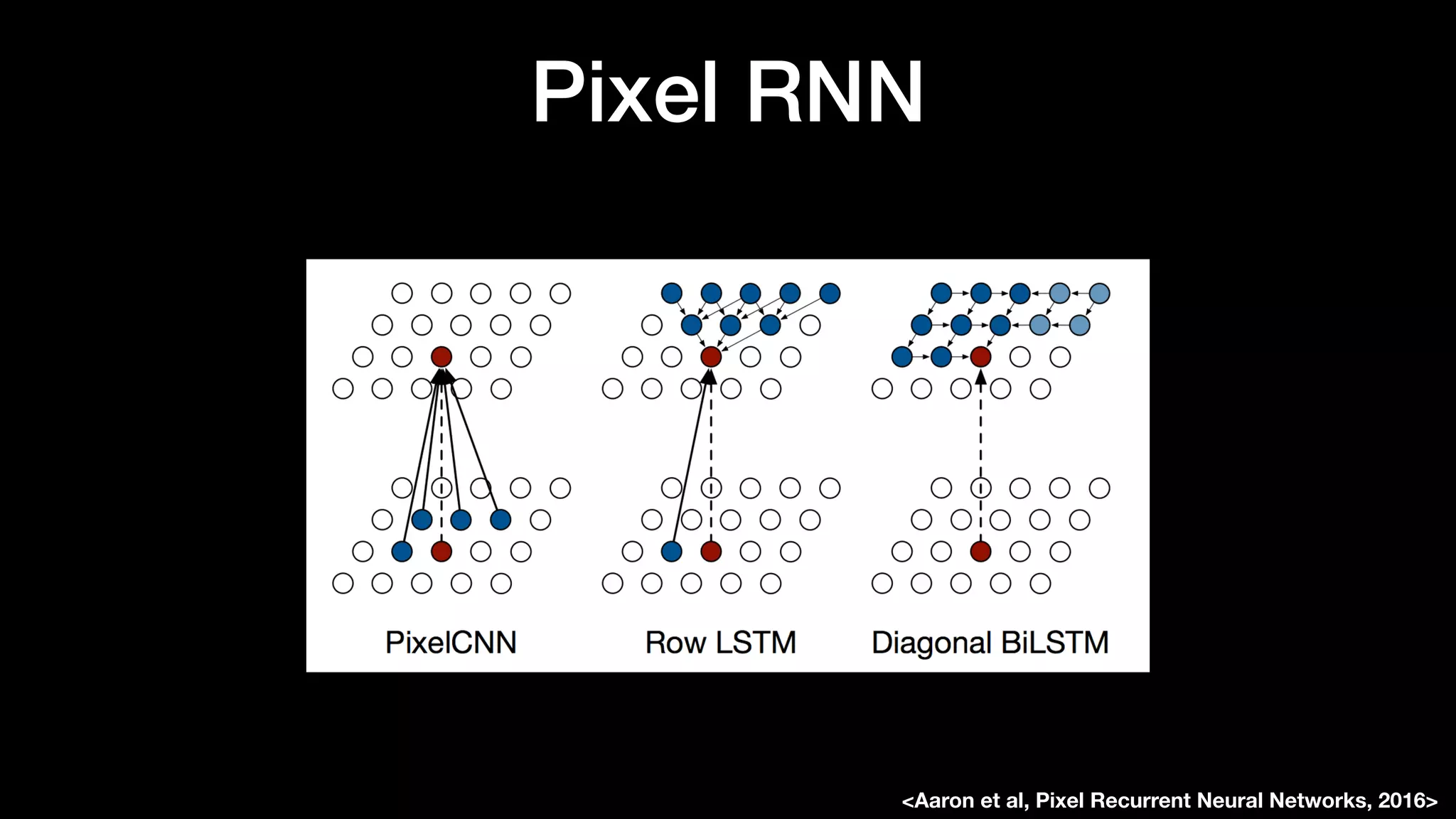
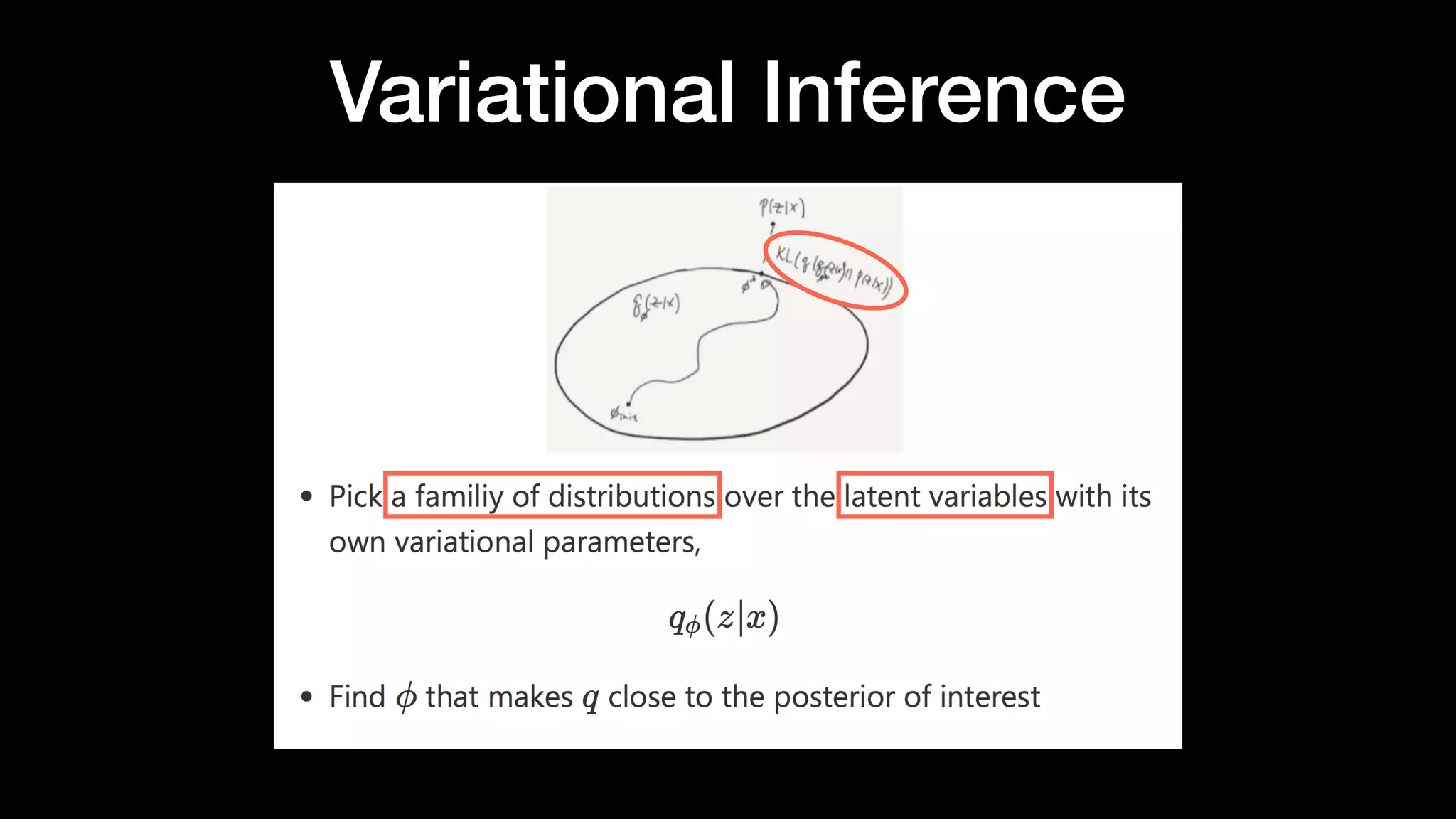
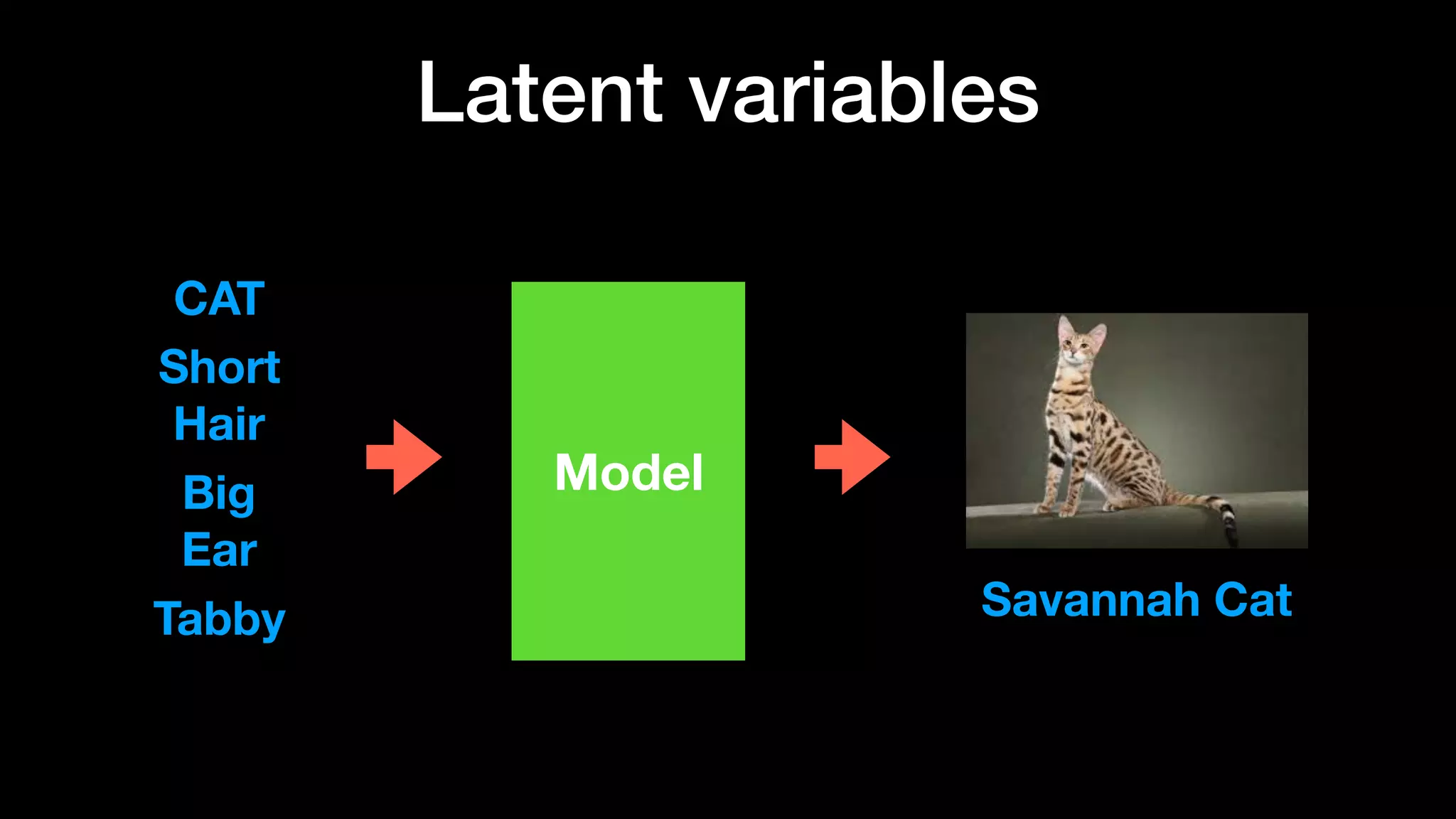
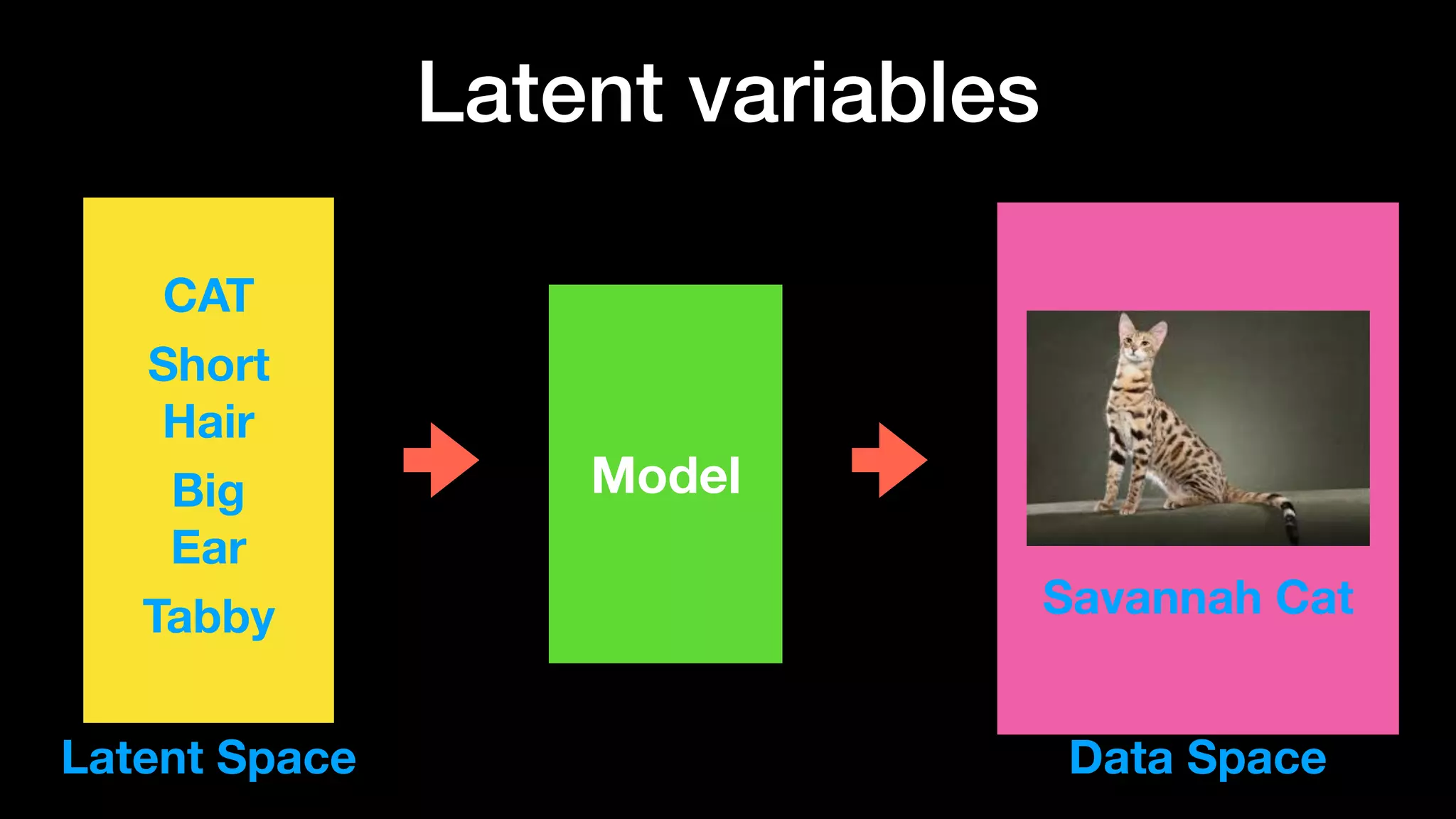
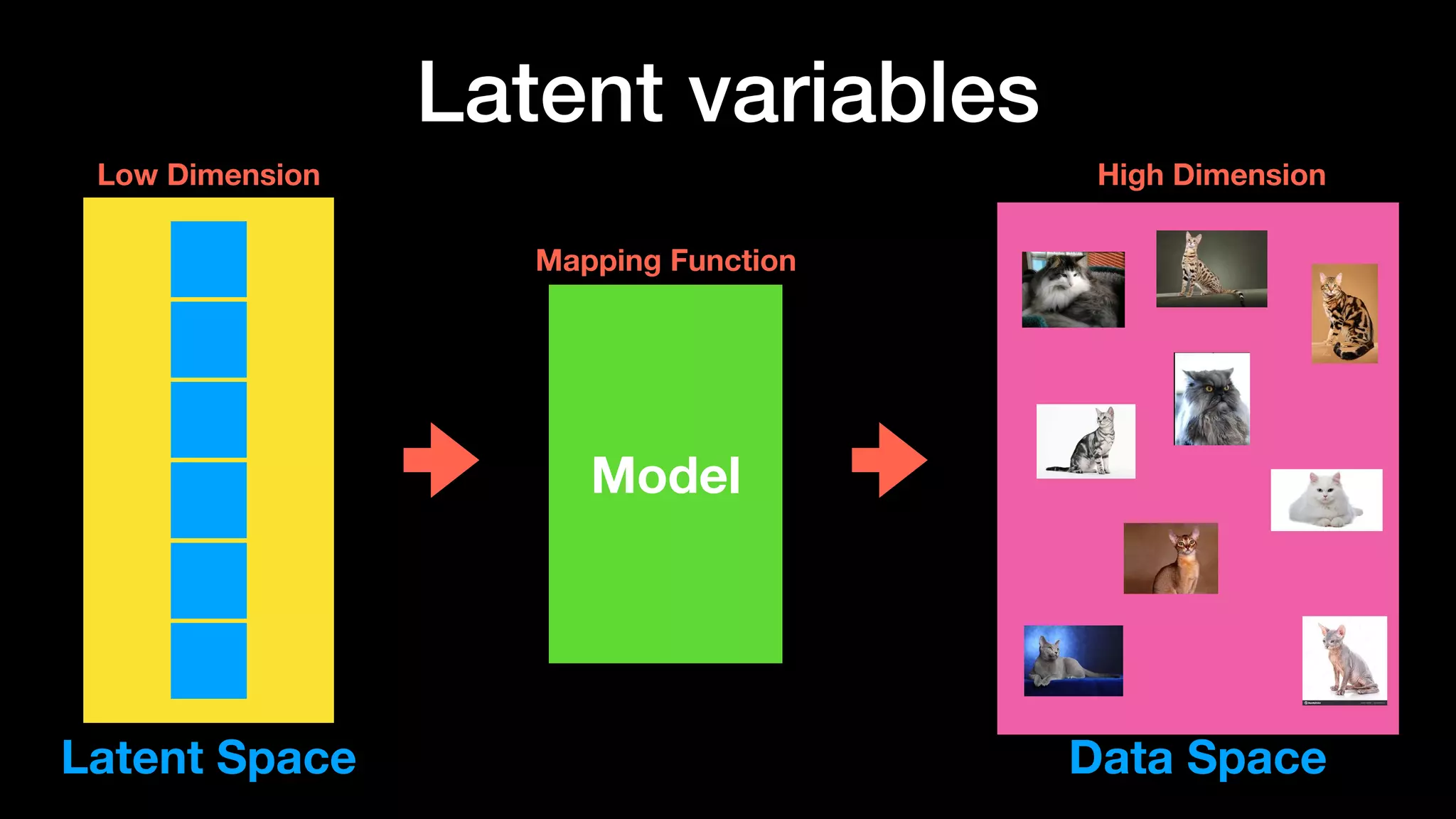
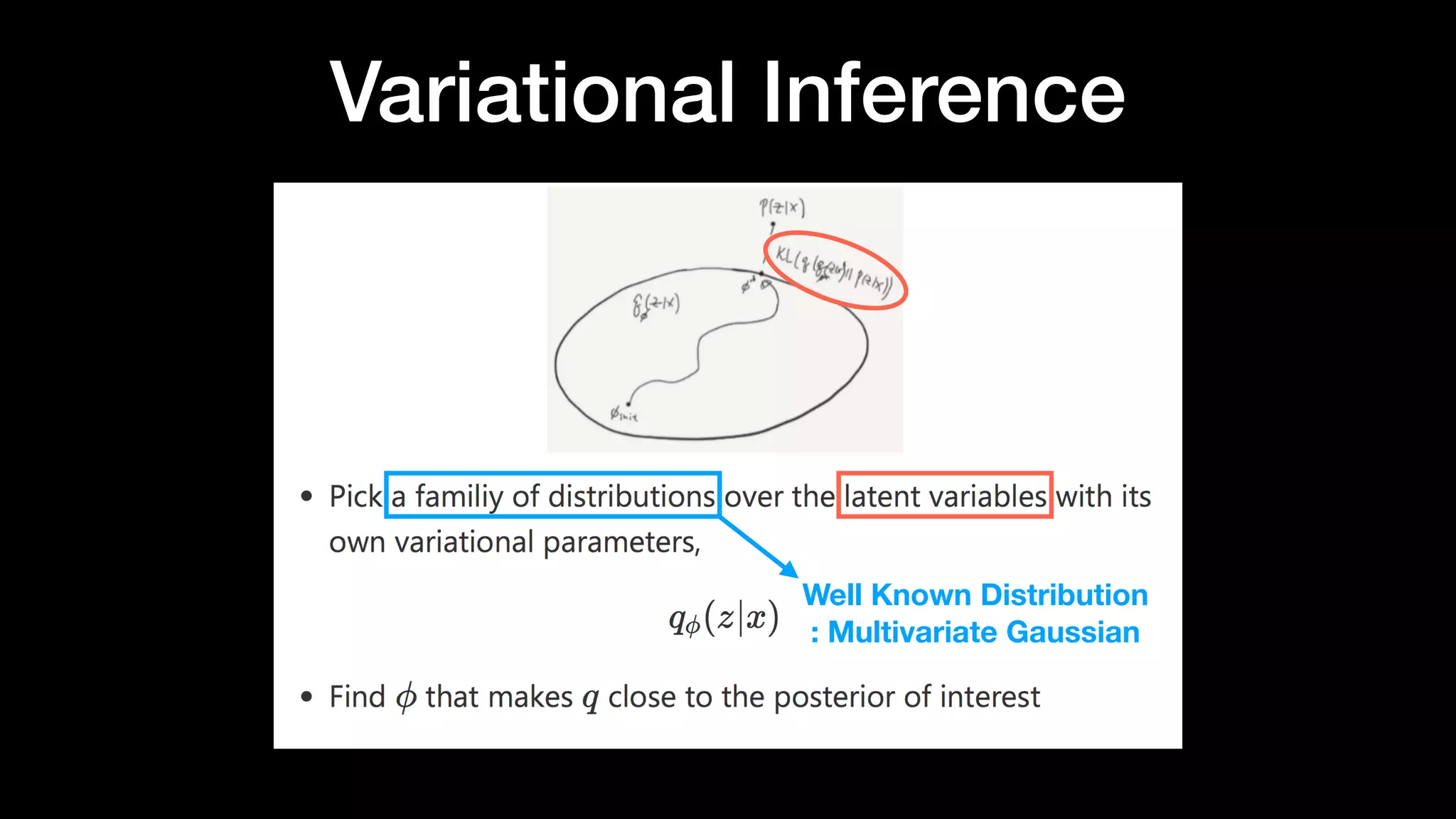
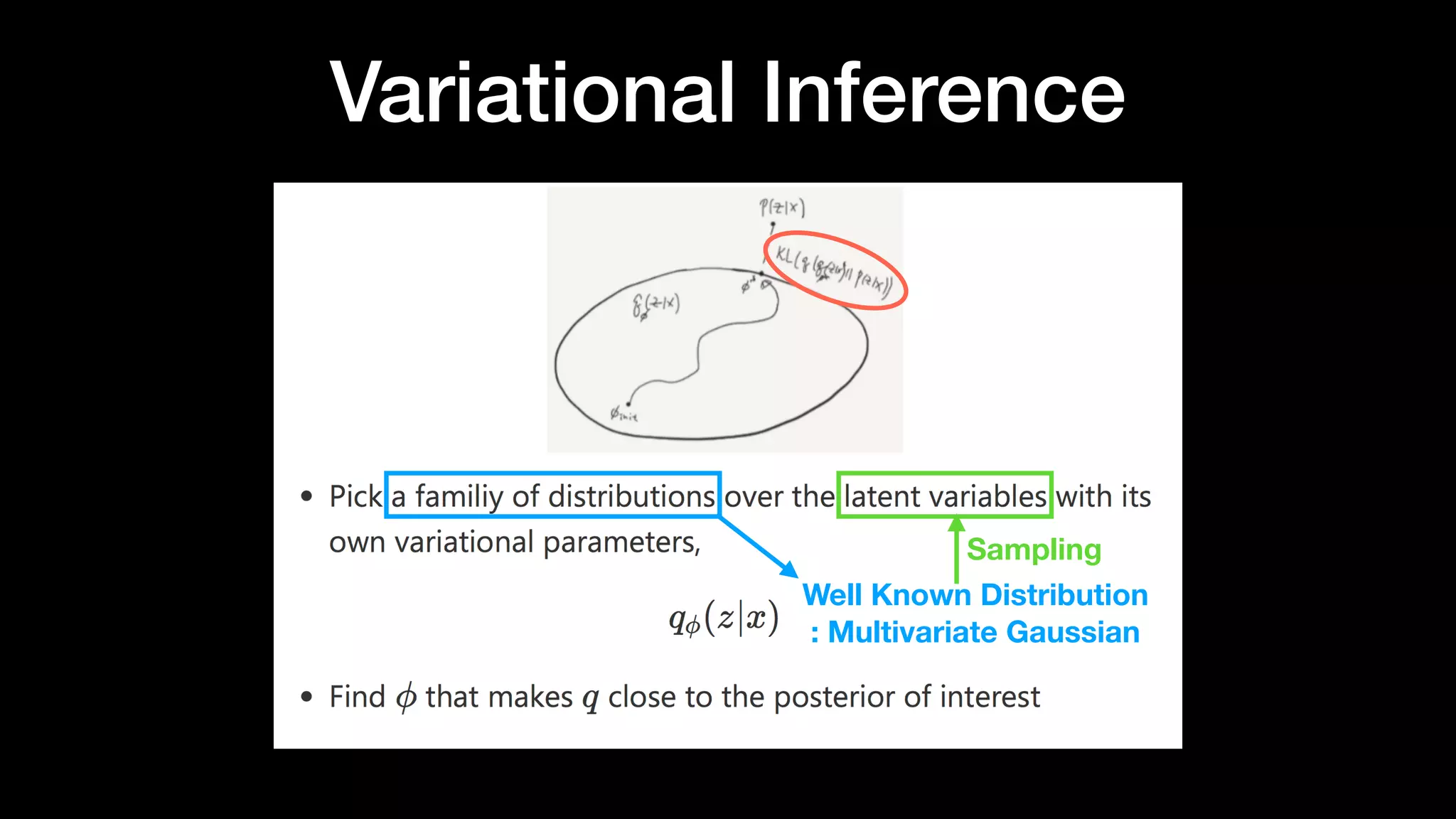
