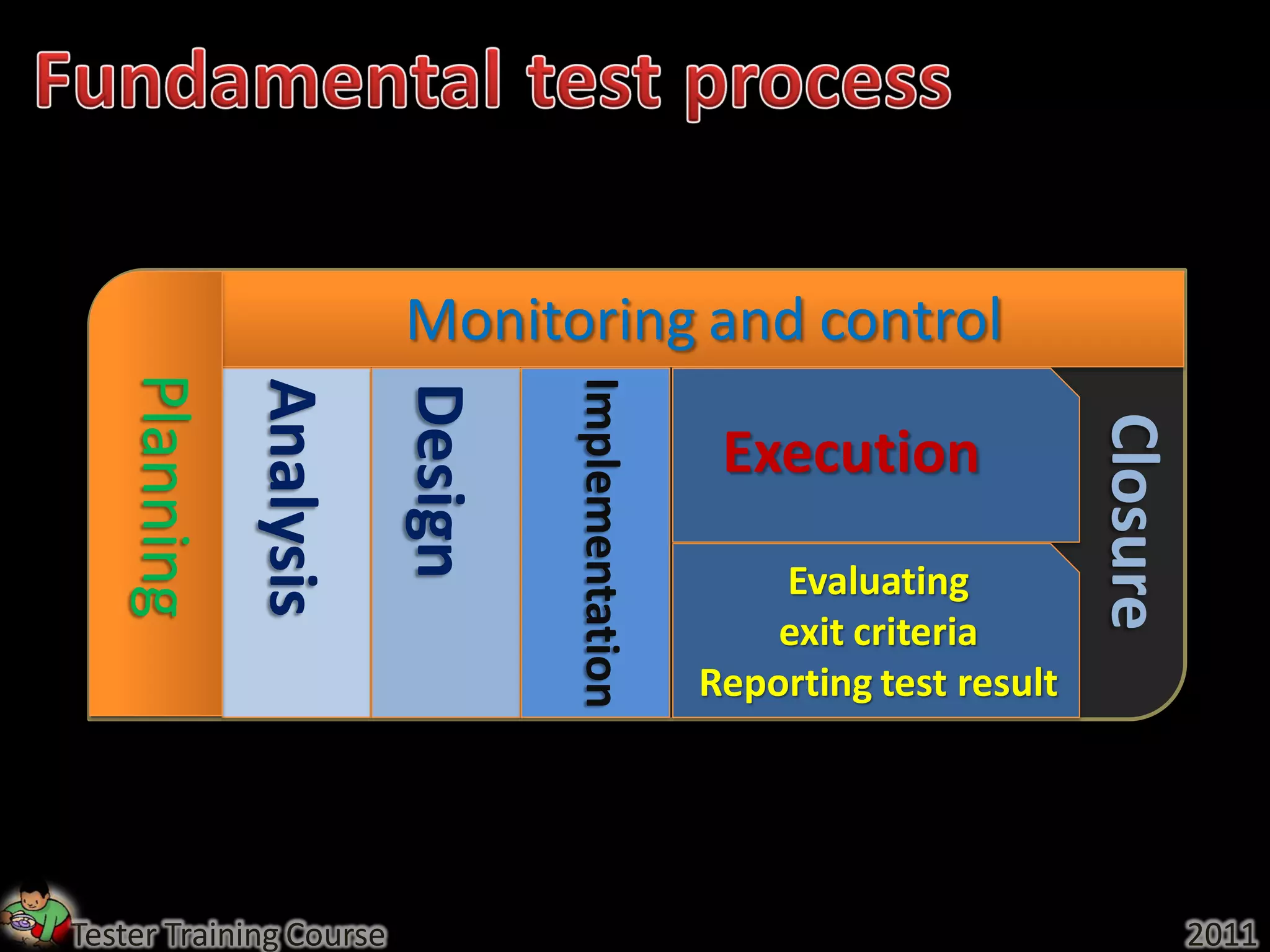
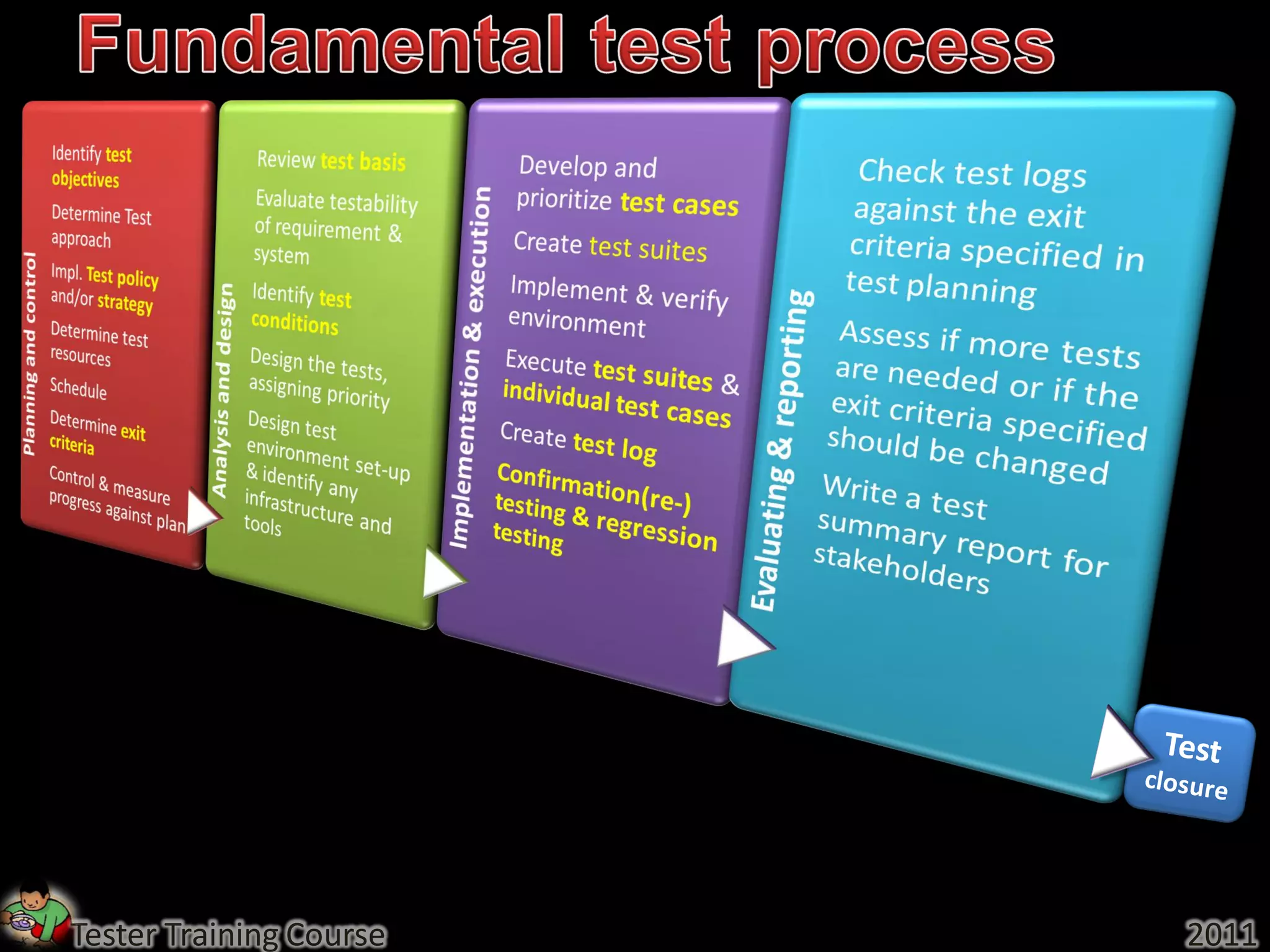
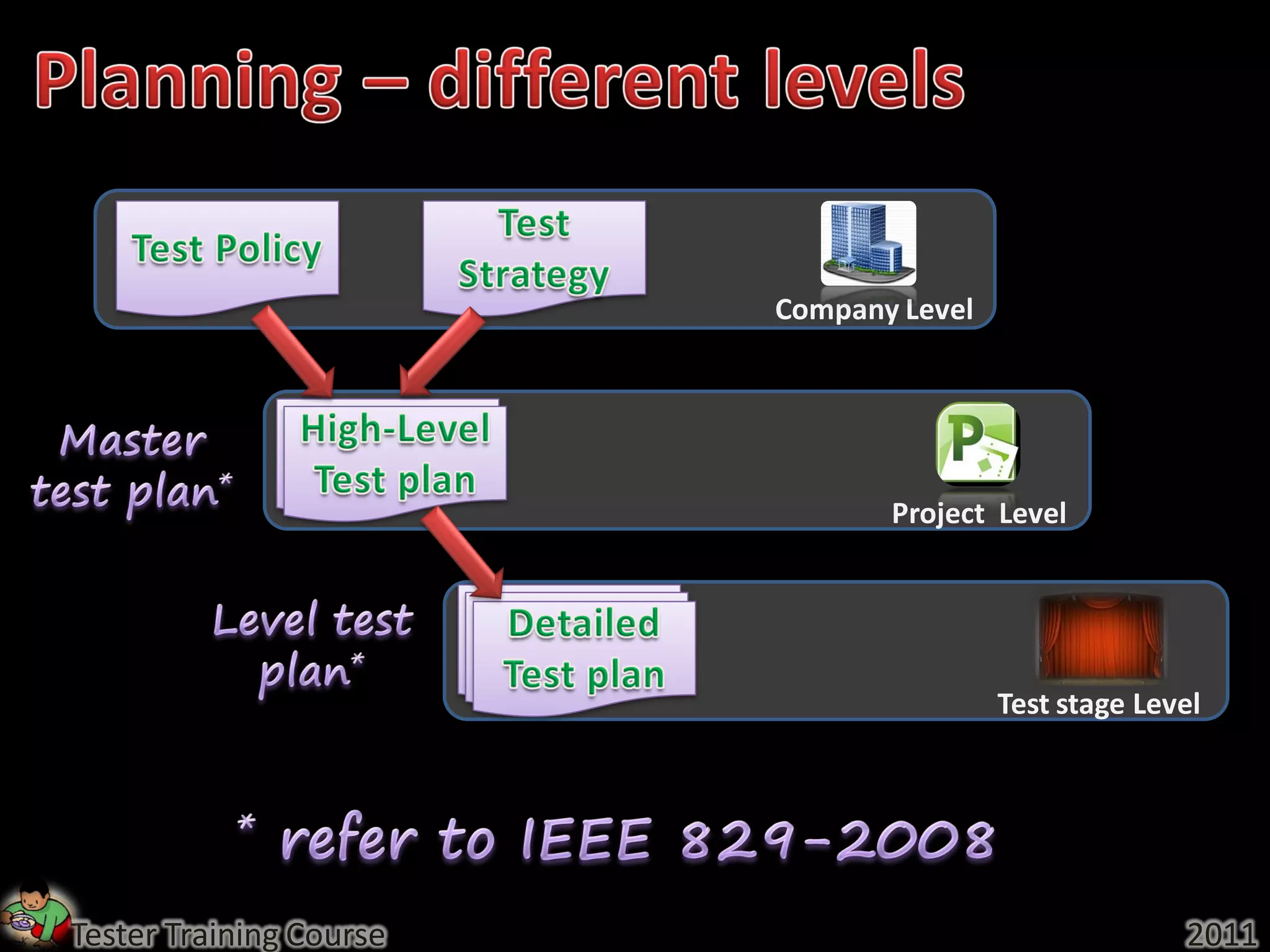
