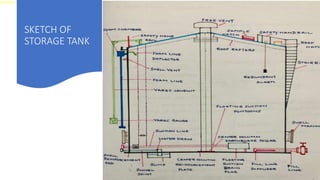
The document discusses storage tank inspections and provides details on:
- Inspection techniques used to evaluate tank floors, shells, roofs, and structures. Inspections include engineering calculations per industry standards.
- Common materials used in tank construction like carbon steel, low-chrome alloys, and stainless steel. Corrosion allowances are also discussed.
- Types of inspections like routine in-service, external, and internal inspections. Factors that determine inspection intervals are outlined.