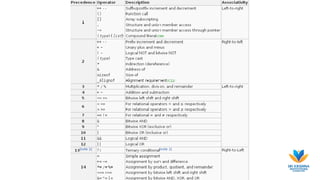
This document summarizes key concepts in C programming including formatted input, formatted output, expressions, and operator precedence. It explains that input and output must be formatted to specify where values are stored in memory. Expressions combine variables, operators, and constants, and are evaluated based on precedence rules. Parentheses, multiplication/division, and addition/subtraction have the highest to lowest precedence. Examples demonstrate how expressions are evaluated based on these rules.