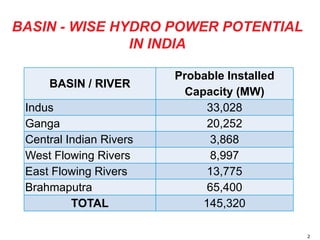
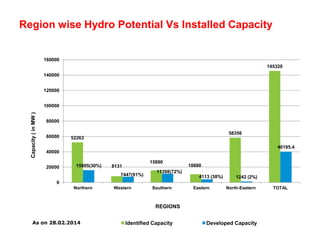
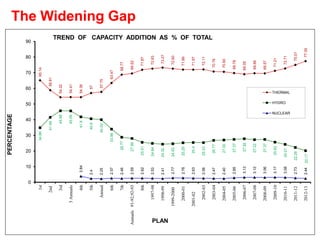
The document discusses the future of hydro power development in India. It notes that India has an identified hydro power potential of 145,320 MW but has only developed 40,195 MW so far, representing around 27.6% of its potential. Several challenges are hindering further development, including lengthy forest clearance processes, uncertainty around project approvals, issues evacuating power from remote areas, and high costs of land acquisition. The document calls for reforms like upfront forest clearances, restarting stalled projects, subsidies for infrastructure development, and clarifying policies around forest payments and land costs to boost hydro power development and meet India's energy needs.