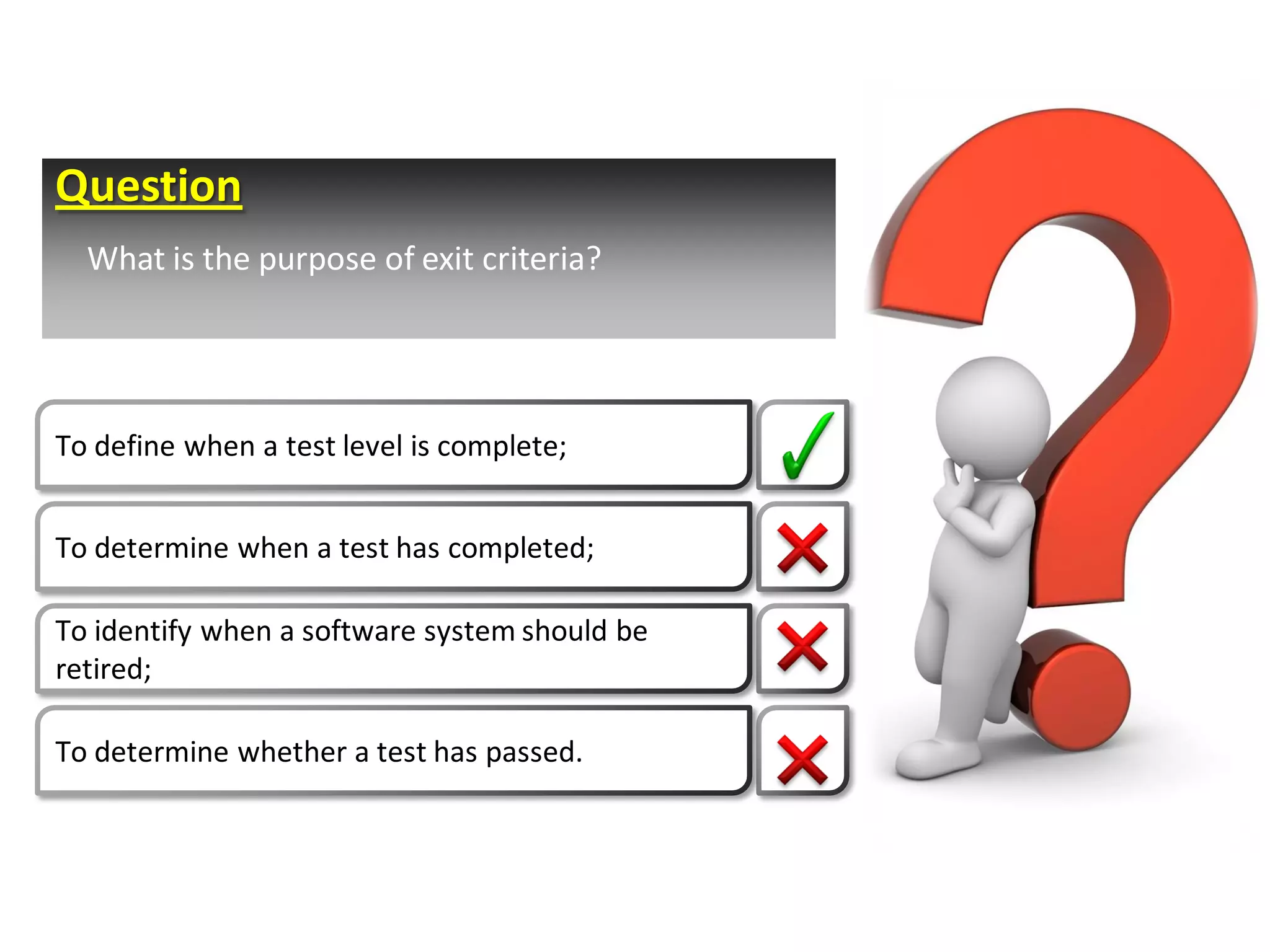
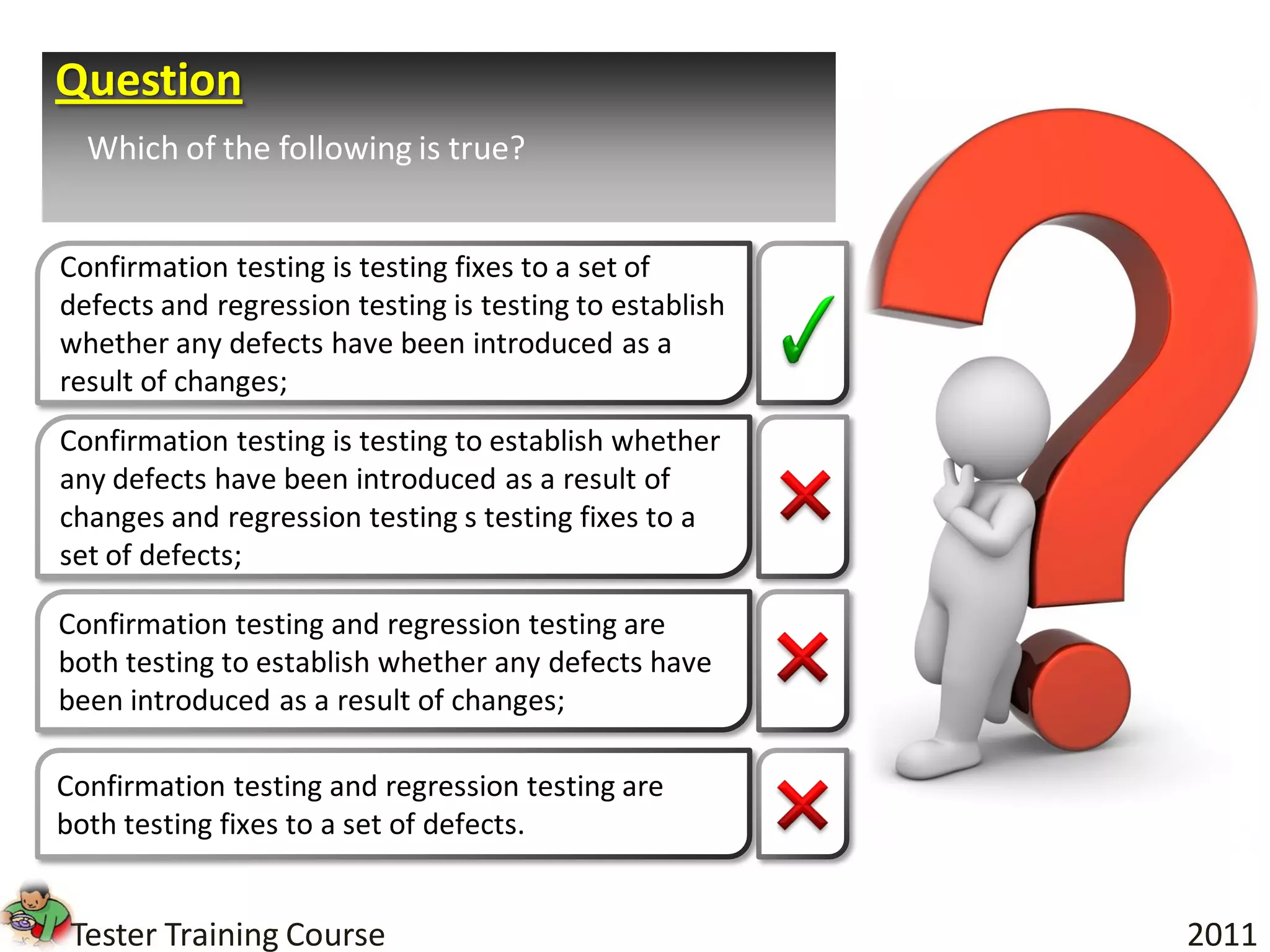
This document provides an overview of fundamentals of software testing. It discusses the five parts of the fundamental test process in broad chronological order: planning and control, analysis and design, implementation and execution, evaluating exit criteria and reporting, and test closure activities. It also covers topics like regression testing, confirmation testing, the differences between re-testing and regression testing, and the importance of independence in testing.