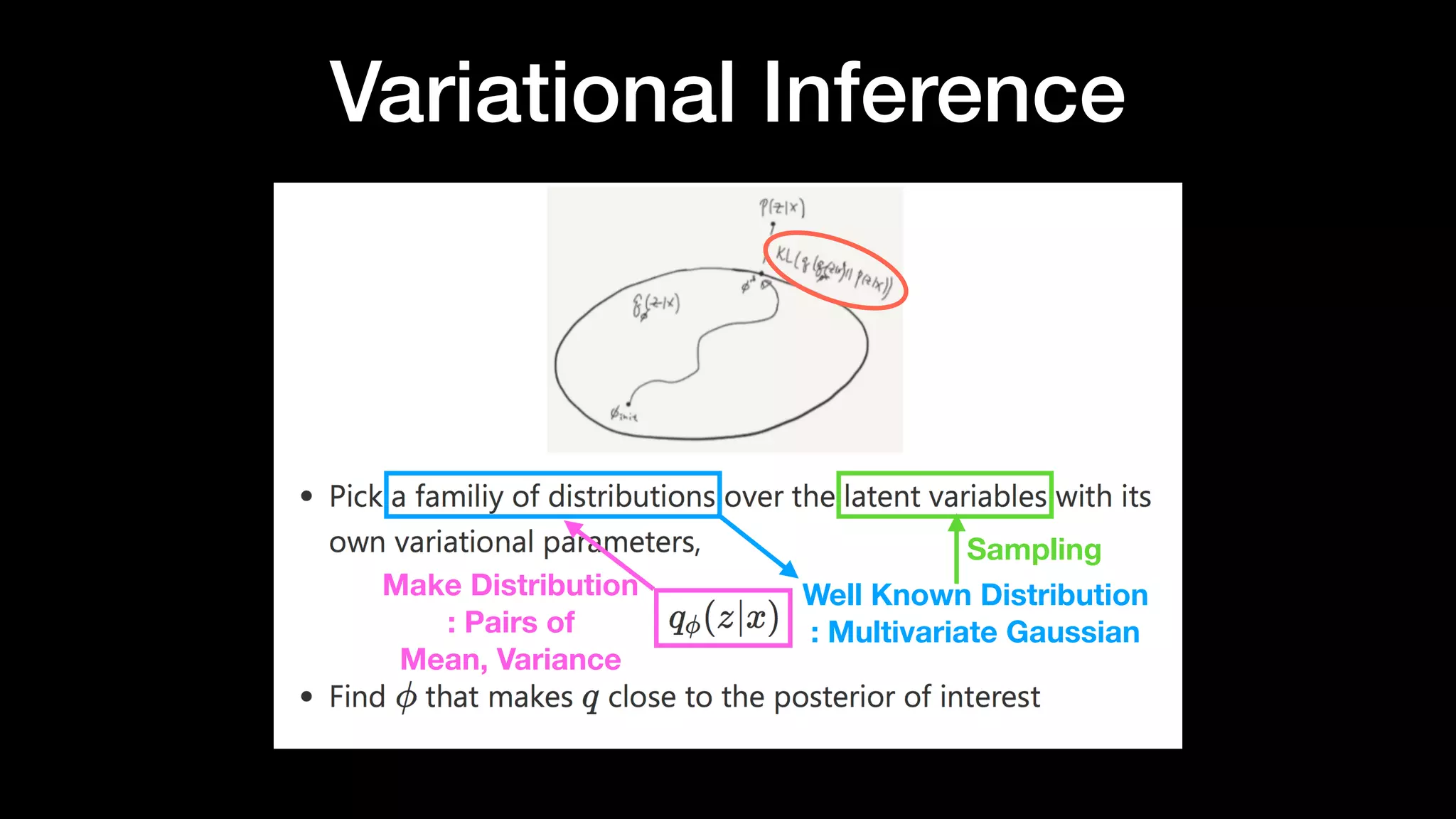
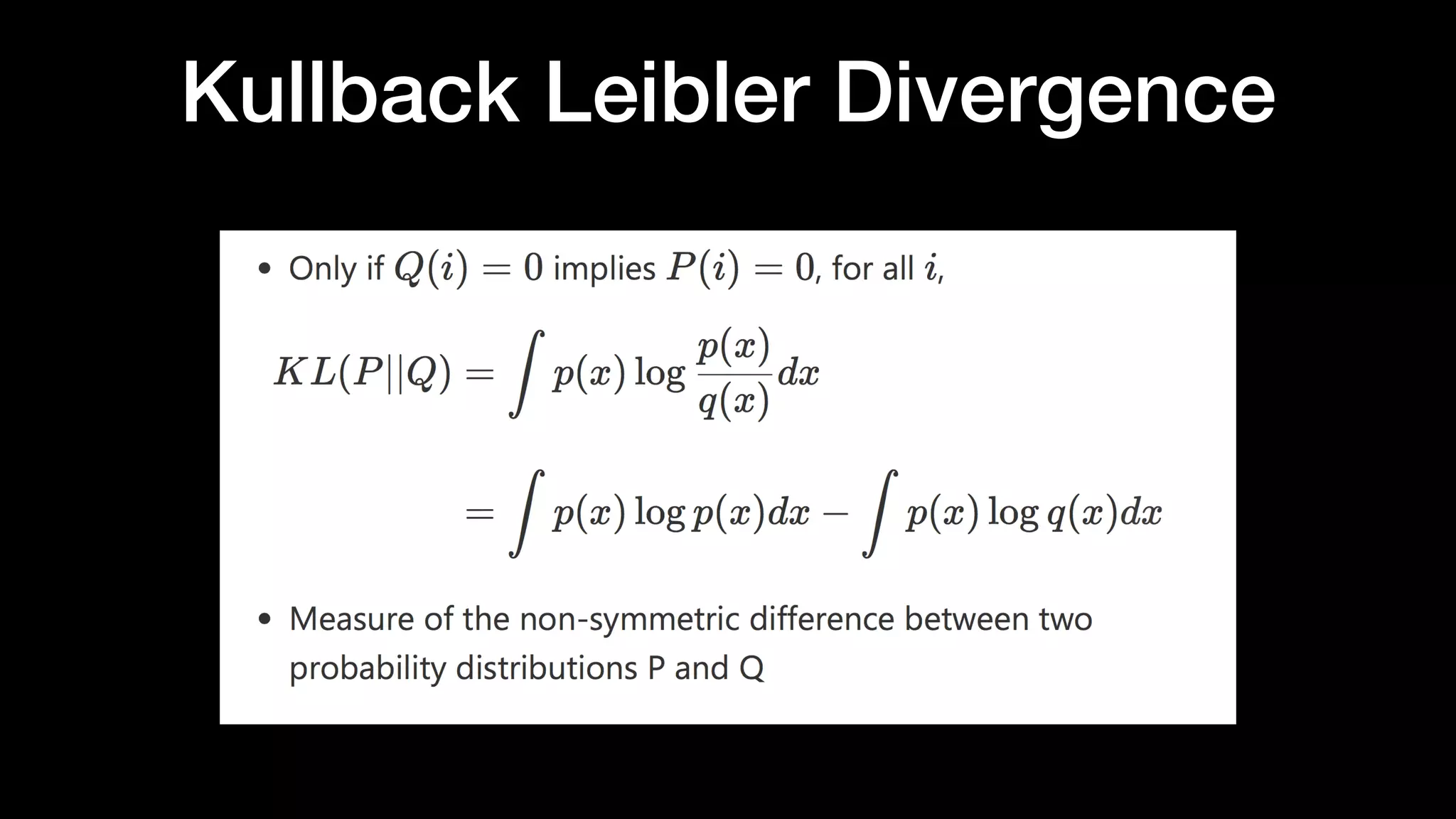
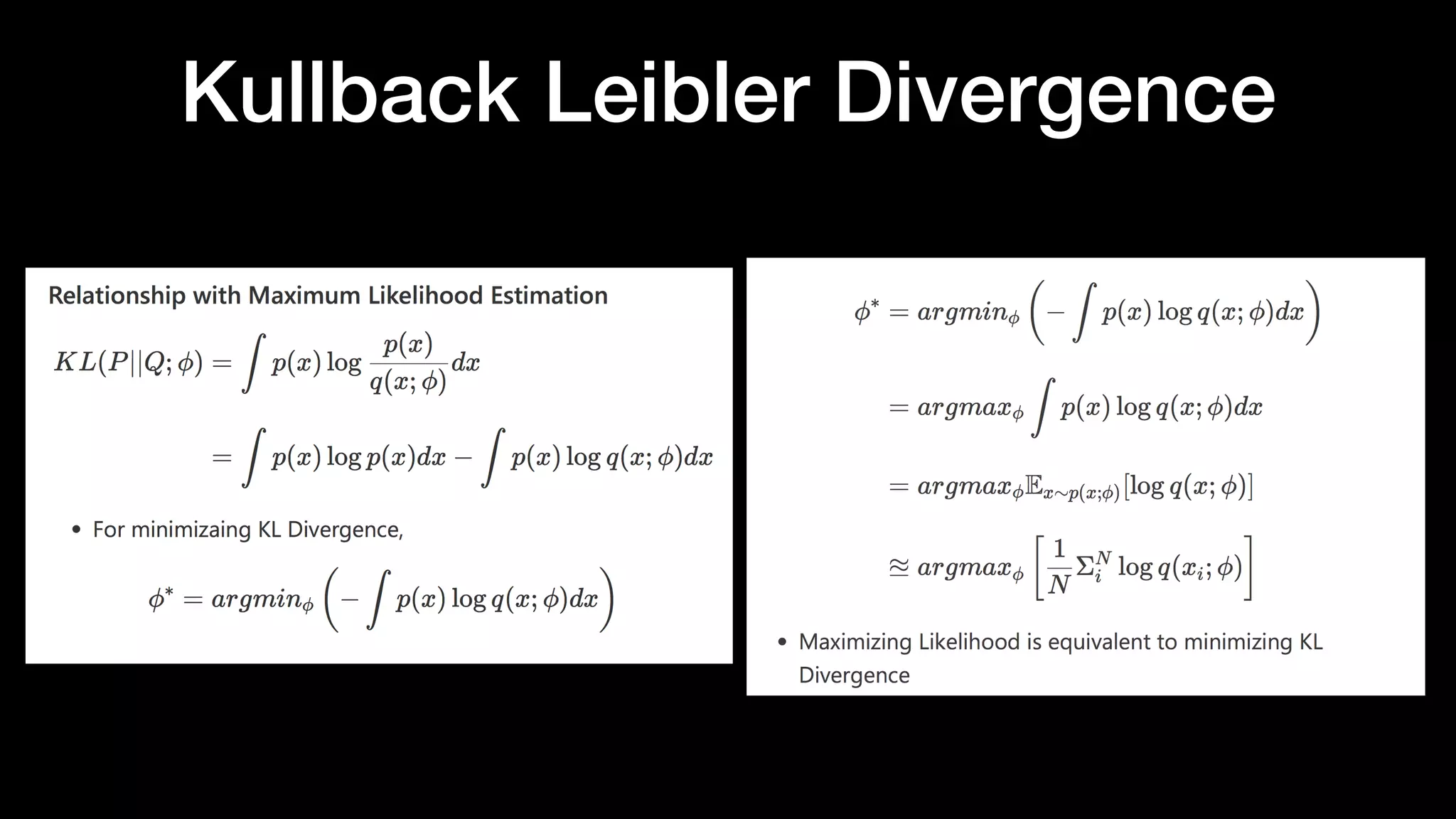
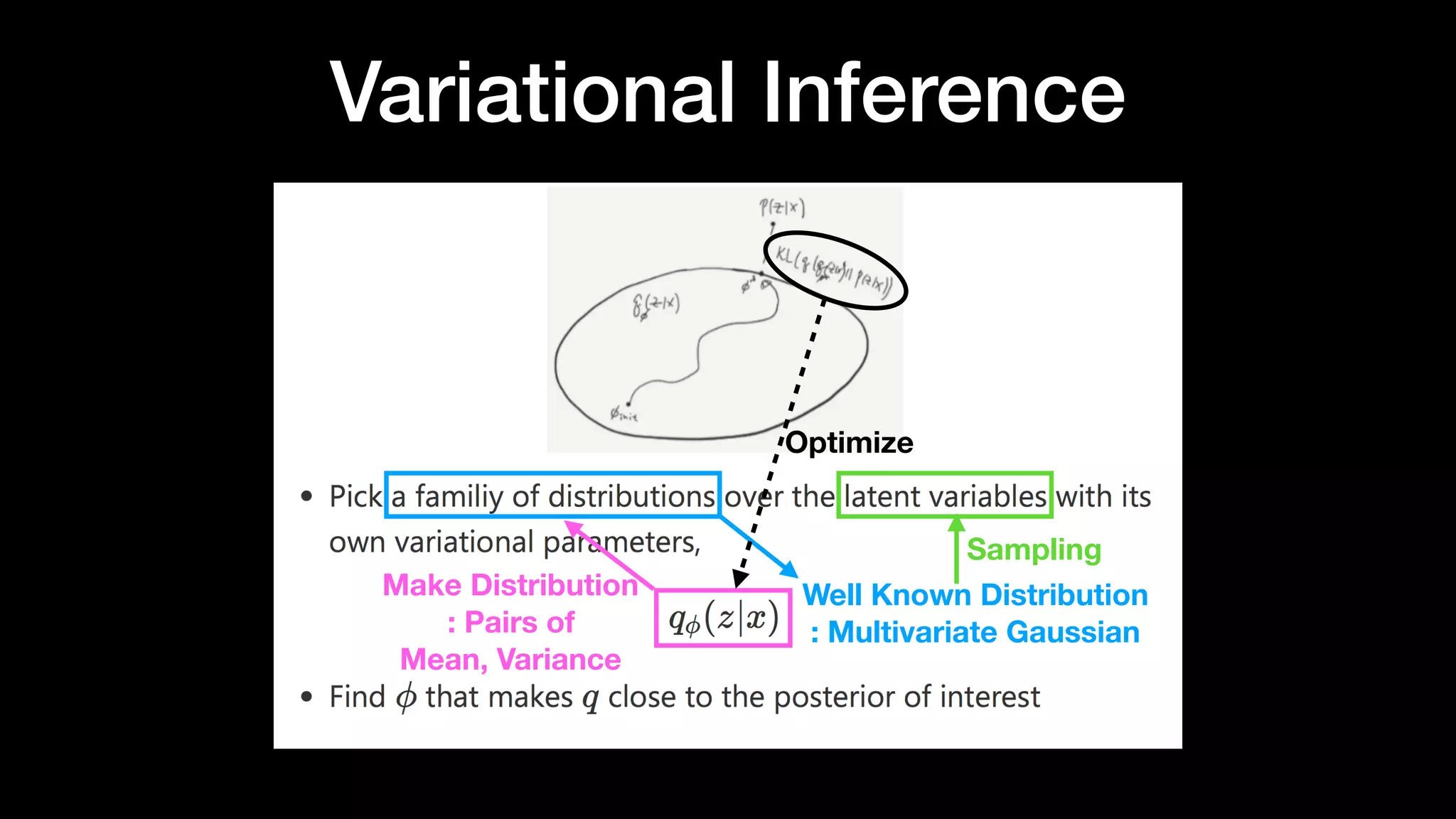
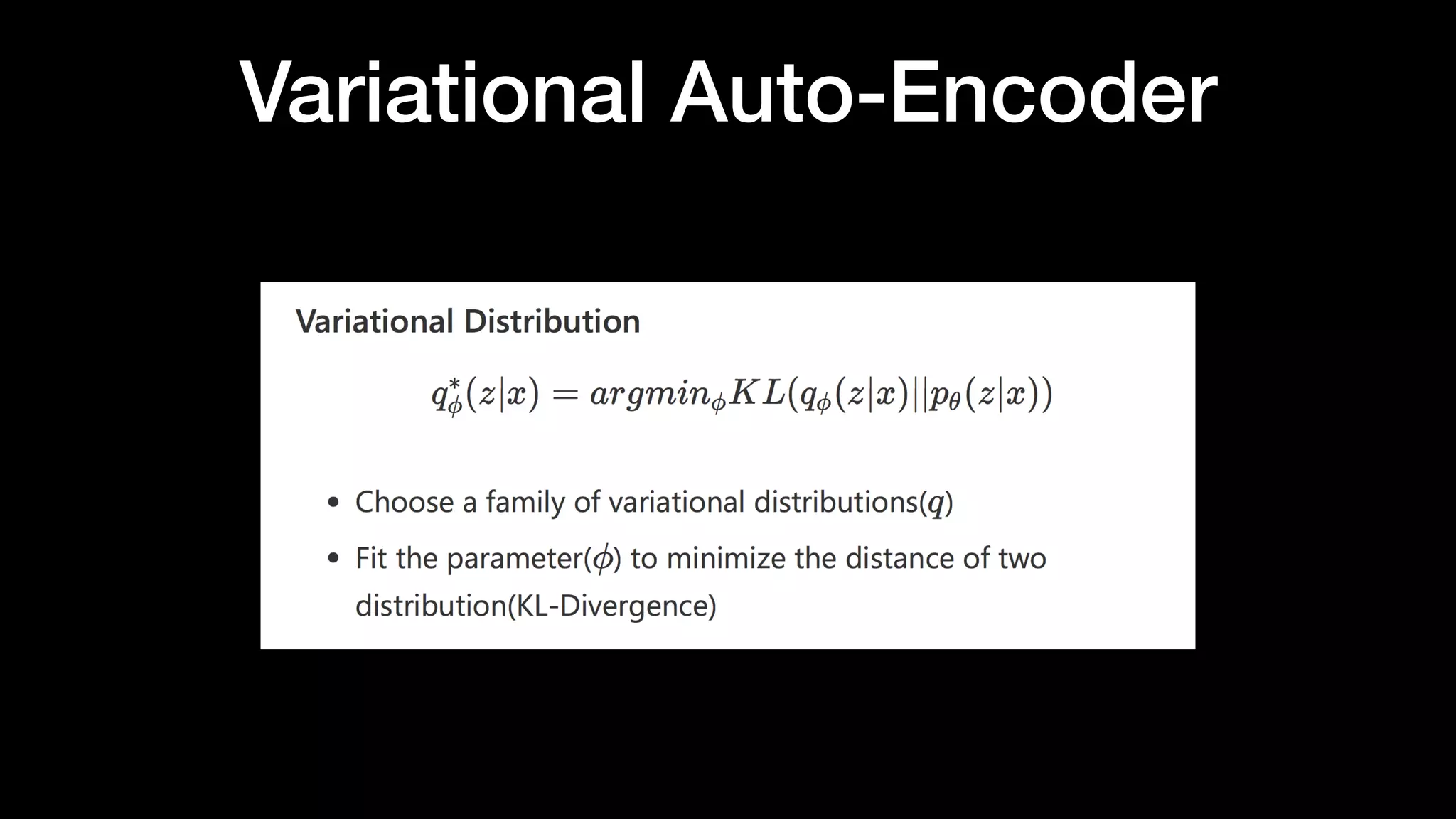
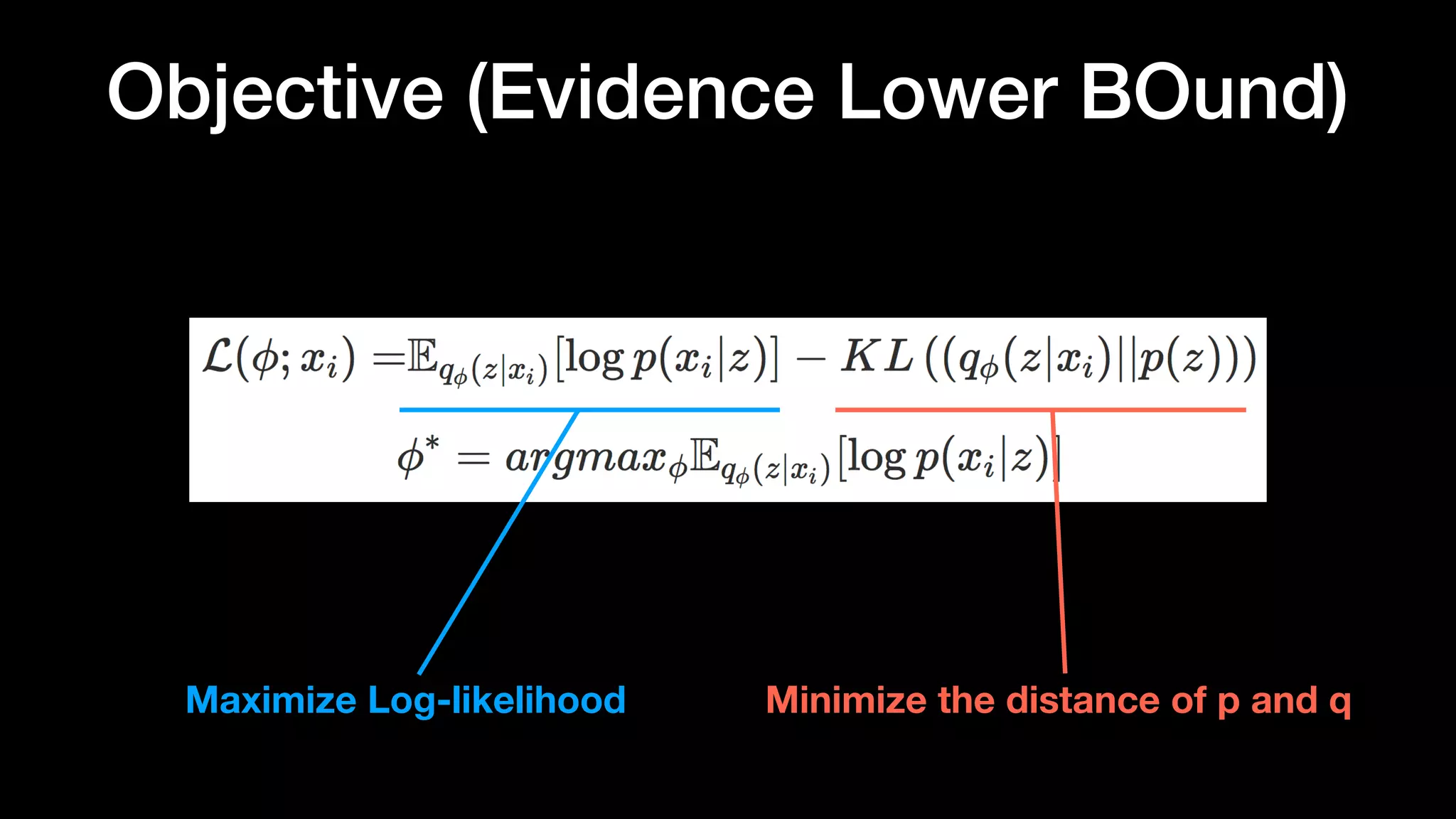
