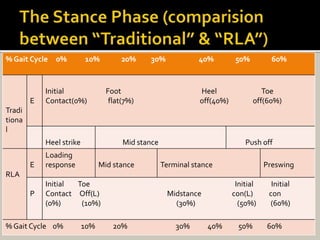
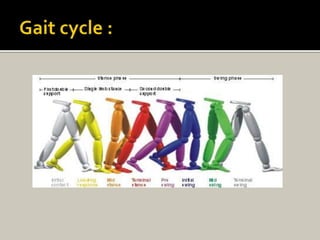
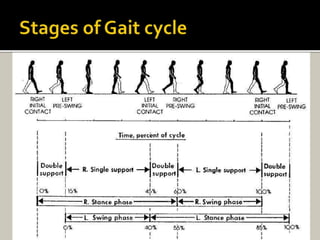
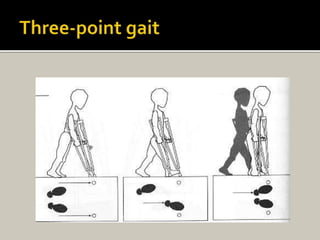
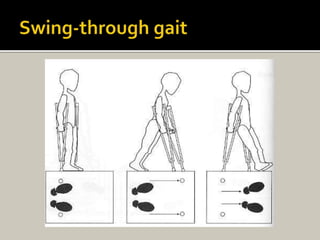
Human locomotion, also known as gait, involves coordinated rotary movements of the body produced by alternating movements of the lower extremities. This carries the head, arms, and trunk (HAT), which makes up 75% of total body weight. There are two phases in one gait cycle for each extremity - the stance phase when the foot is in contact with the ground (60% of cycle) and swing phase when it is not (40% of cycle). Gait can be described using temporal variables like stance time and spatial variables like stride length.