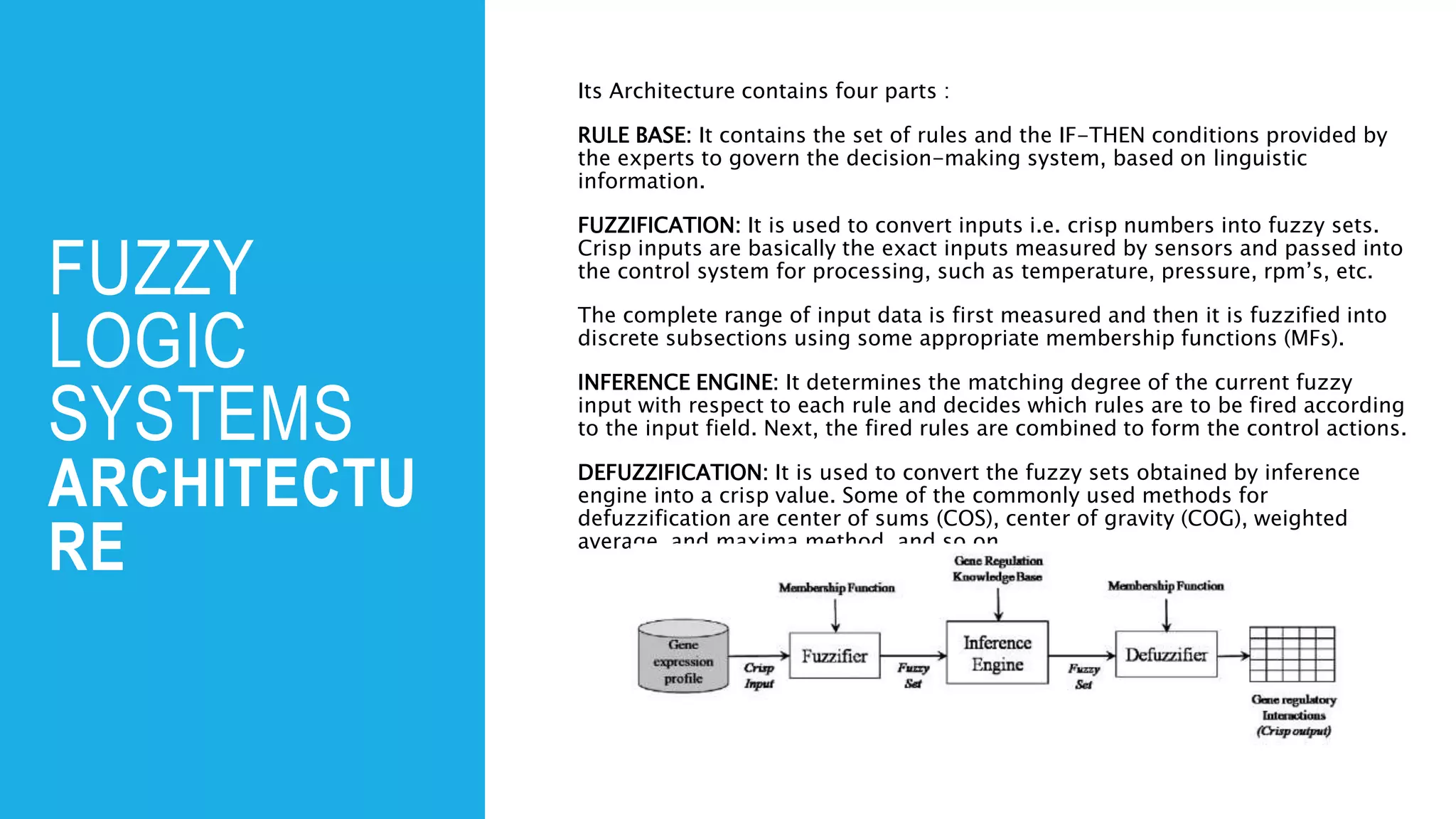
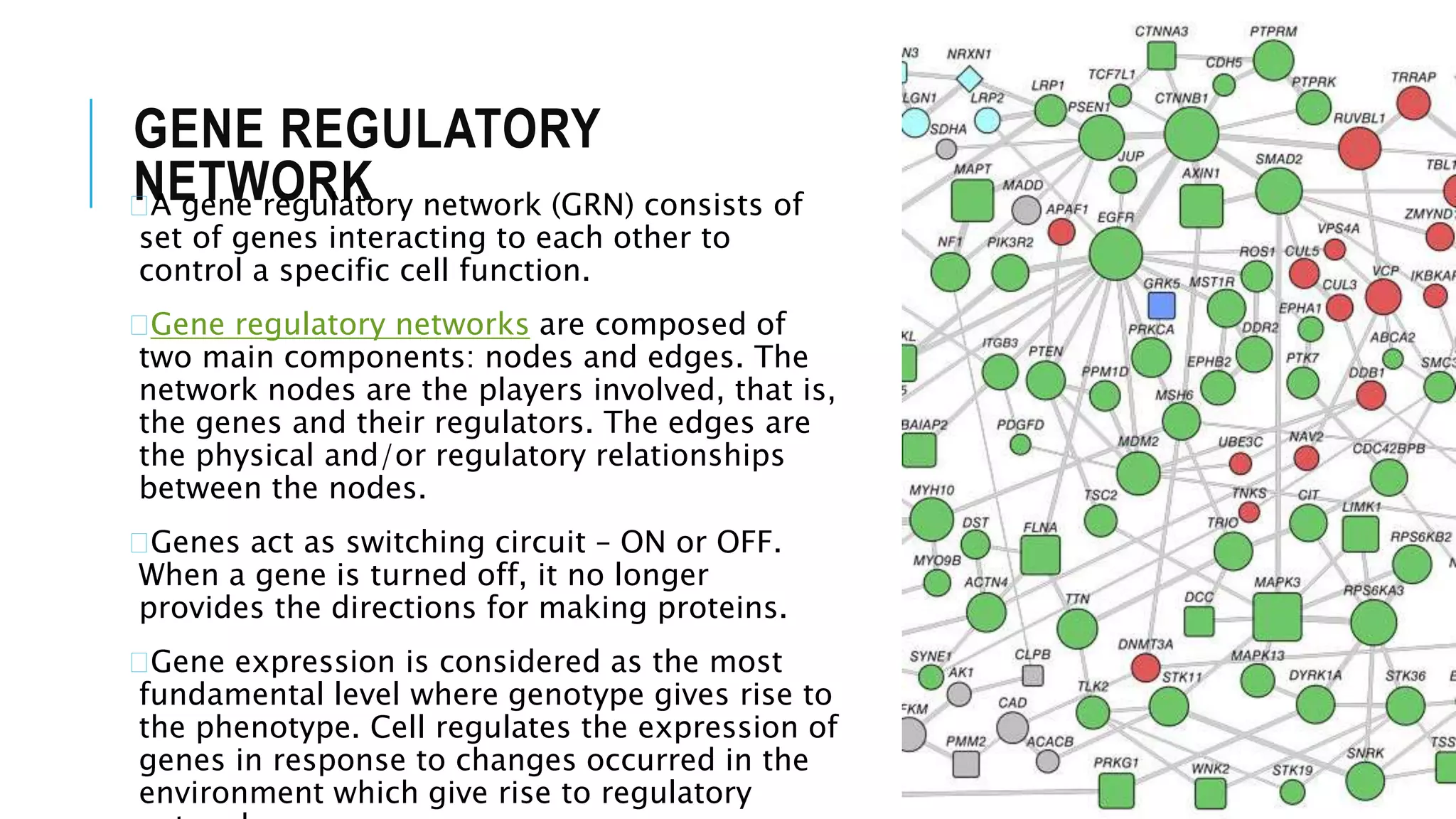
The document discusses the application of fuzzy logic in gene regulatory network (GRN) inference, describing fuzzy logic as a system that handles reasoning with degrees of truth rather than binary values. It outlines the architecture of fuzzy logic systems, including components such as rule base, fuzzification, inference engine, and defuzzification, and explains how these processes are used to model complex biological systems. Additionally, it introduces various algorithms and hybrid approaches developed to enhance GRN inference by utilizing fuzzy logic.