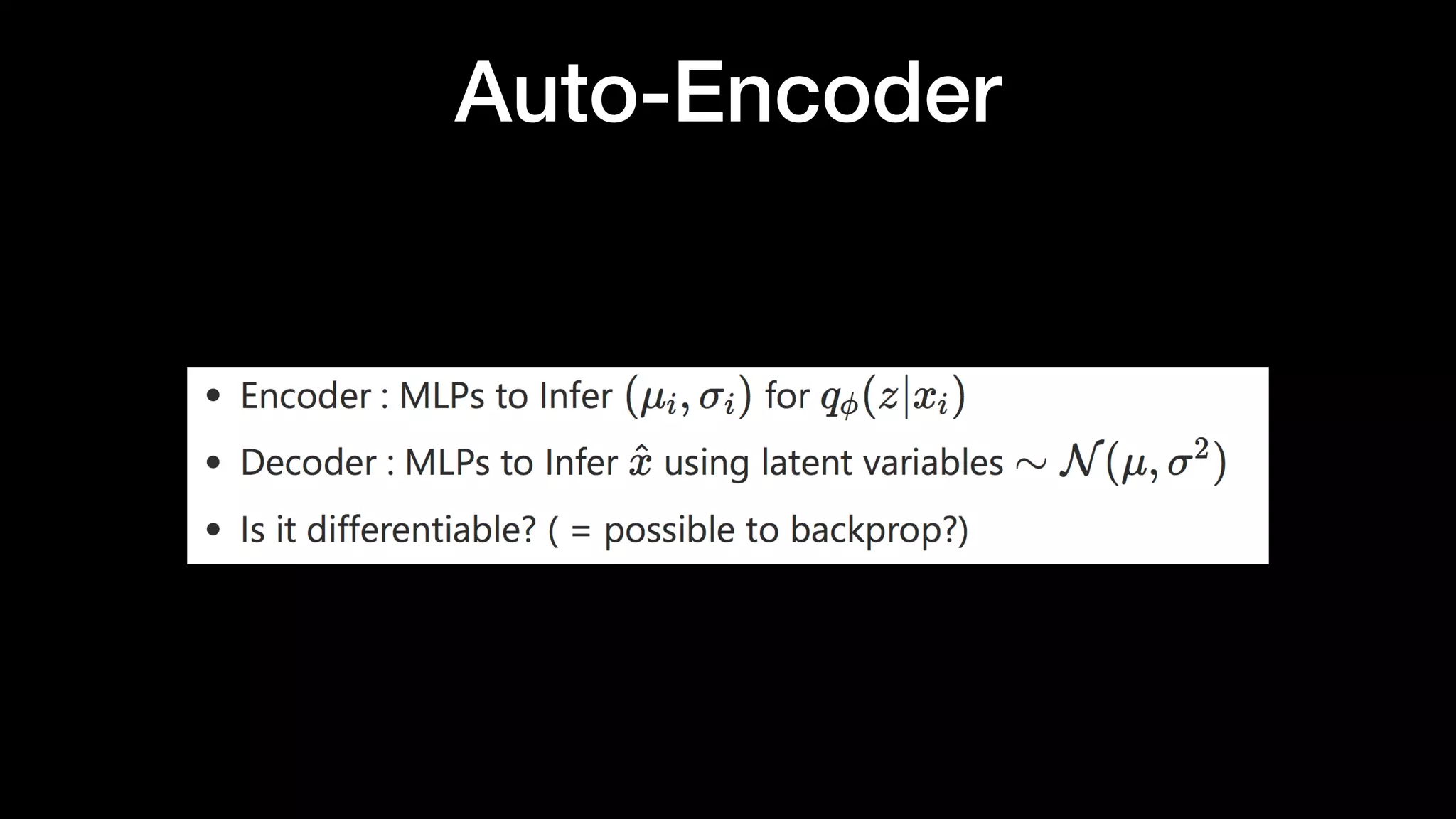
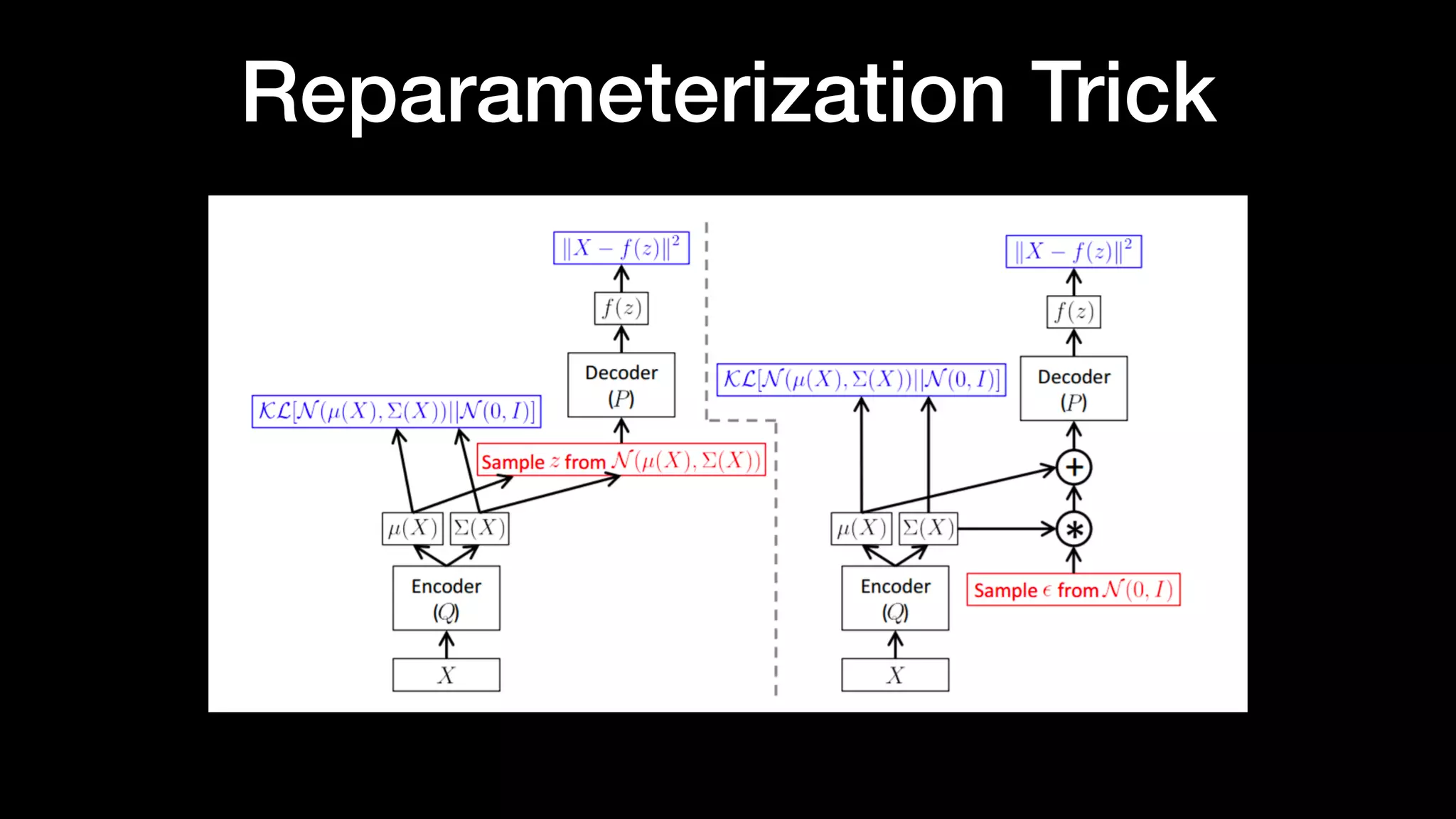
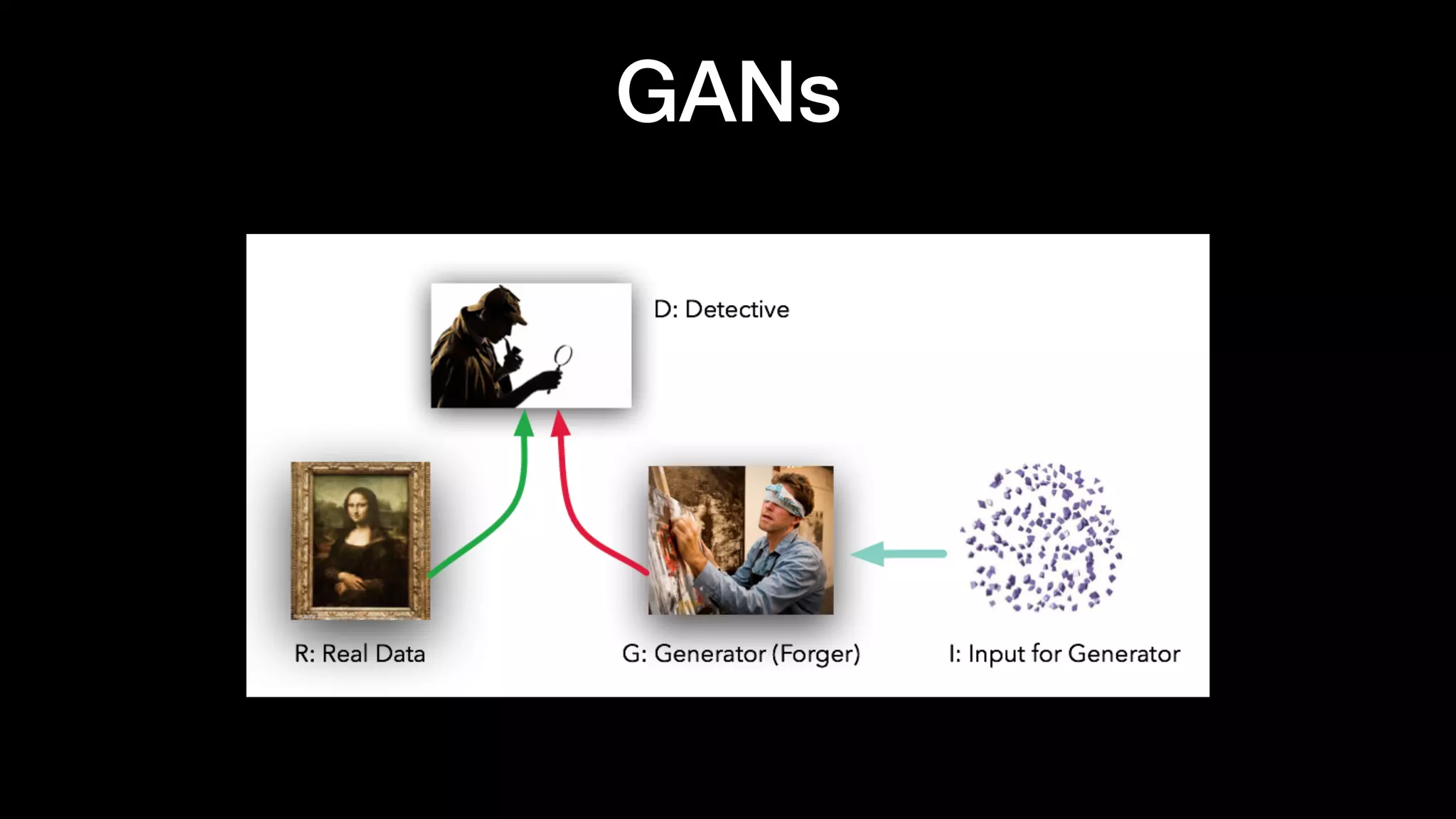
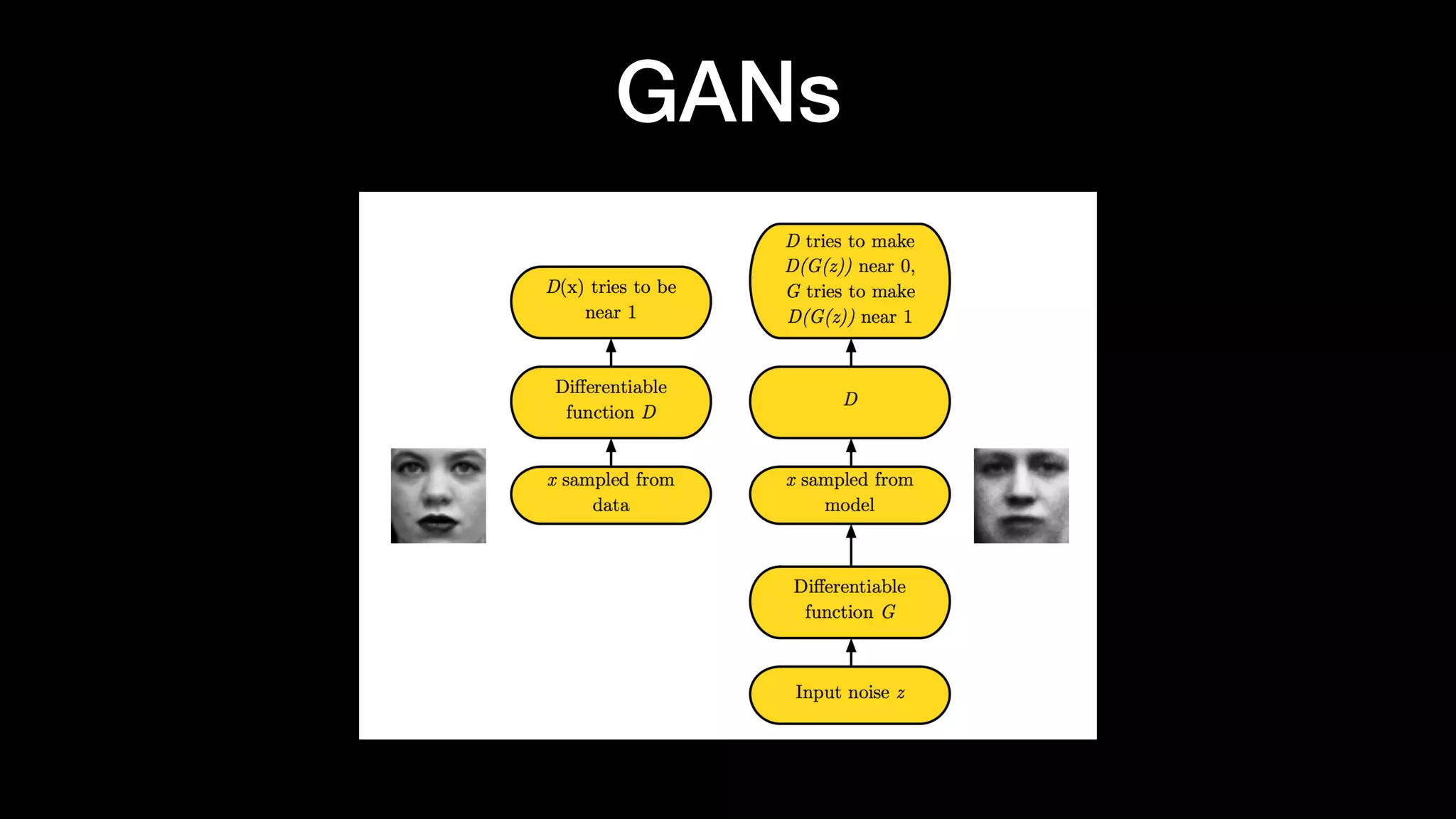
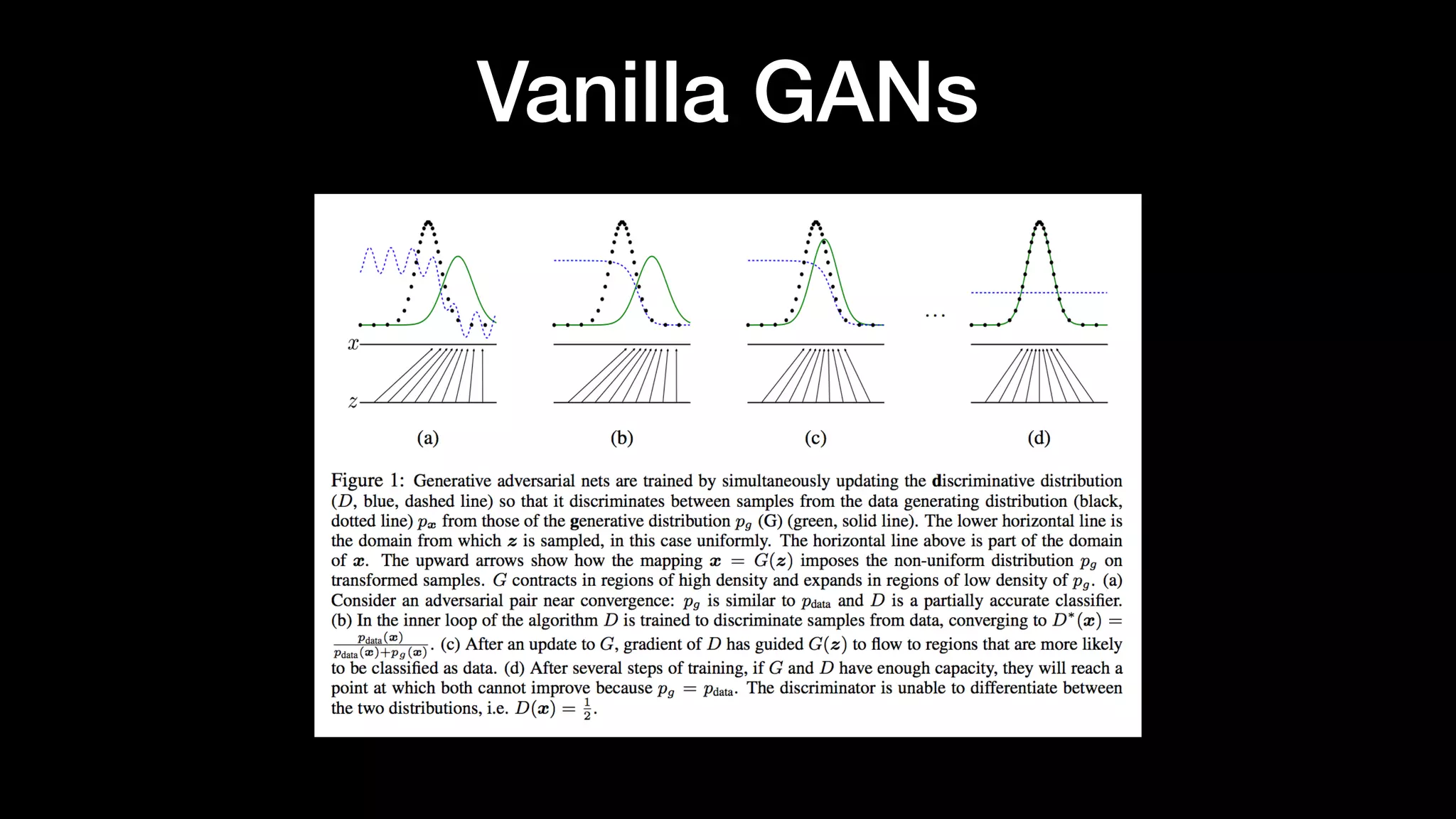
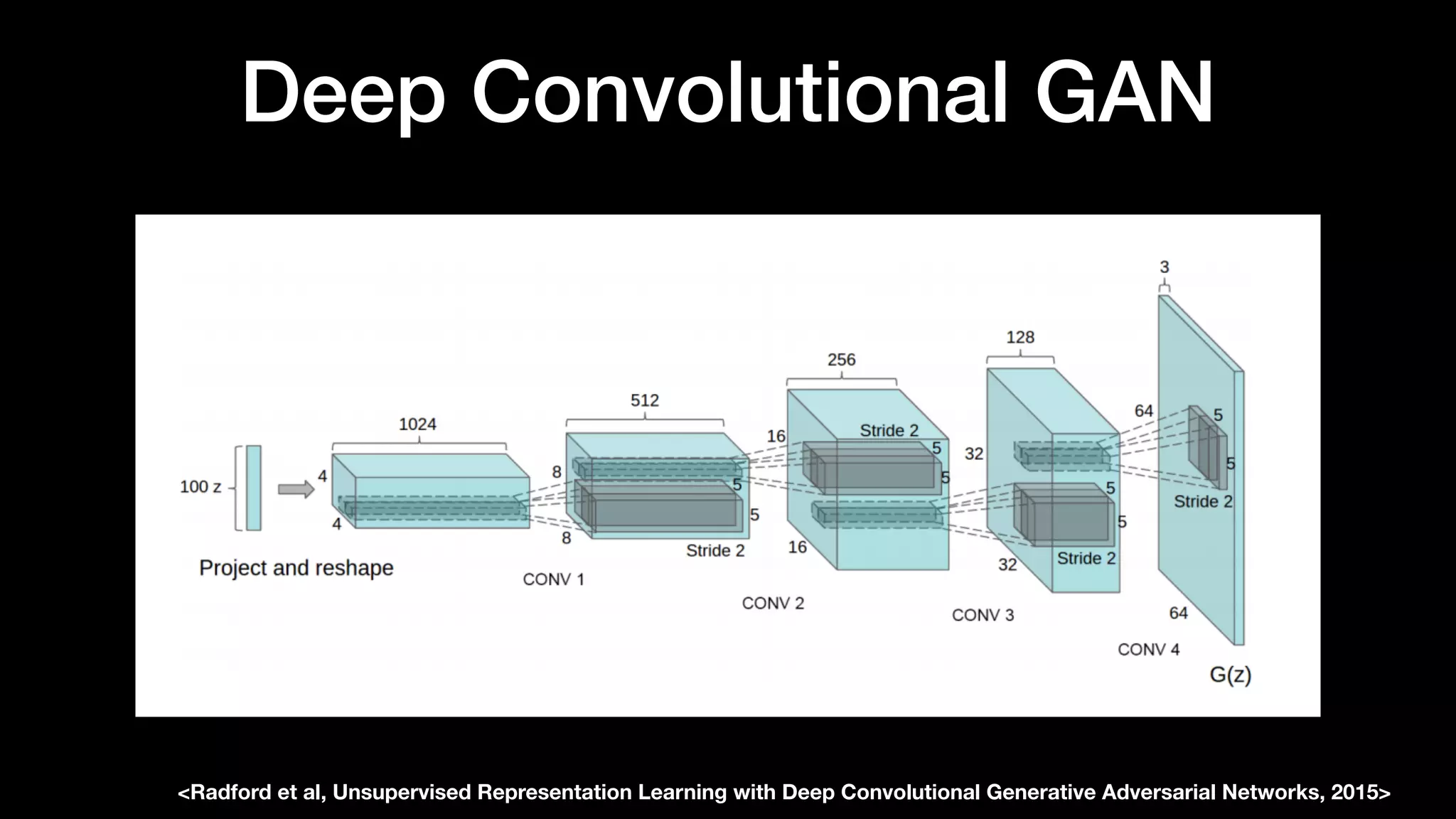
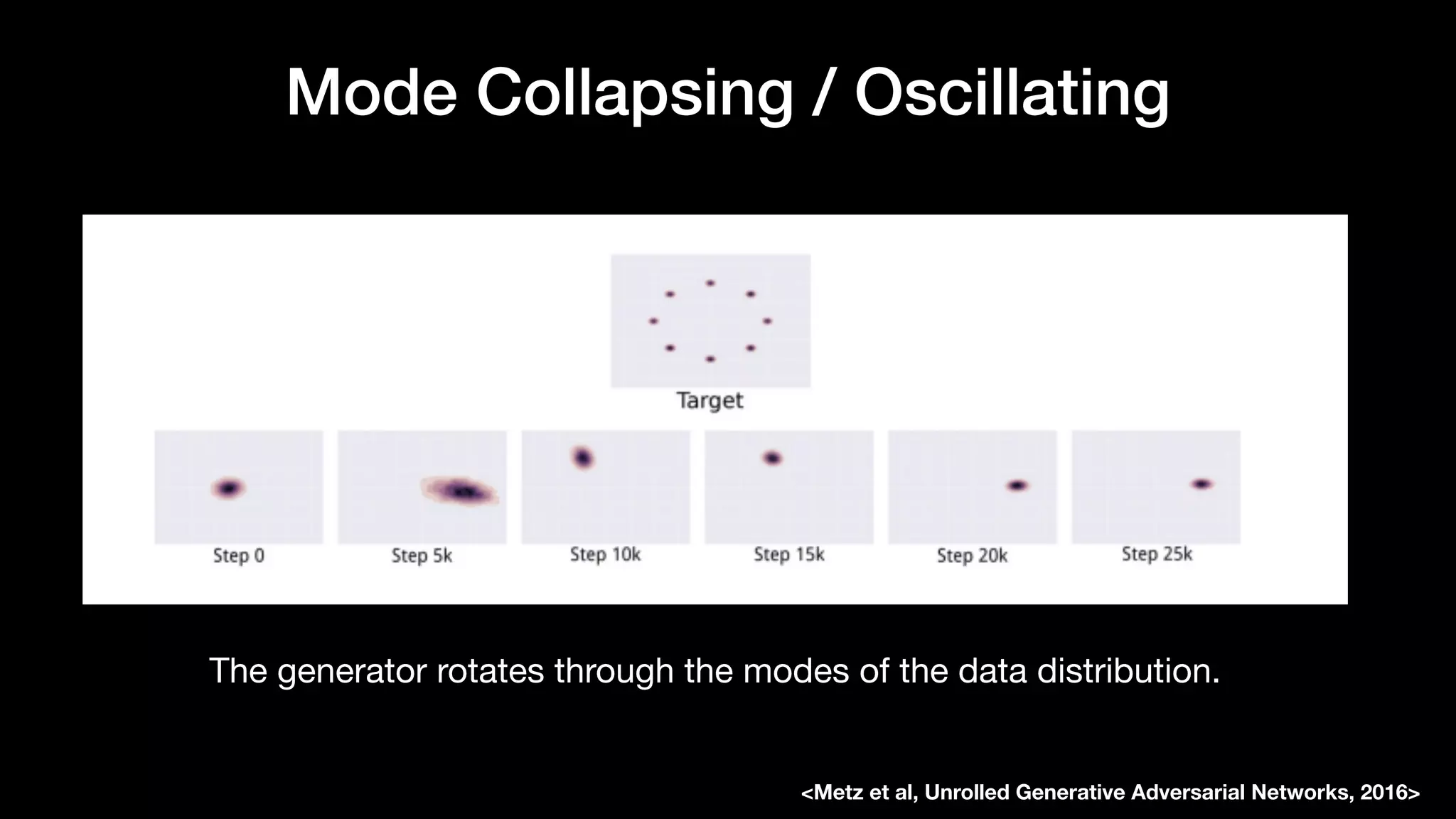
