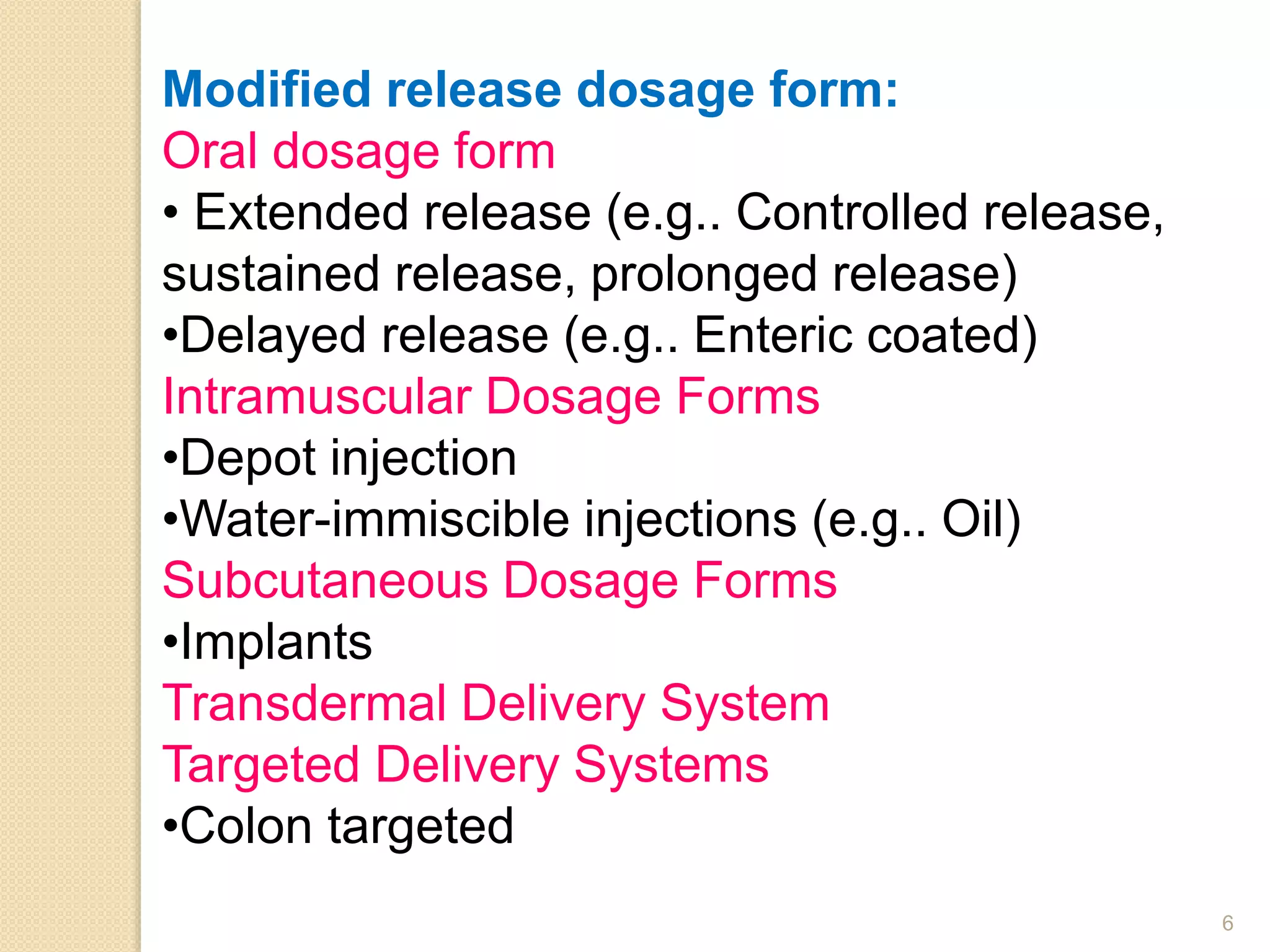
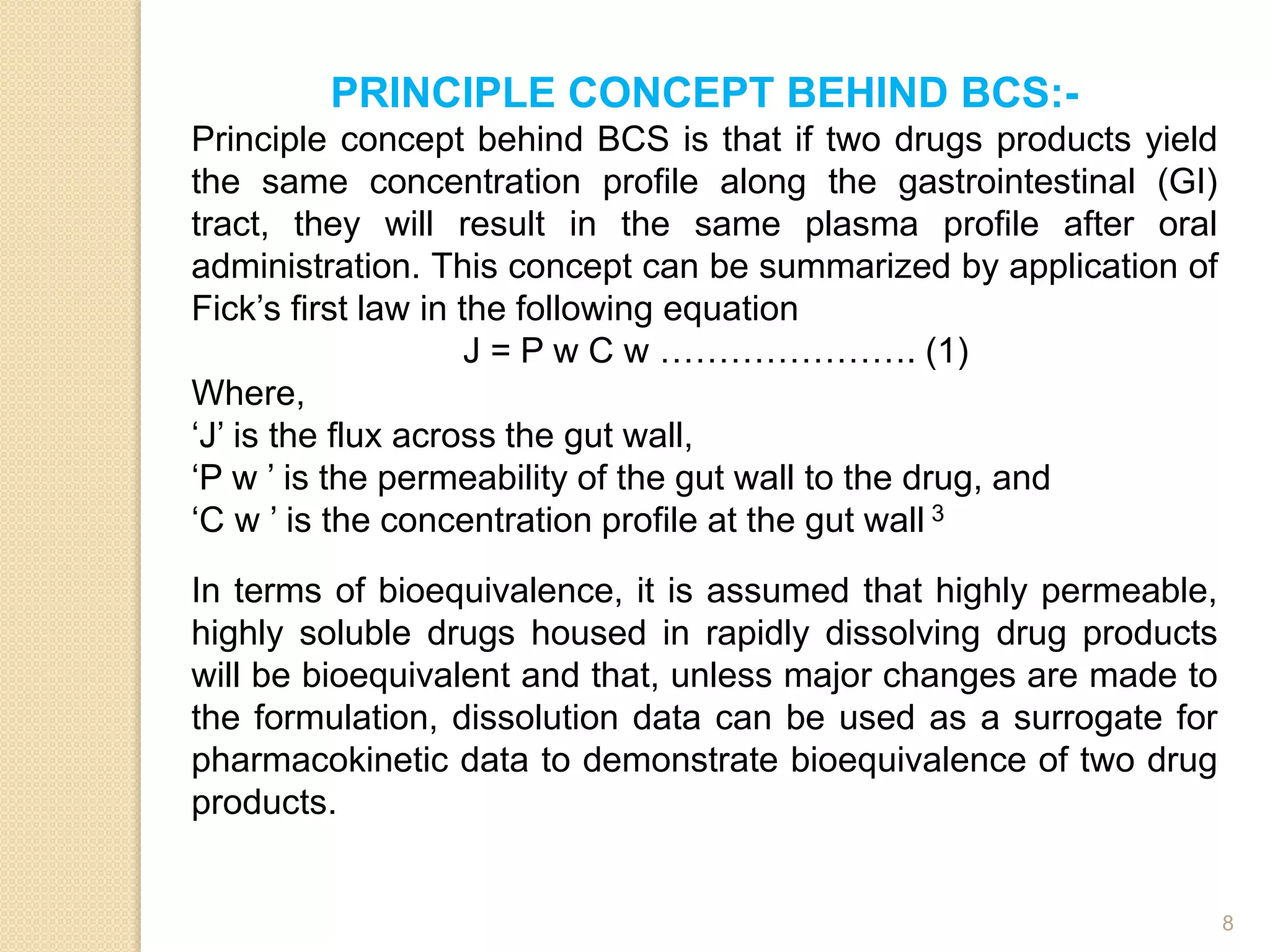
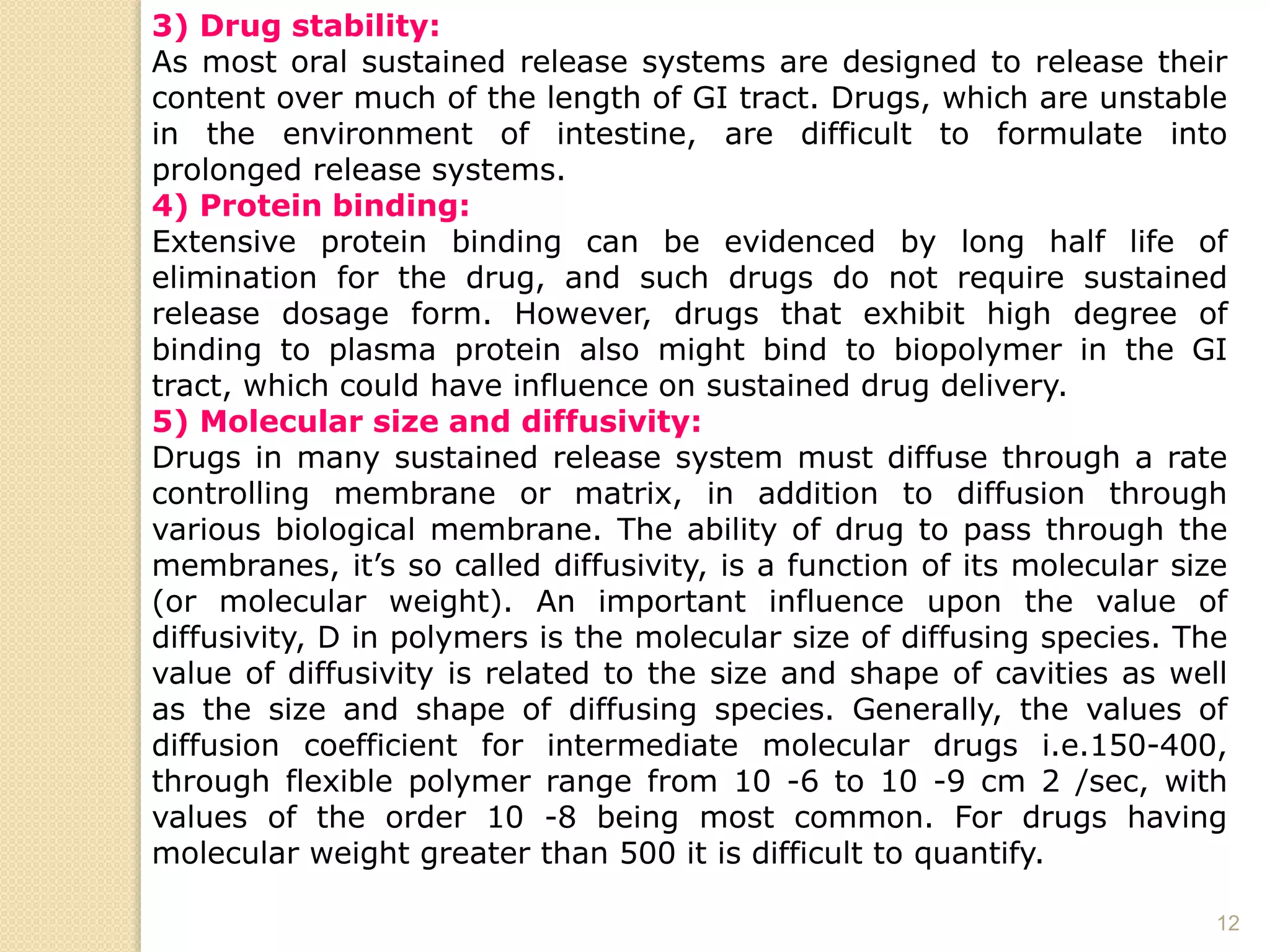
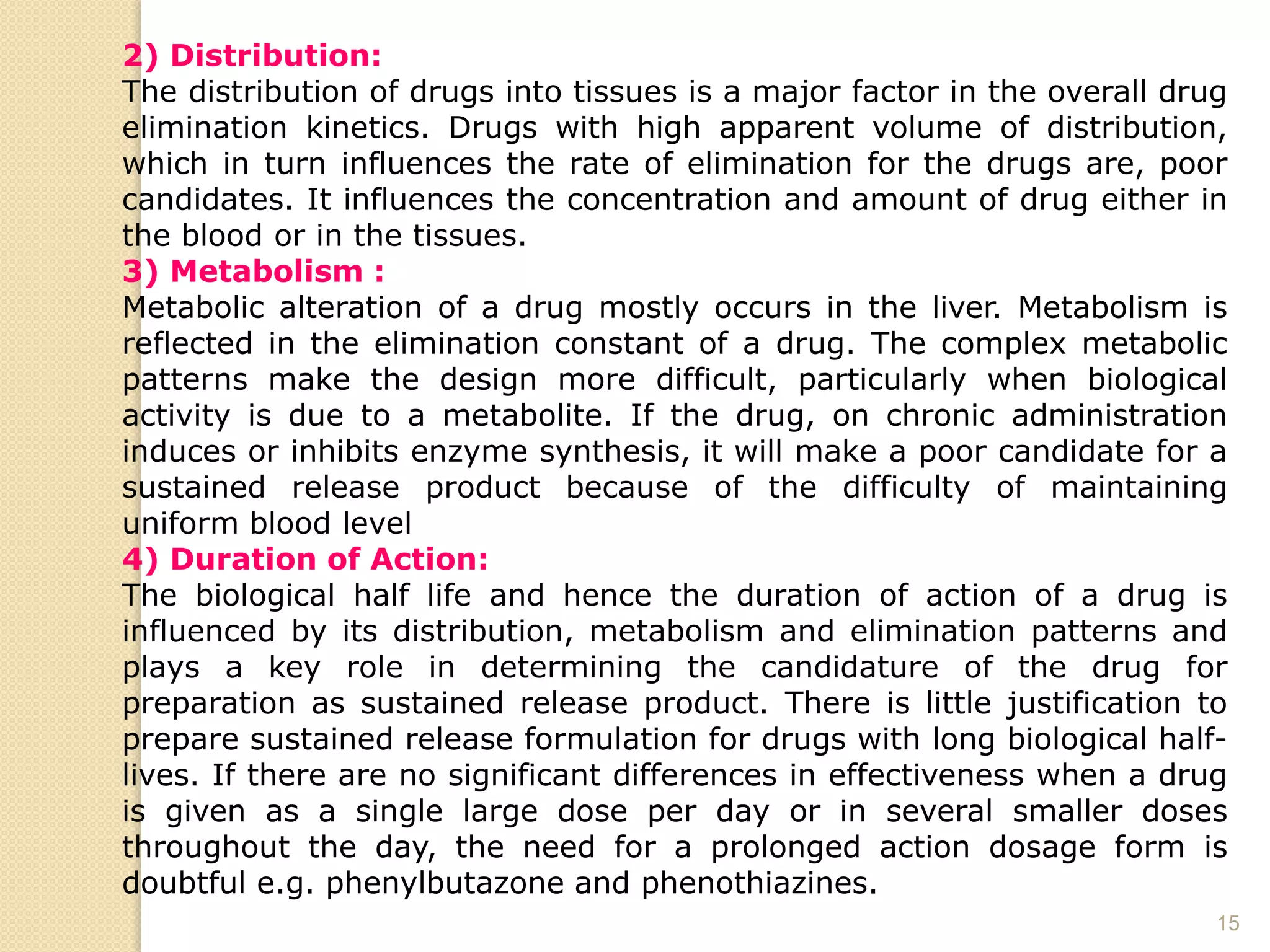
The document discusses the concept of modified drug release, outlining different terminologies, advantages, and disadvantages of such formulations compared to conventional dosage forms. It also explains the Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) for drug substances and factors affecting the design of sustained release systems. Various drug characteristics and their suitability for sustained release formulations are highlighted, alongside the importance of the therapeutic index in assessing drug safety.