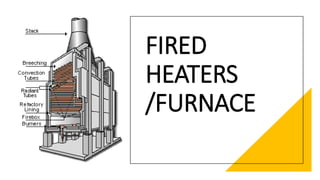
Furnaces are key equipment in petroleum processing that provide heat through burning fuel. They have radiant and convection sections. The radiant section contains radiant tubes that receive direct heat from burners and transfer 85% of the heat. The convection section preheats feed before it enters the radiant tubes. Regular inspections check furnace components like tubes, refractory lining, and anchors for deformation, cracking, or deterioration. Different metallurgies are used depending on the processing application and conditions.