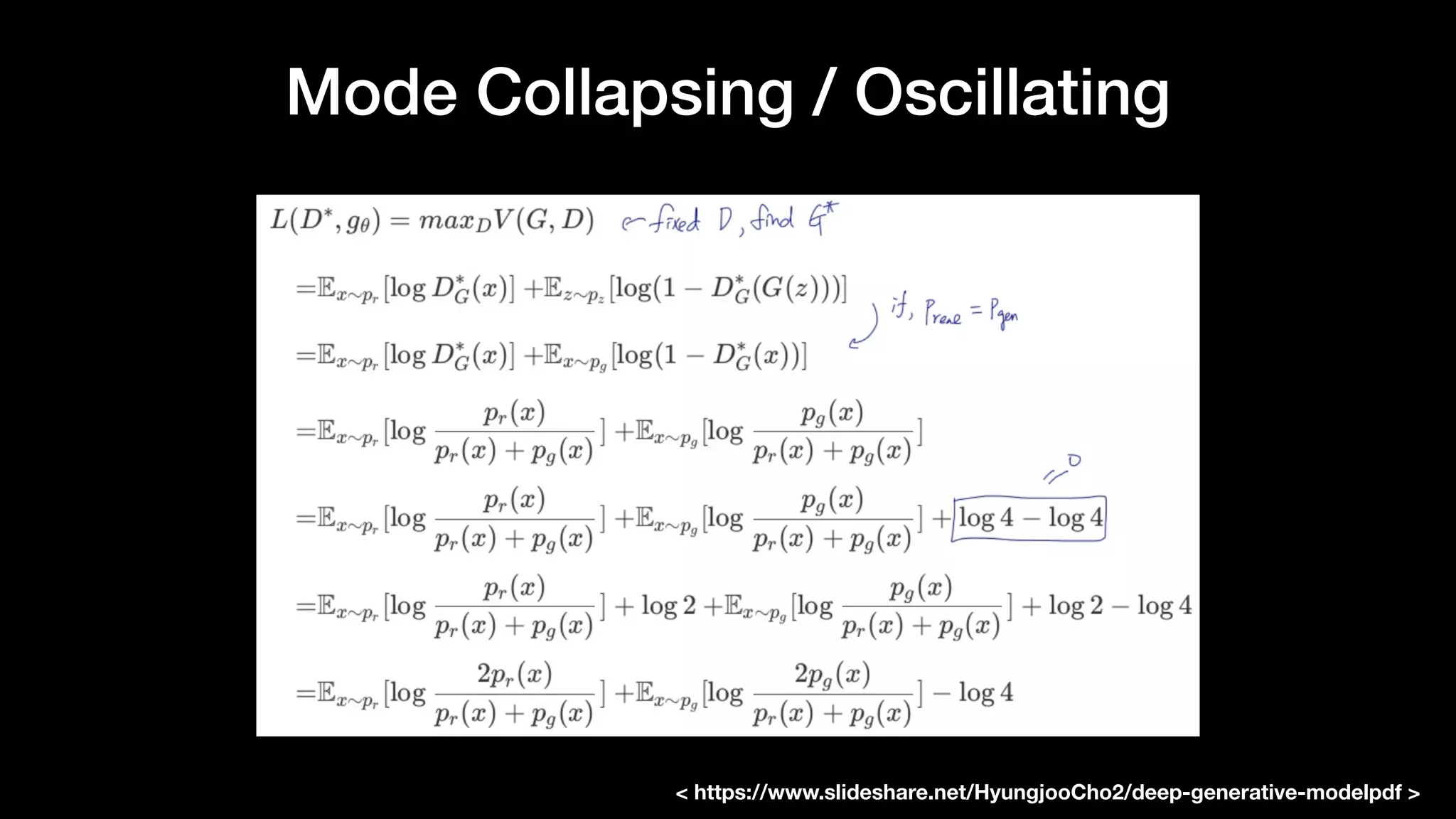
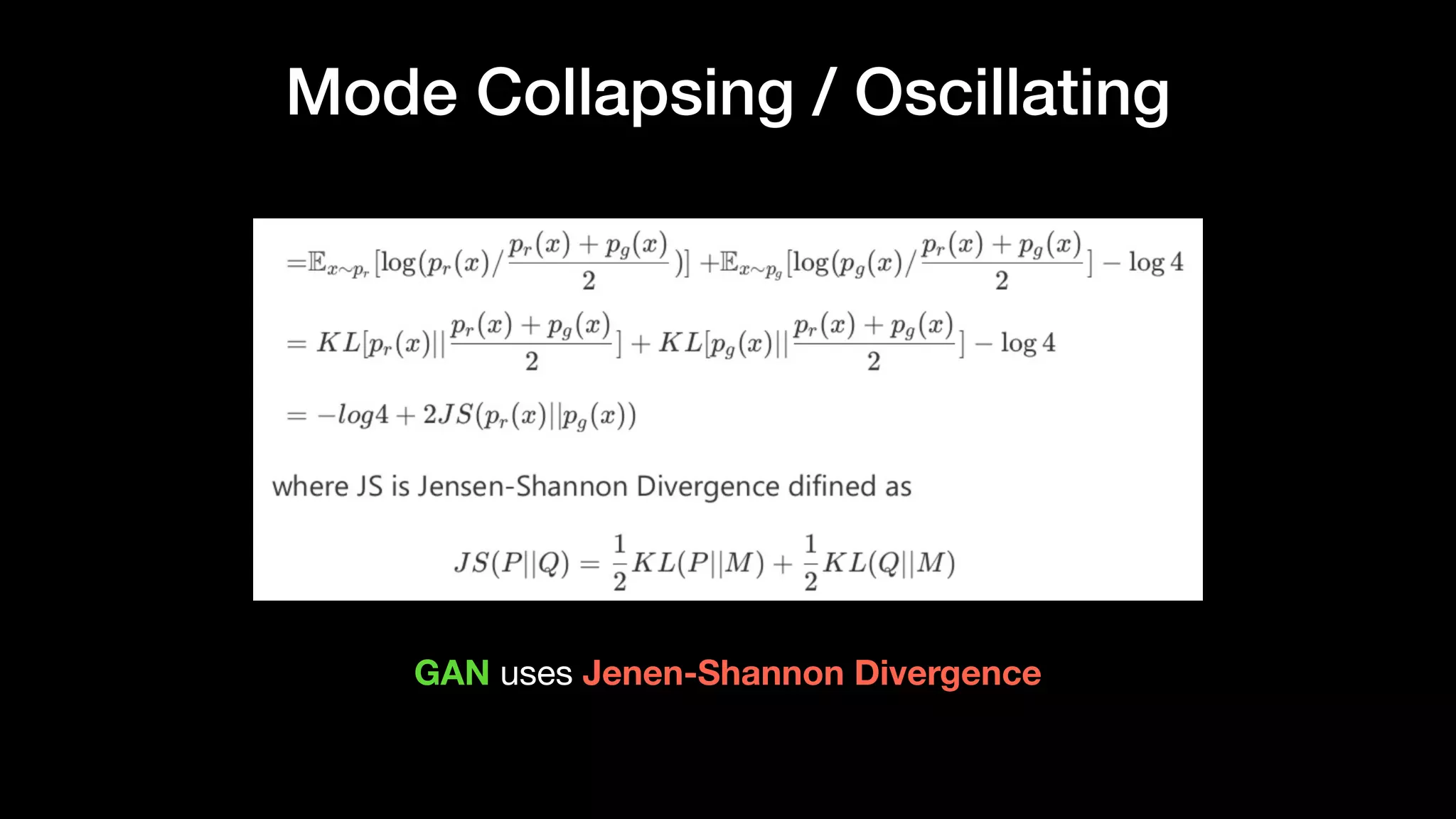
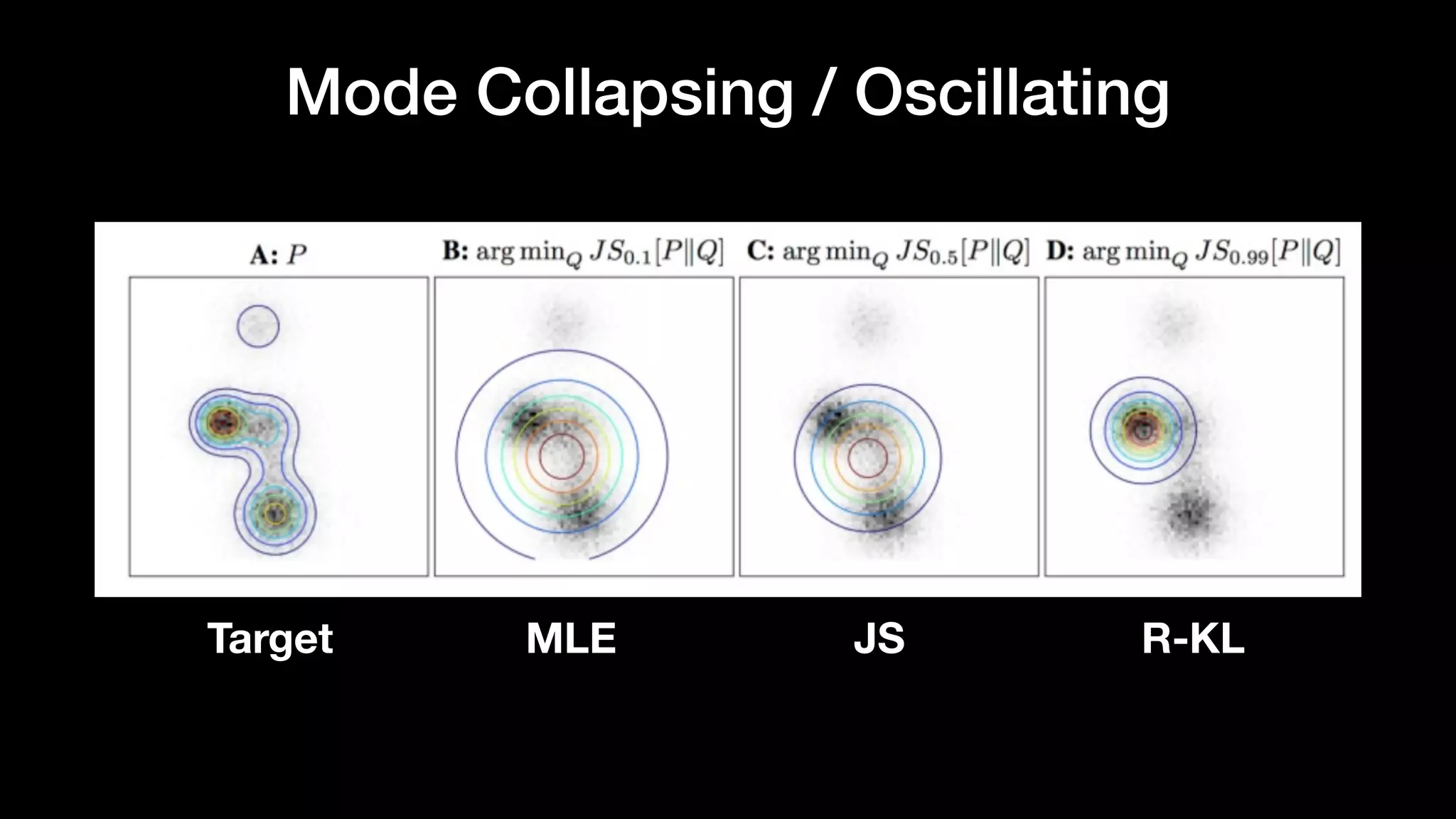
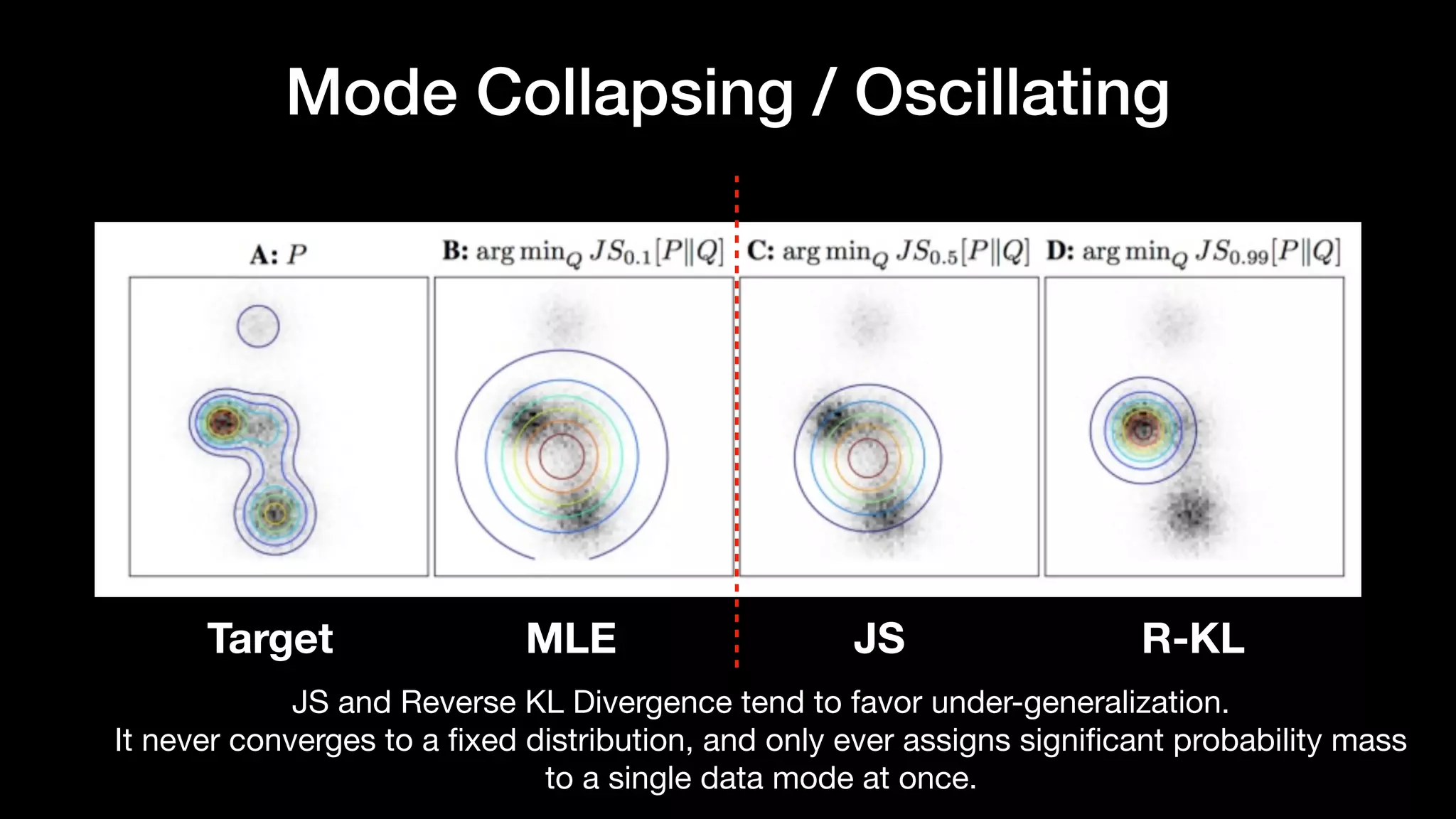
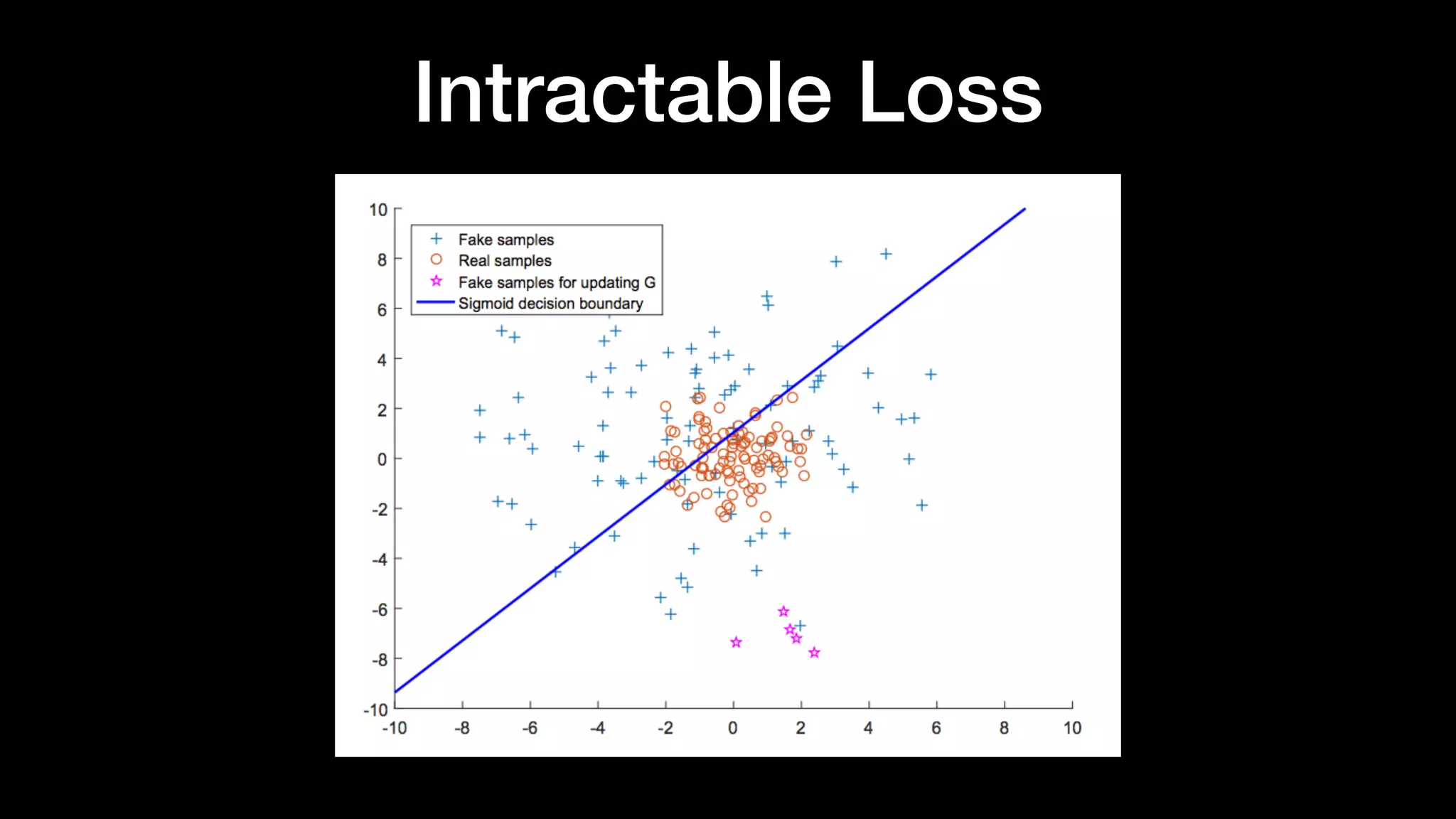
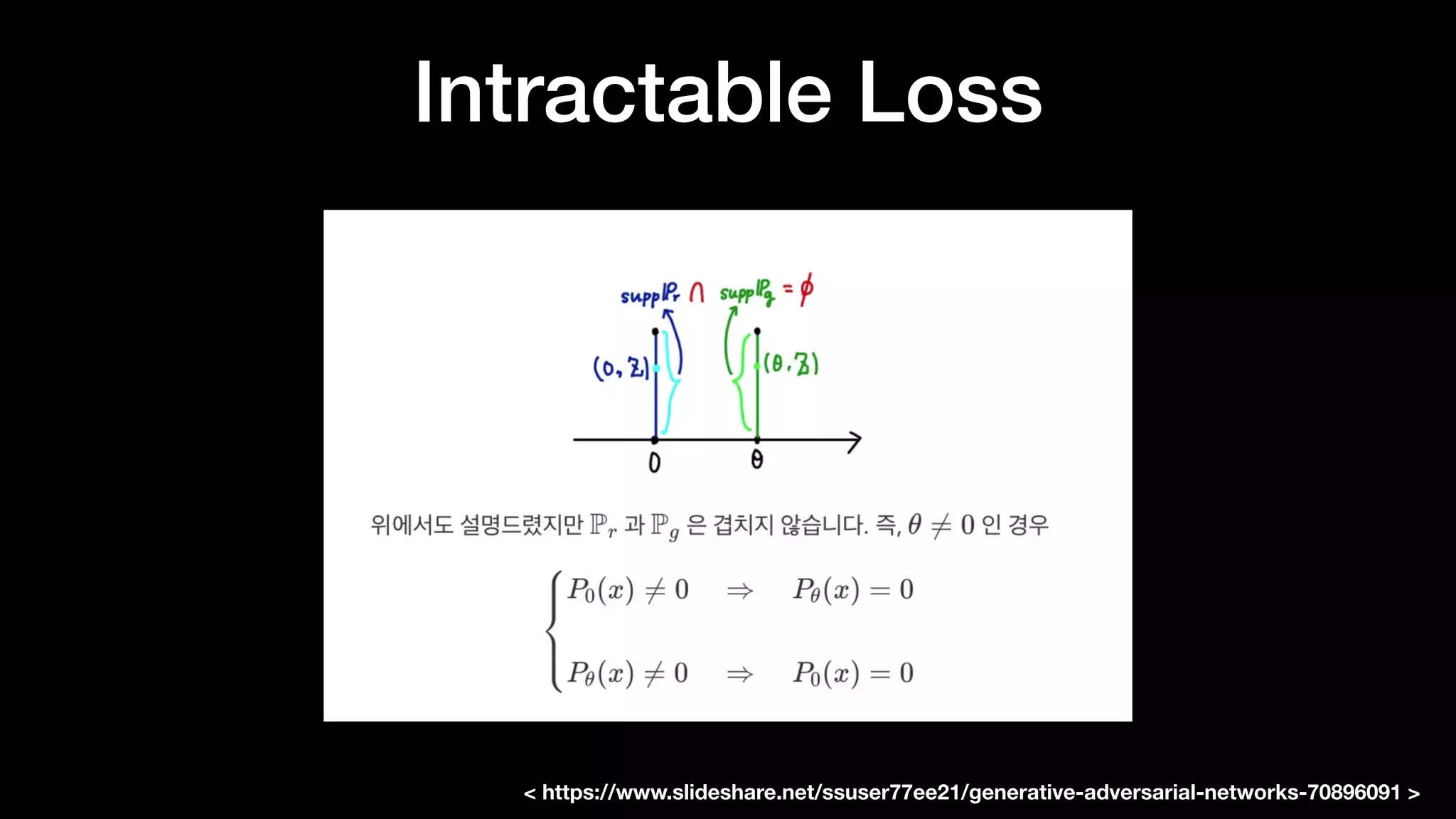
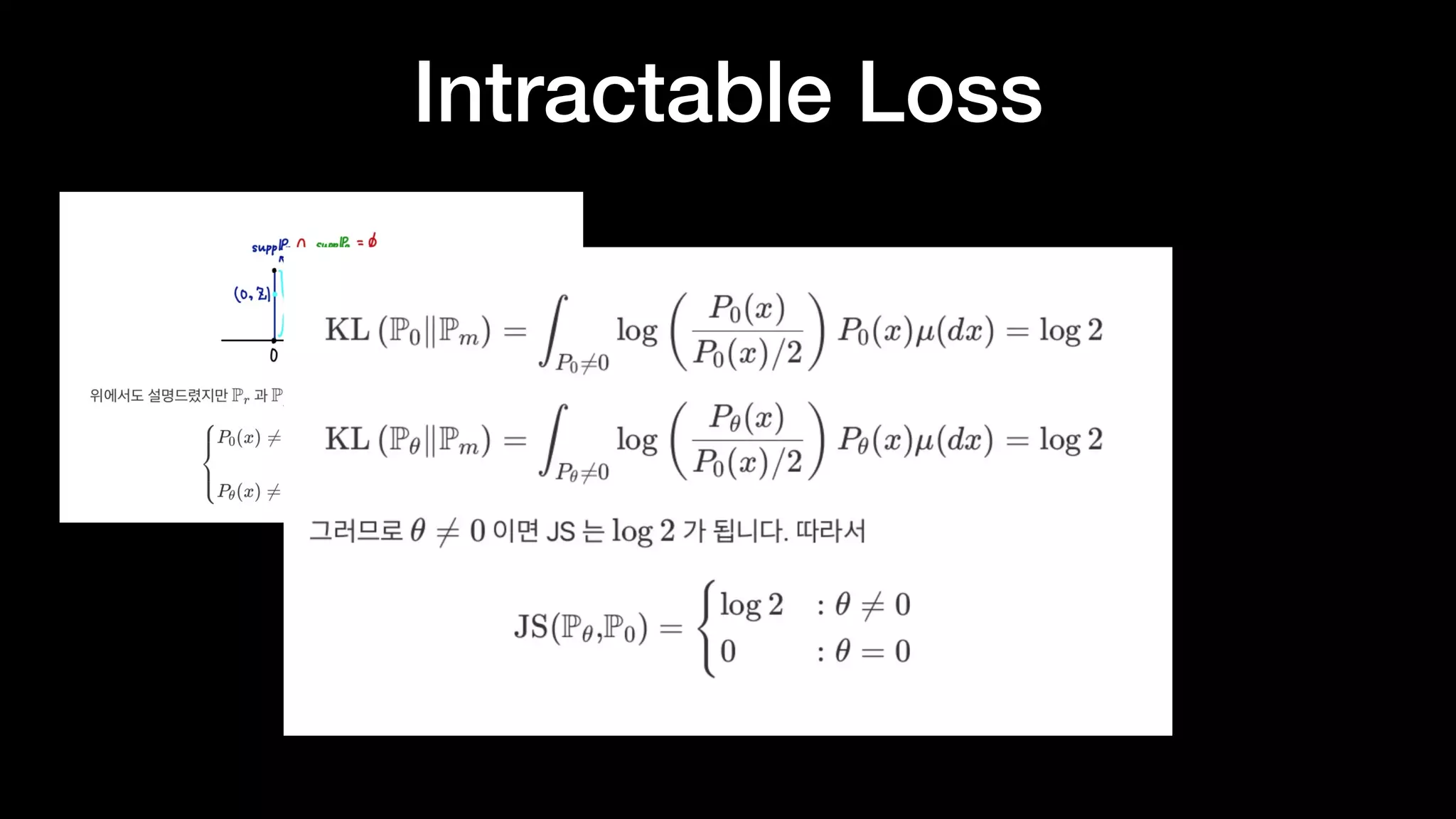
