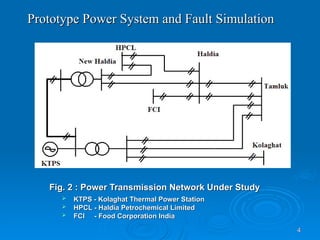
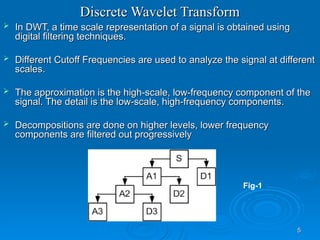
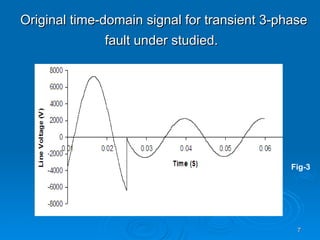
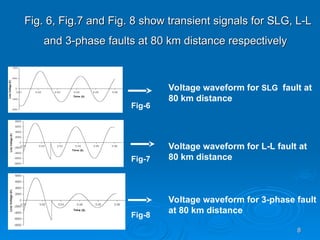
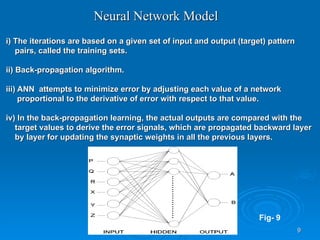
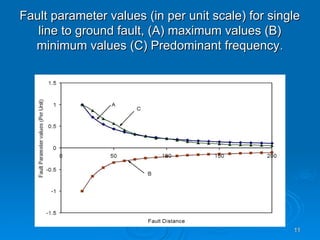
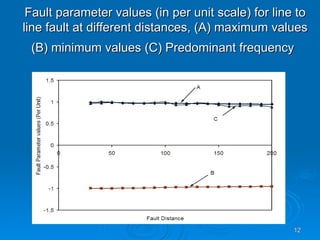
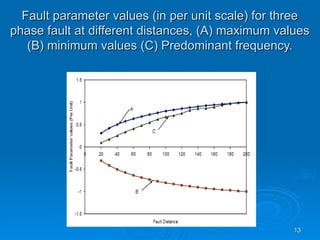
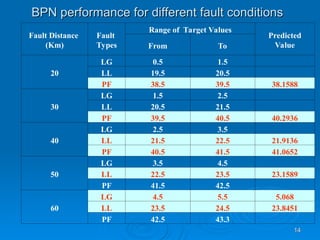
The document discusses utilizing a wavelet-assisted neural network for analyzing faults in transmission lines, focusing on abnormal voltage and current values to determine appropriate protective measures. It describes the use of discrete wavelet transform (DWT) for signal analysis and the implementation of a back-propagation neural network (BPN) for fault detection and prediction based on training patterns. The study highlights the performance of the neural network in identifying different fault conditions and provides various fault parameter values.