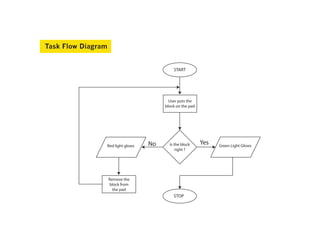
This document describes Fun-In-Flow, an educational tool to teach flowcharts to 12-14 year olds. It uses interactive blocks representing flowchart symbols that students manipulate to solve problems. The tool focuses on making learning fun through tangible interaction with the symbols. Previous research explored visual programming environments and flowchart editors, but Fun-In-Flow aims to impart education through edutainment and hands-on practice placing symbolic blocks. The document outlines the tool's content, design, prototyping, and usability testing procedures.