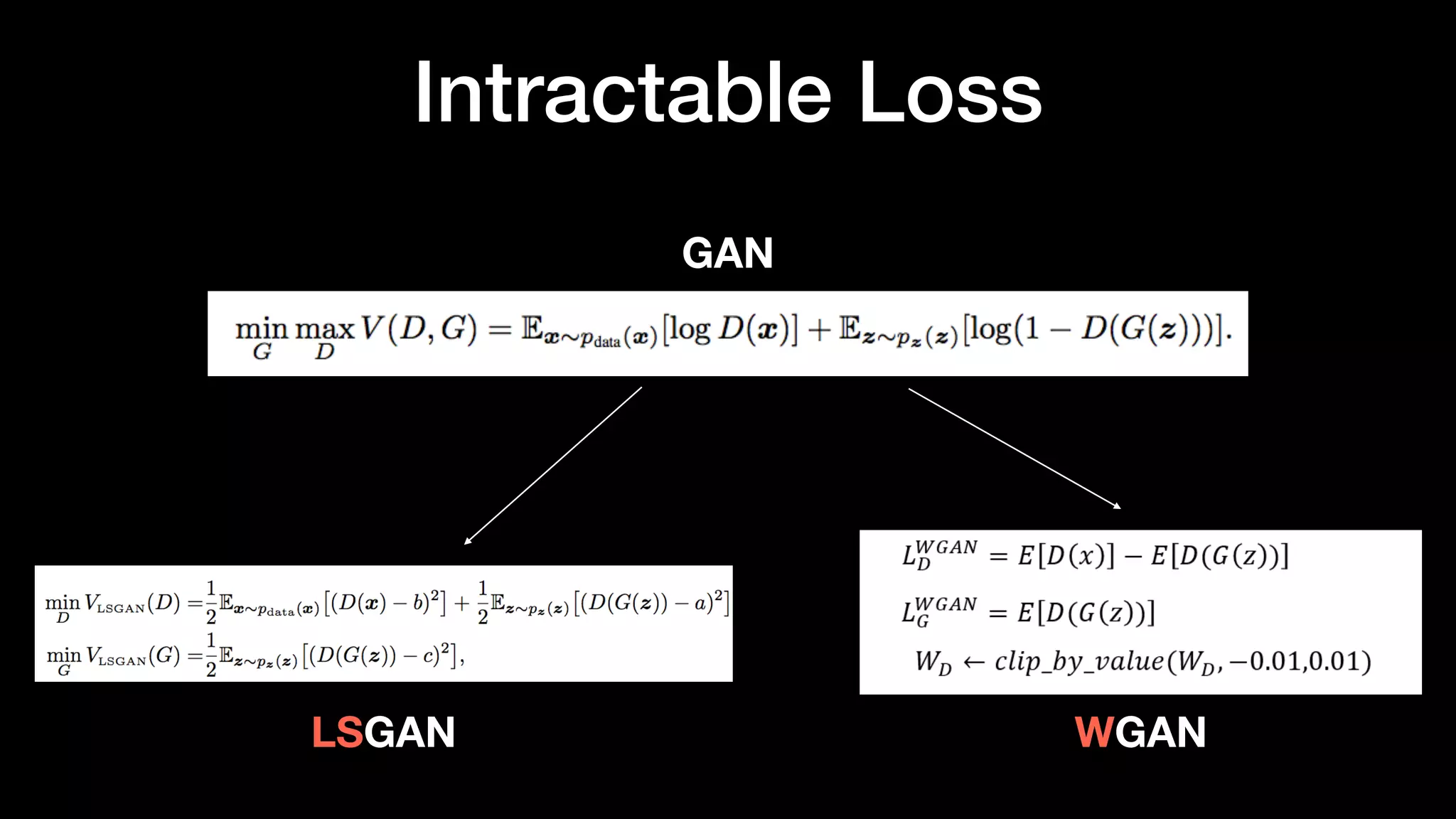
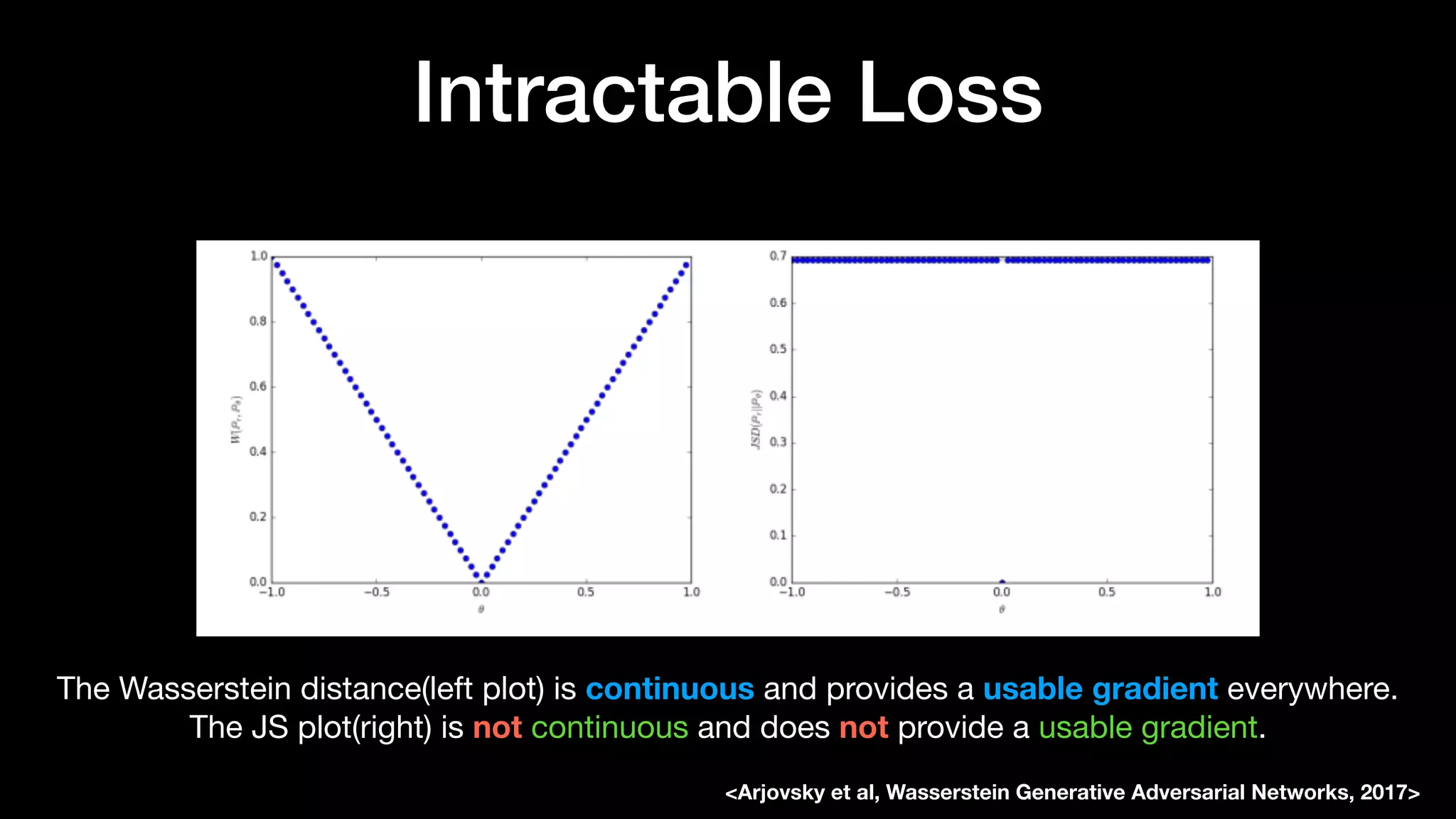
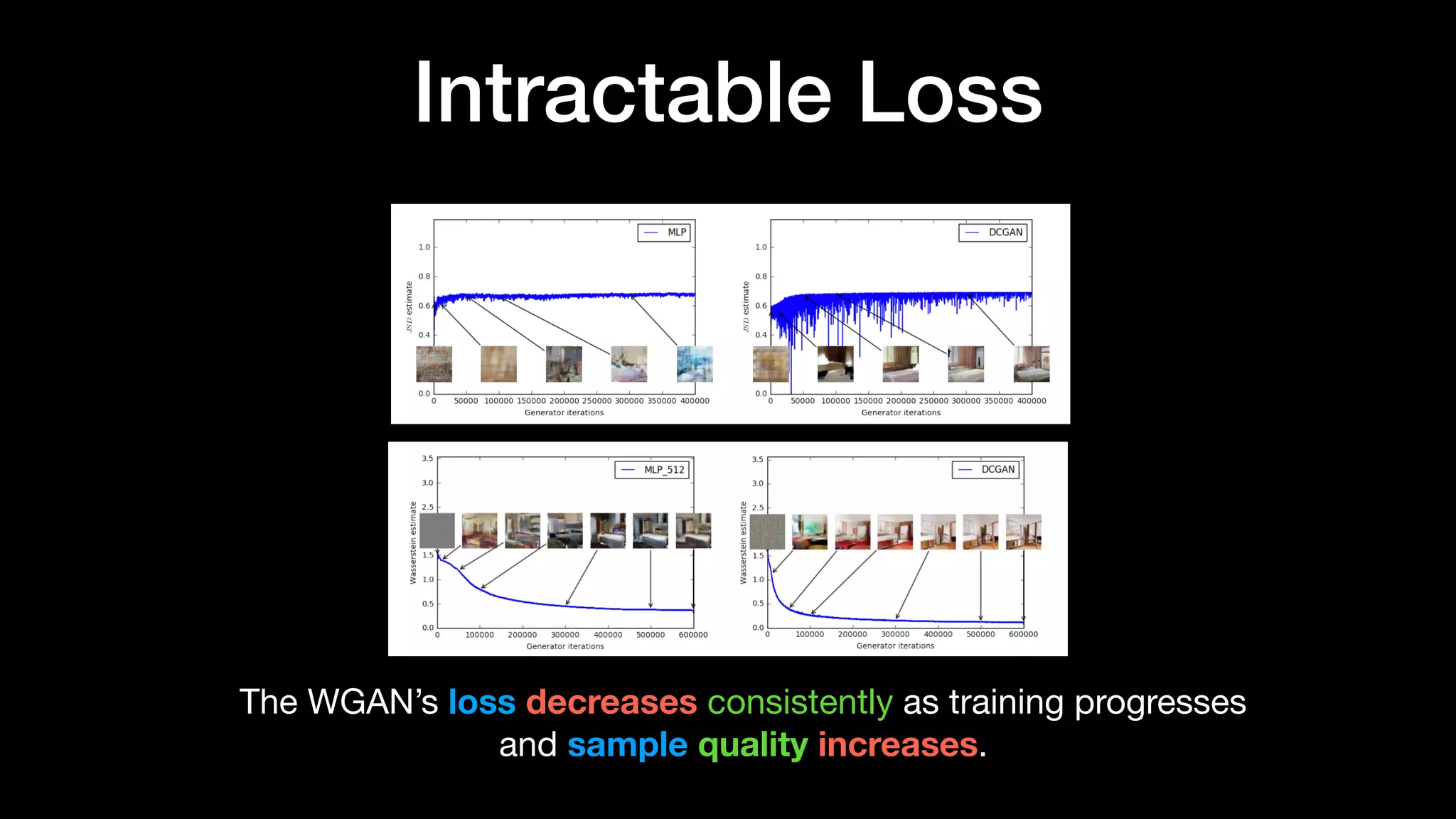
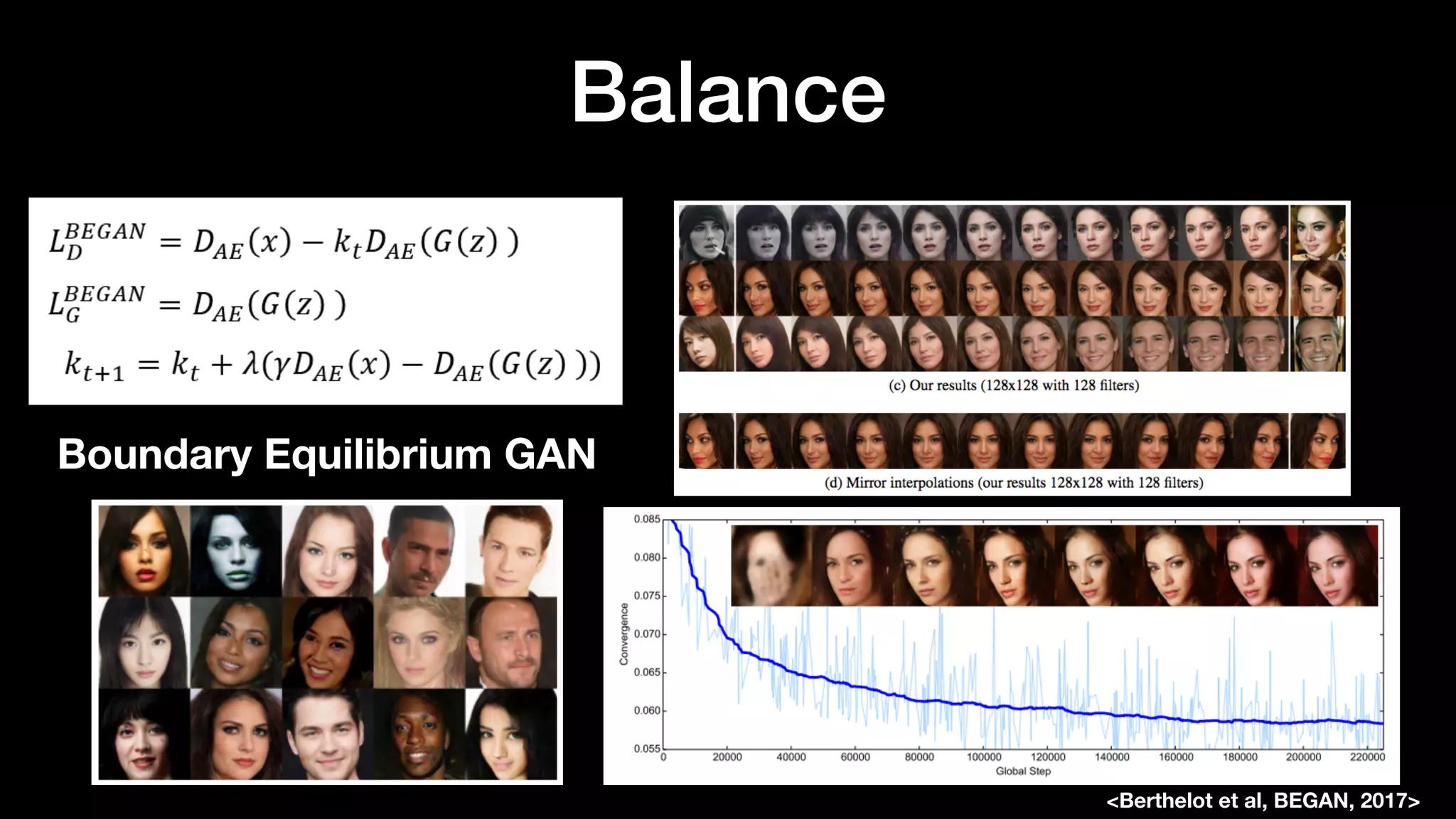
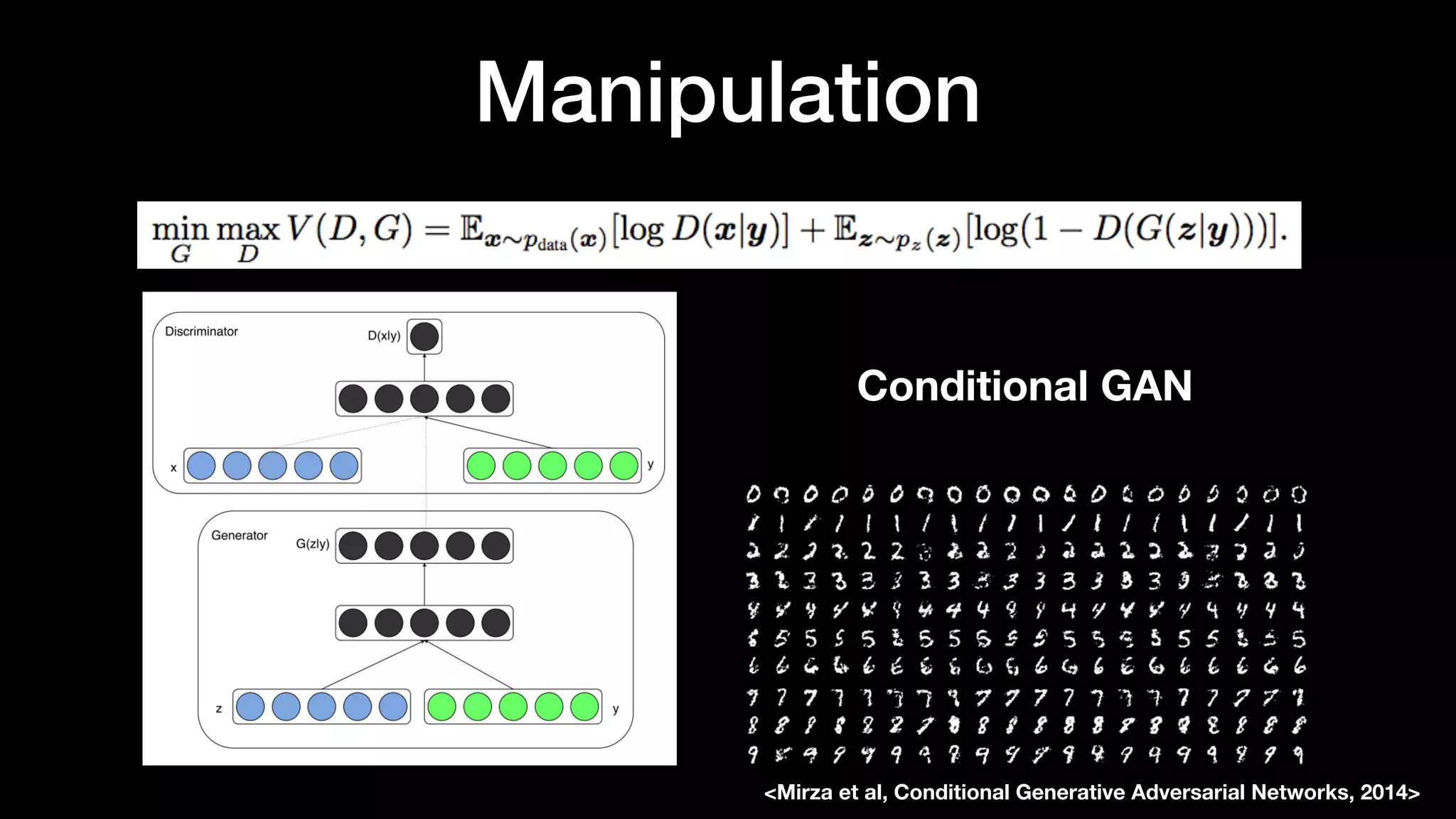
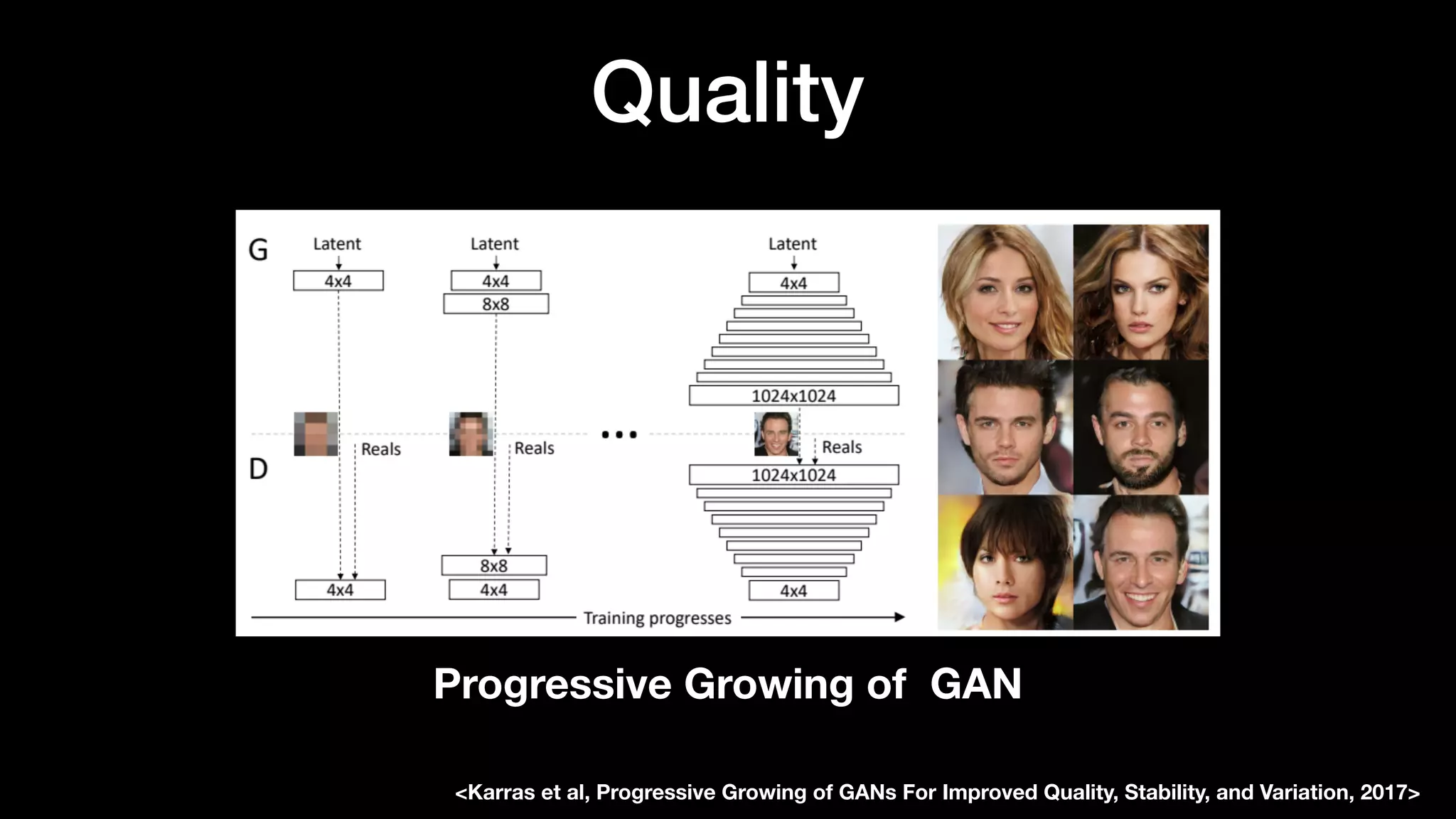
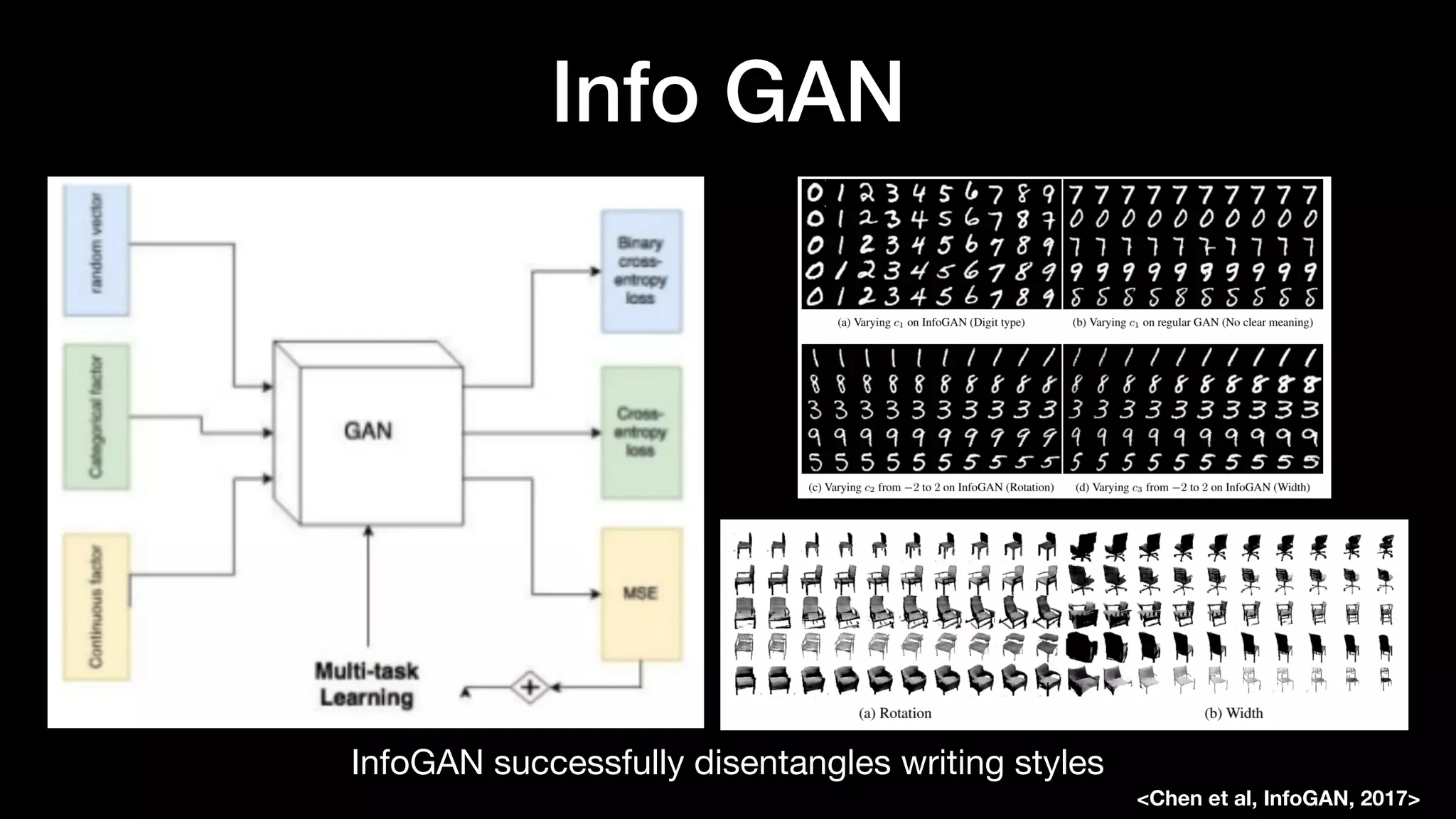
