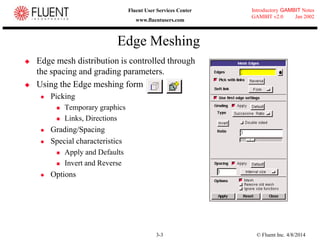
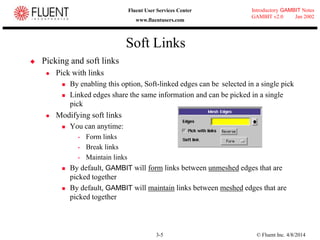
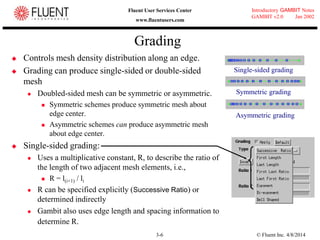
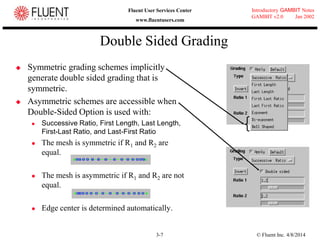
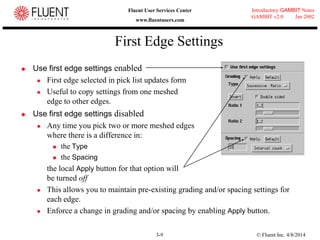
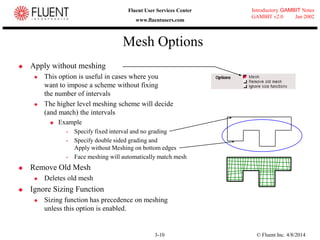
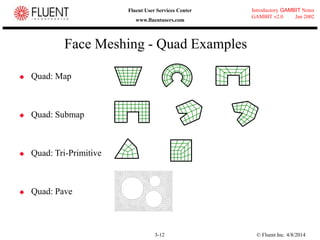
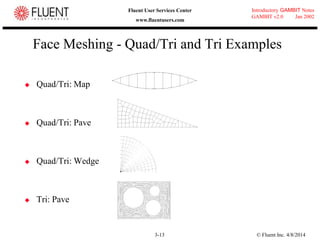
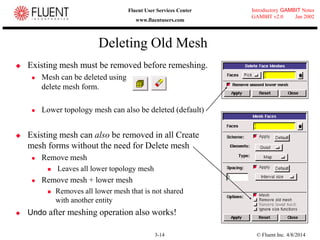
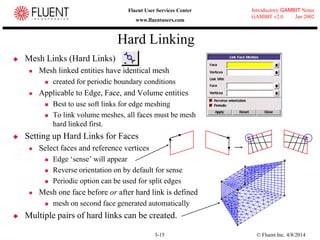
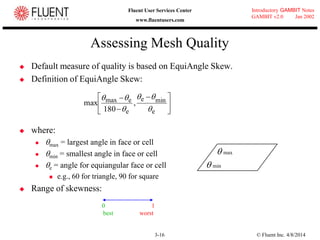
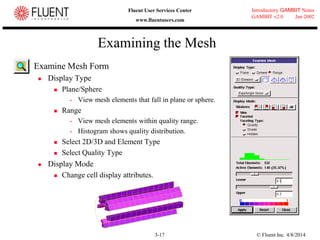
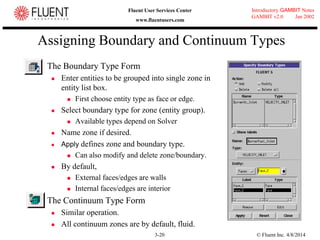
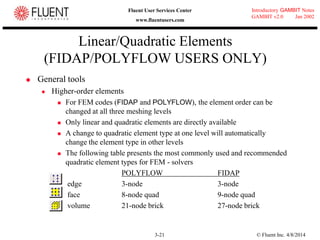
This document provides an overview of meshing tools in GAMBIT including edge meshing, face meshing, examining mesh quality, assigning boundary conditions, and using linear and quadratic elements. Key topics covered include controlling mesh density through grading and spacing, various face meshing schemes for quads and tris, assessing mesh quality using equiangle skew, and assigning boundary and material types.