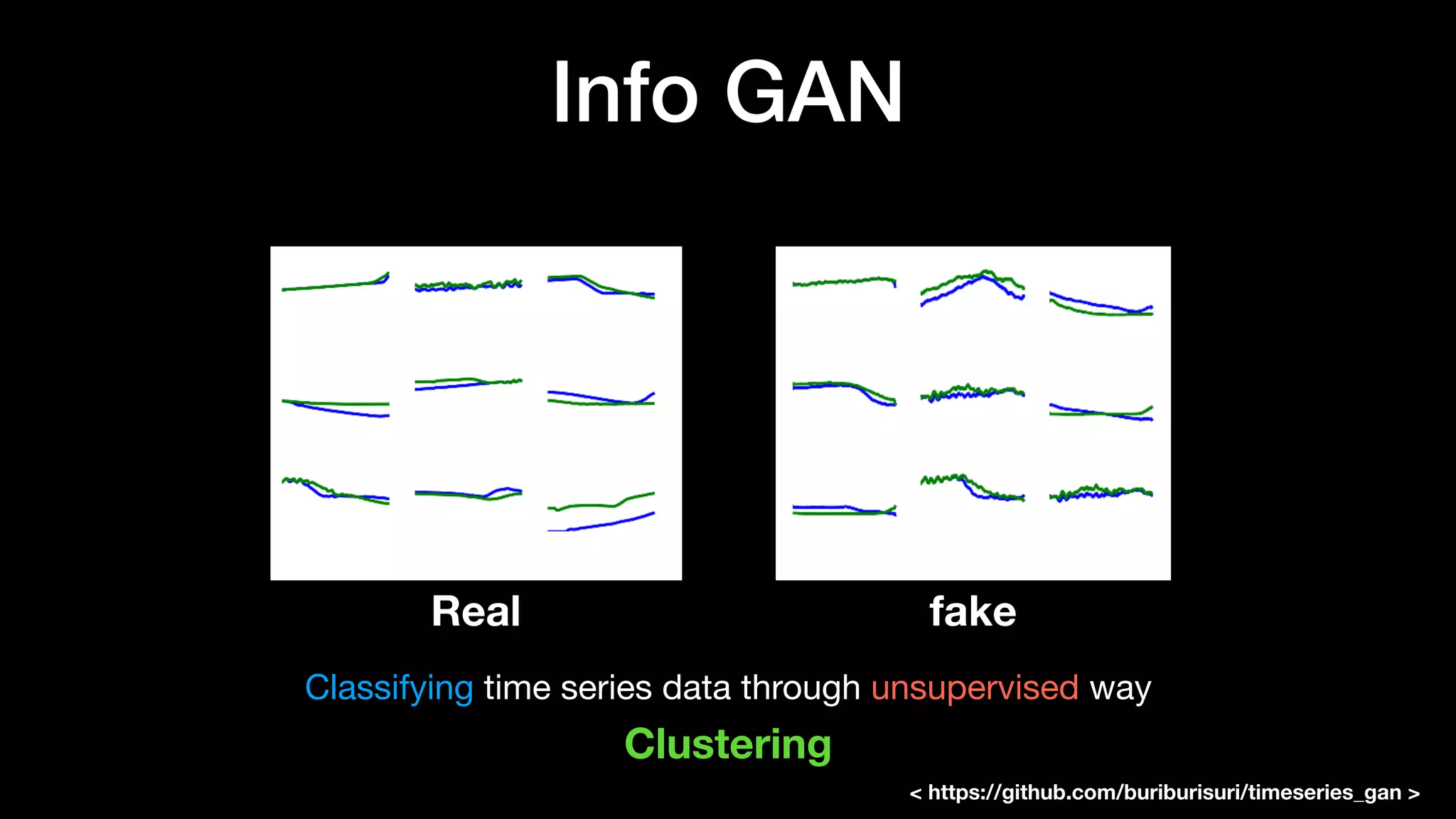
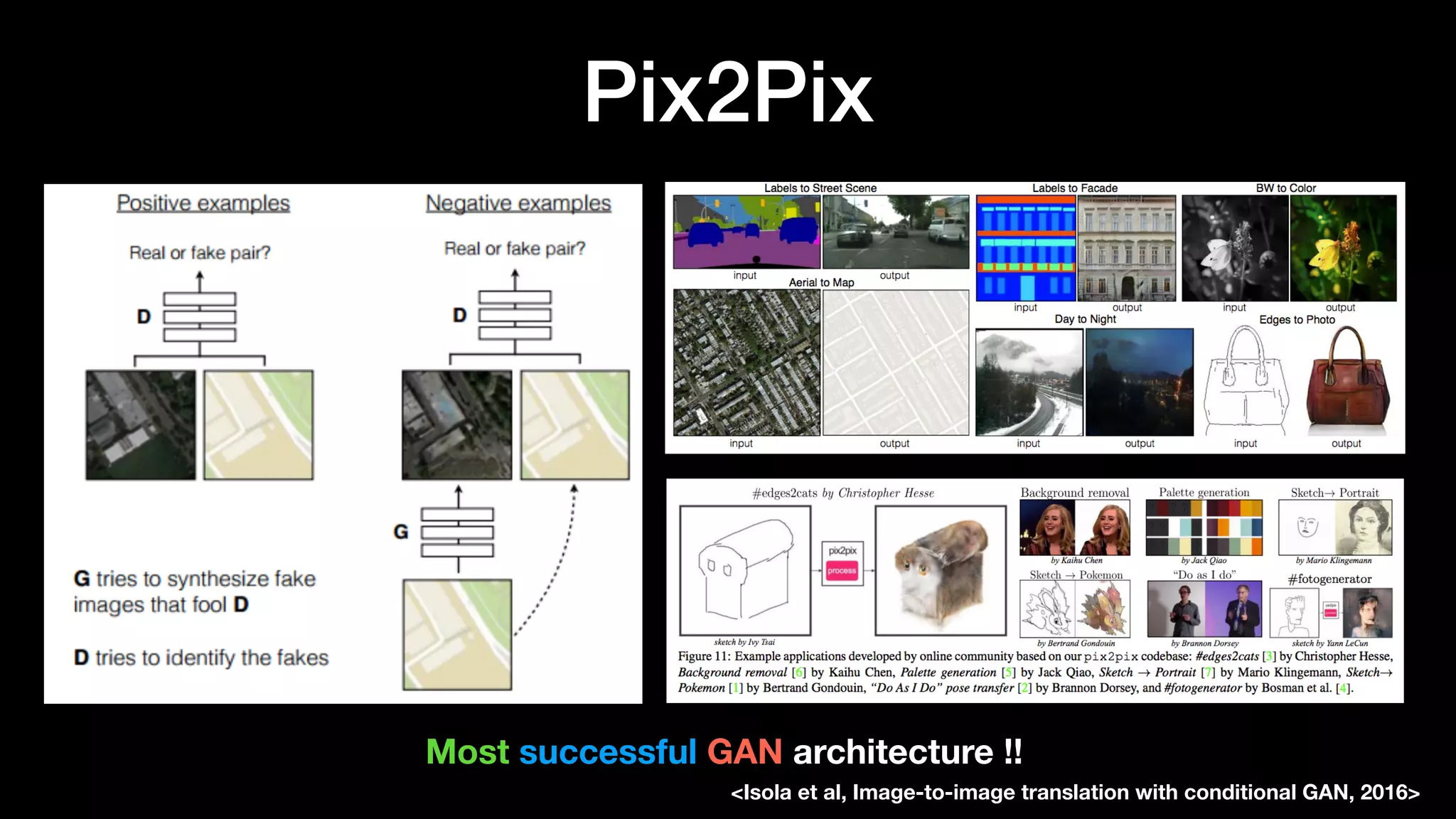
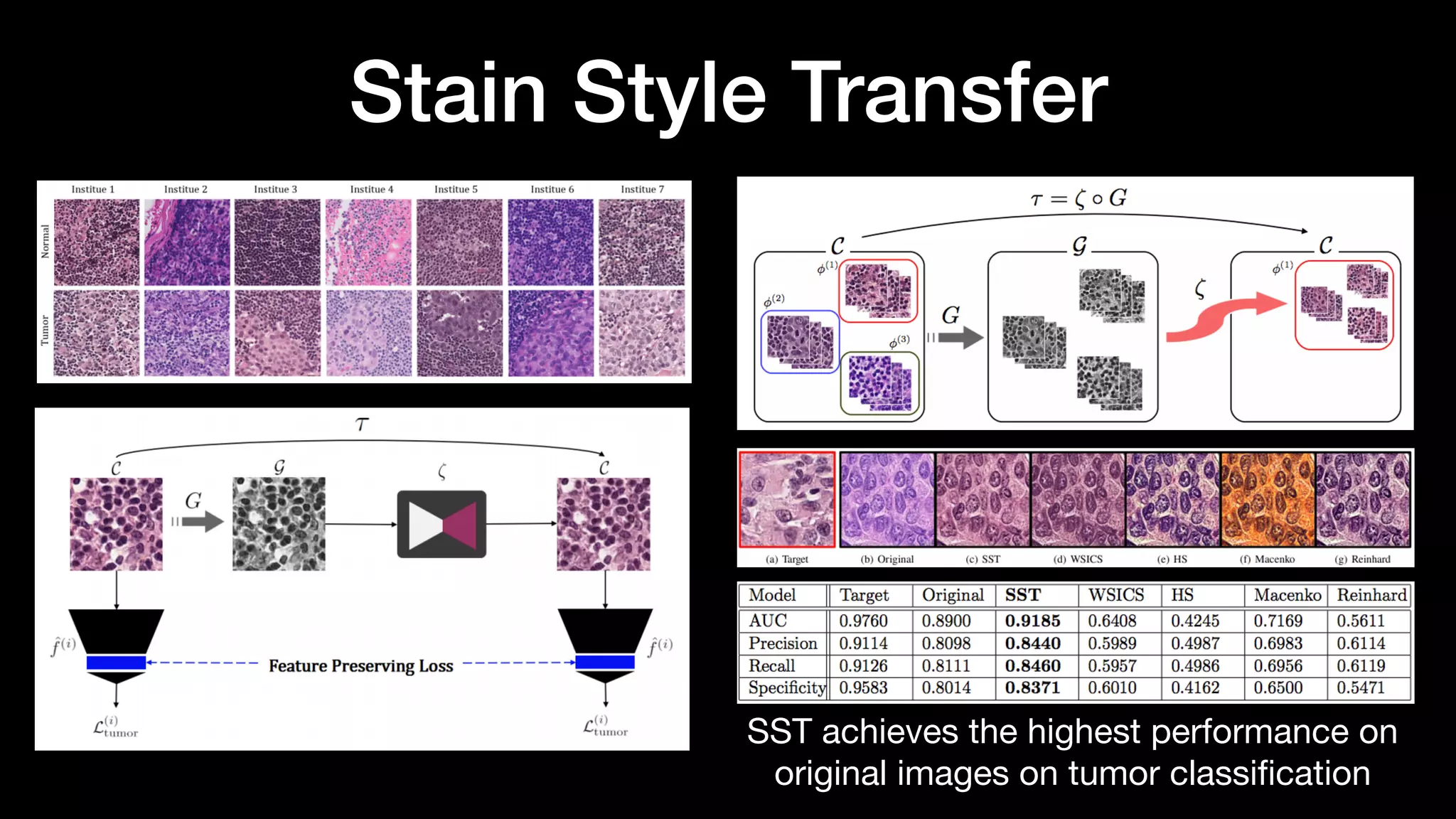
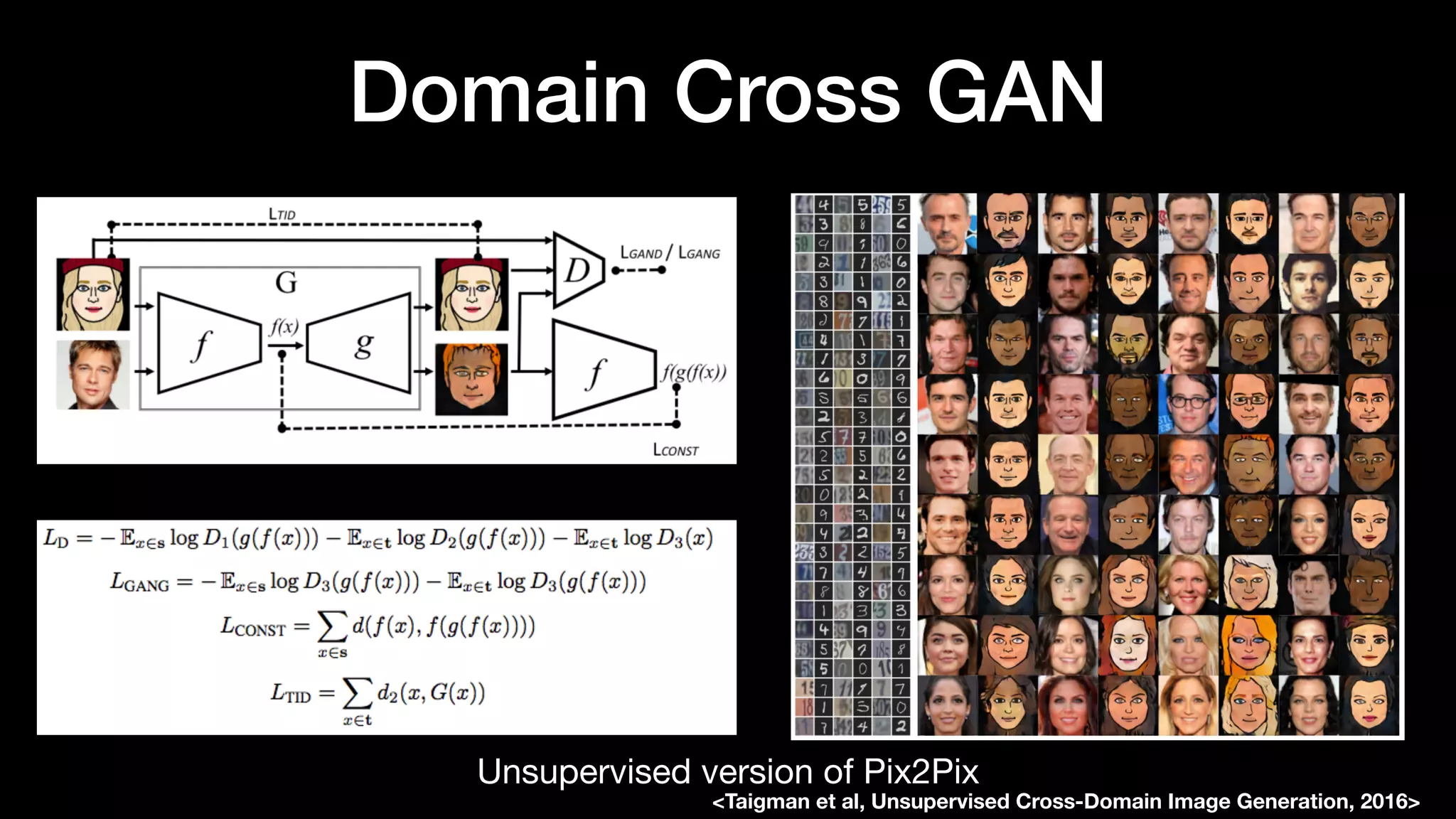
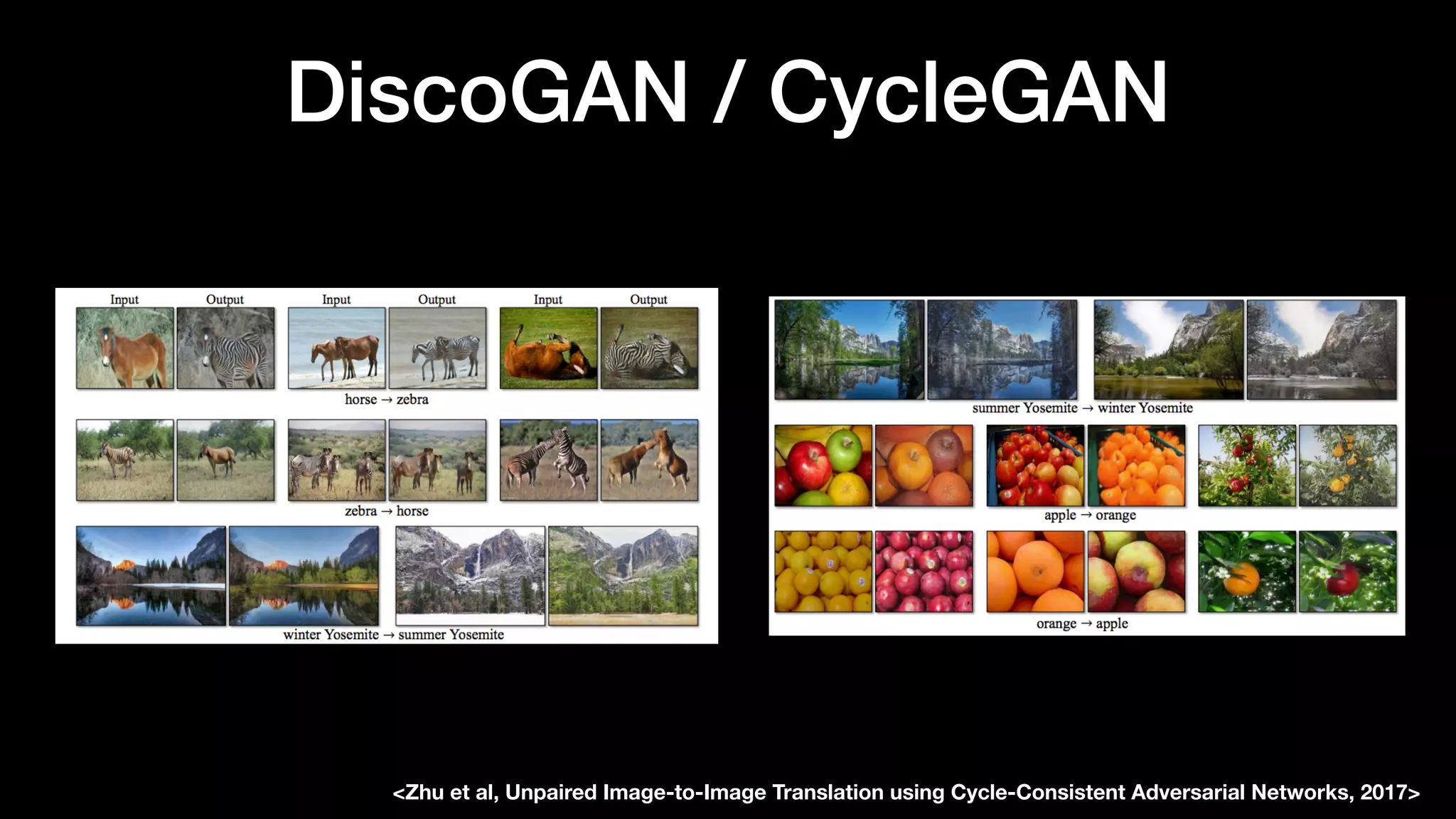
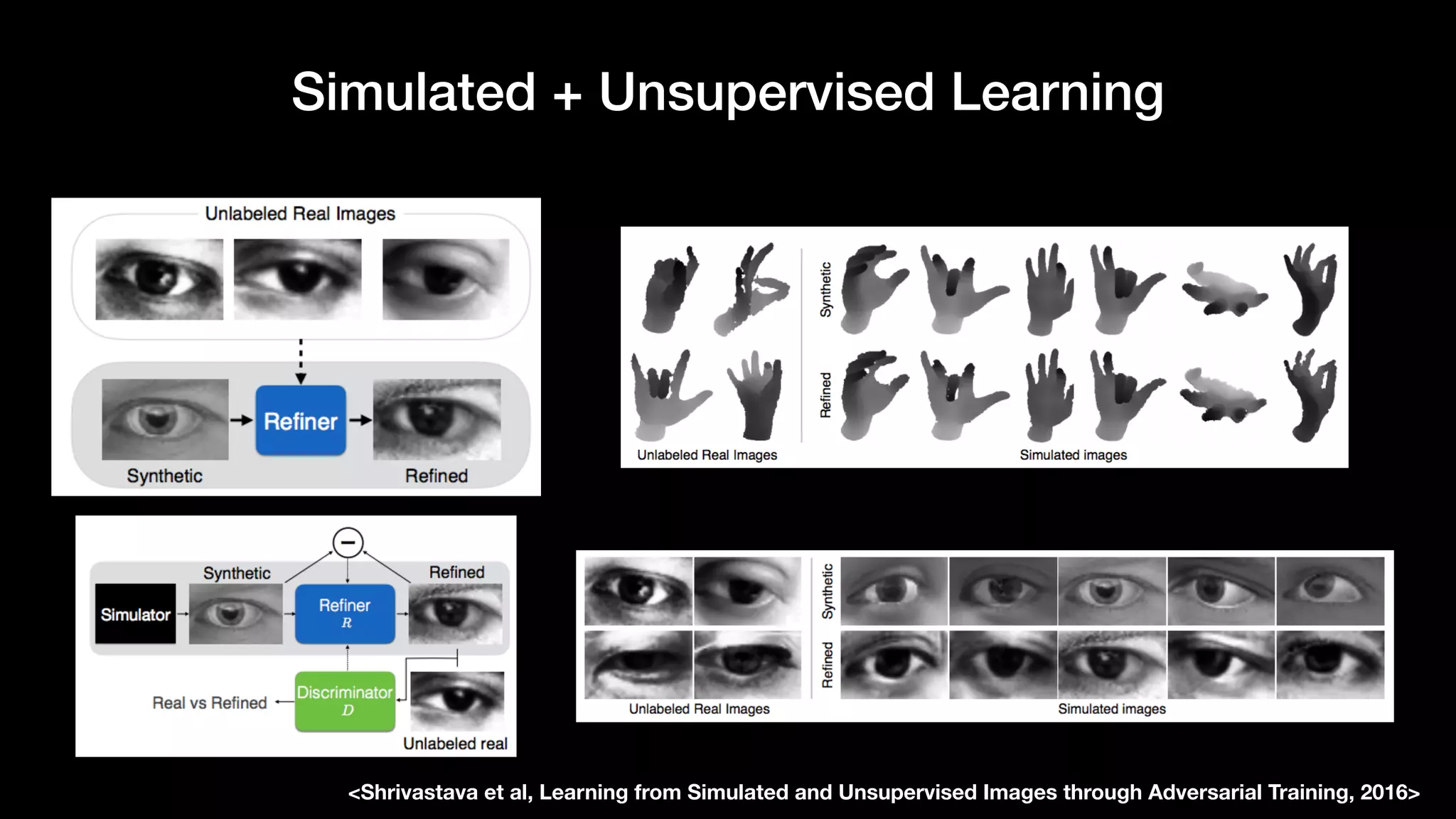
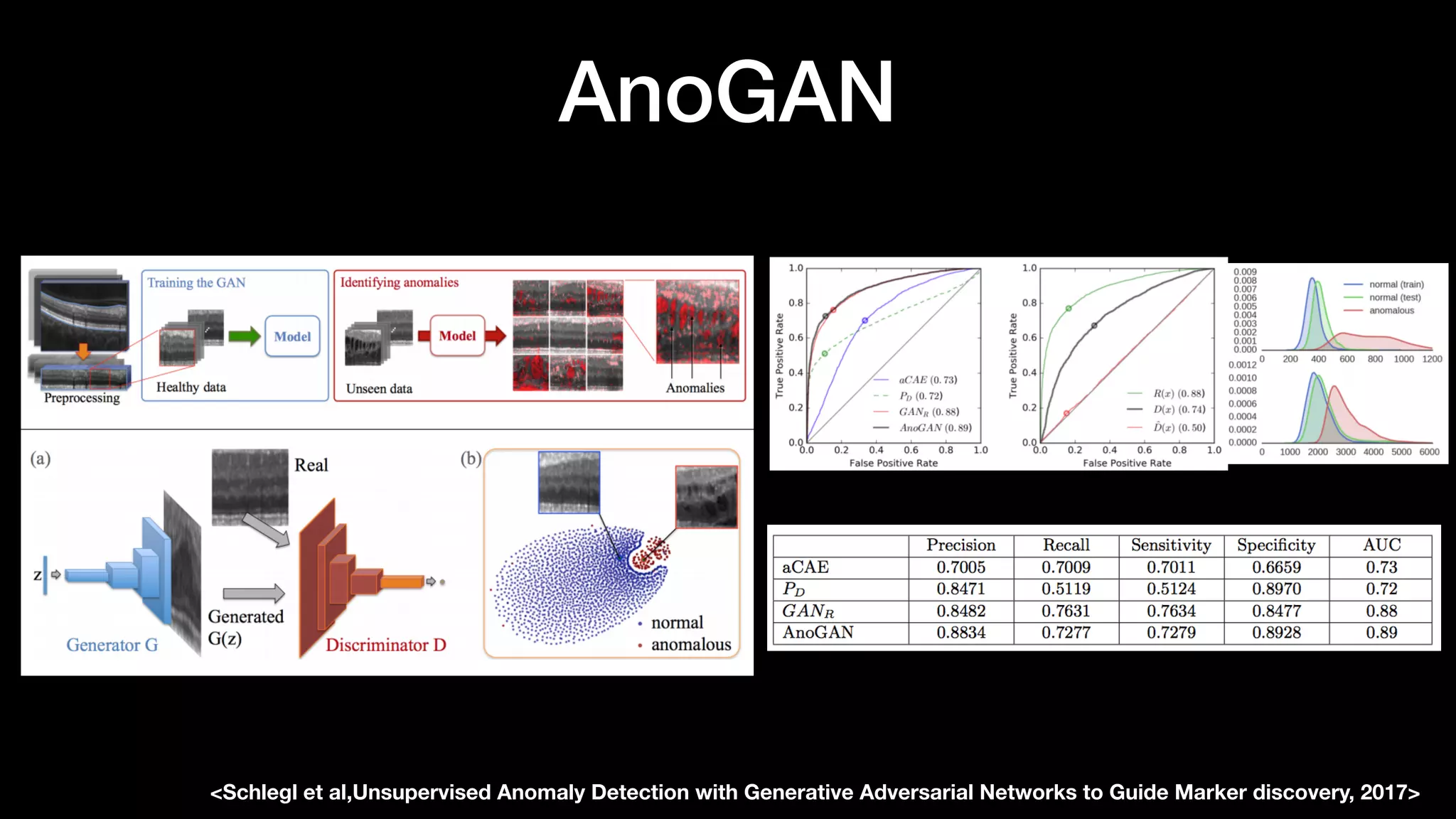
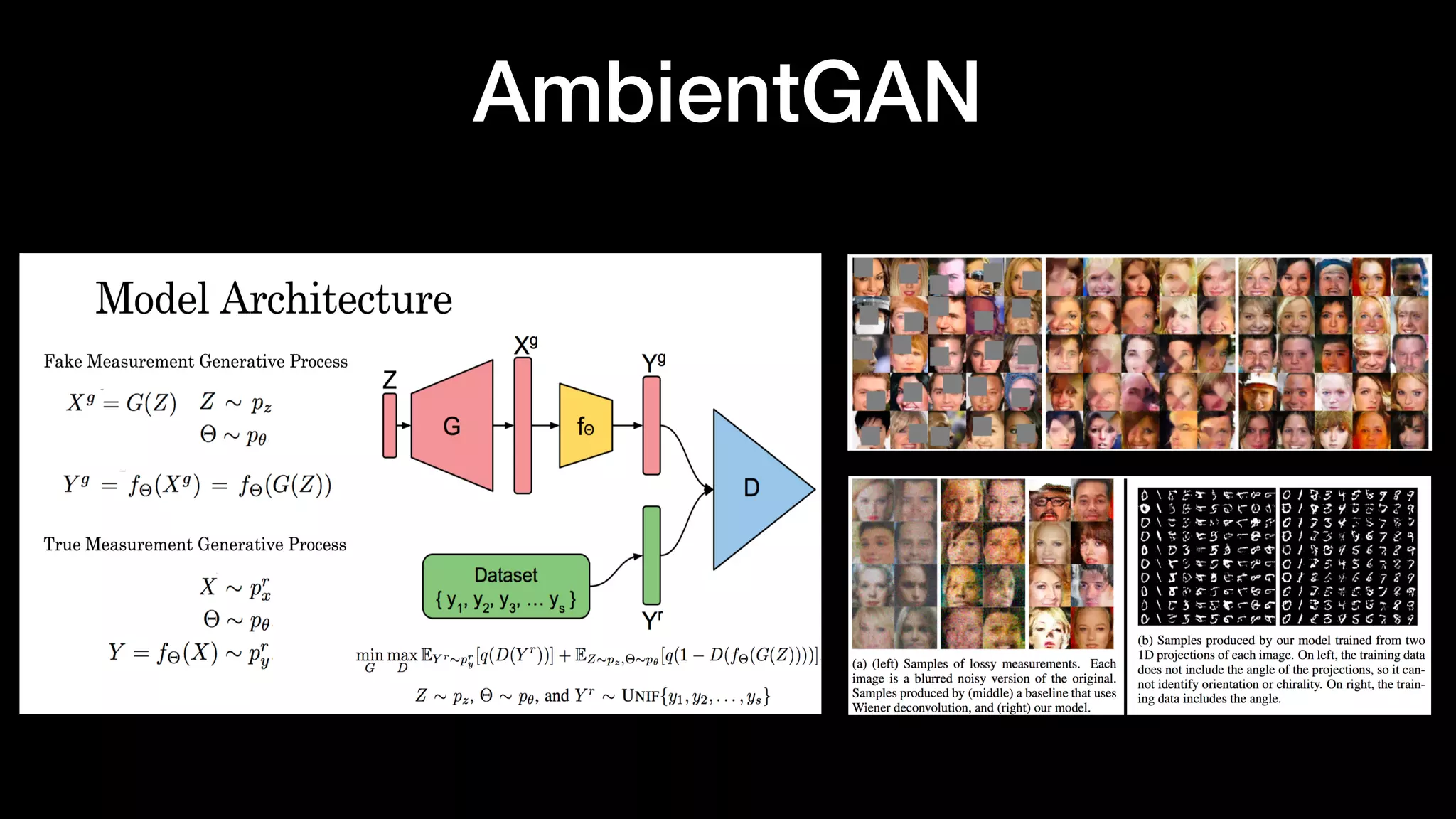
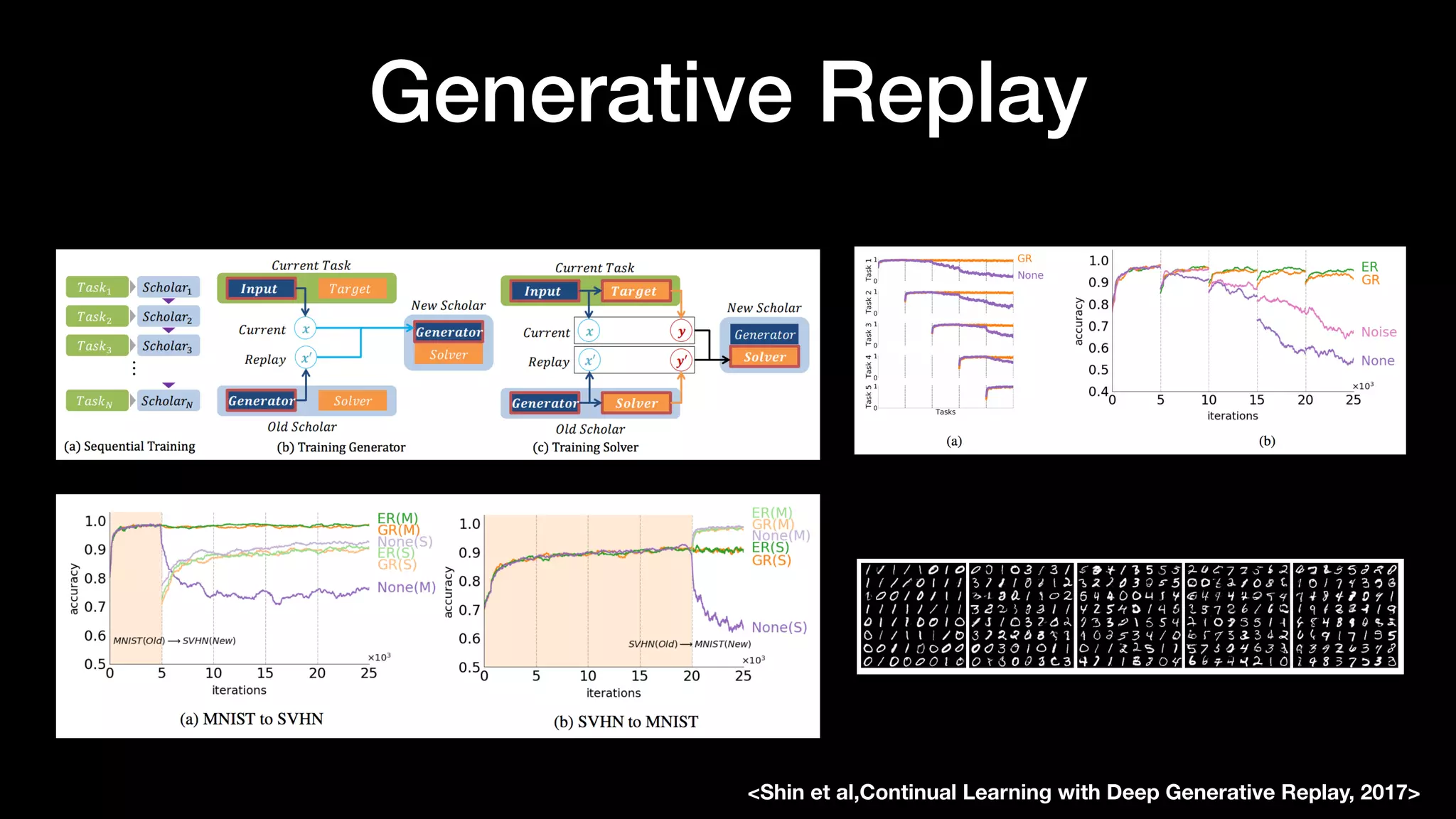
The document discusses different types of generative models including auto-regressive models, variational auto-encoders, and generative adversarial networks. It provides examples of each type of model and highlights some of their features and issues during training. Specific models discussed in more detail include PixelRNNs, DCGANs, WGANs, BEGANs, Pix2Pix, and CycleGANs. The document aims to introduce deep generative models and their applications.