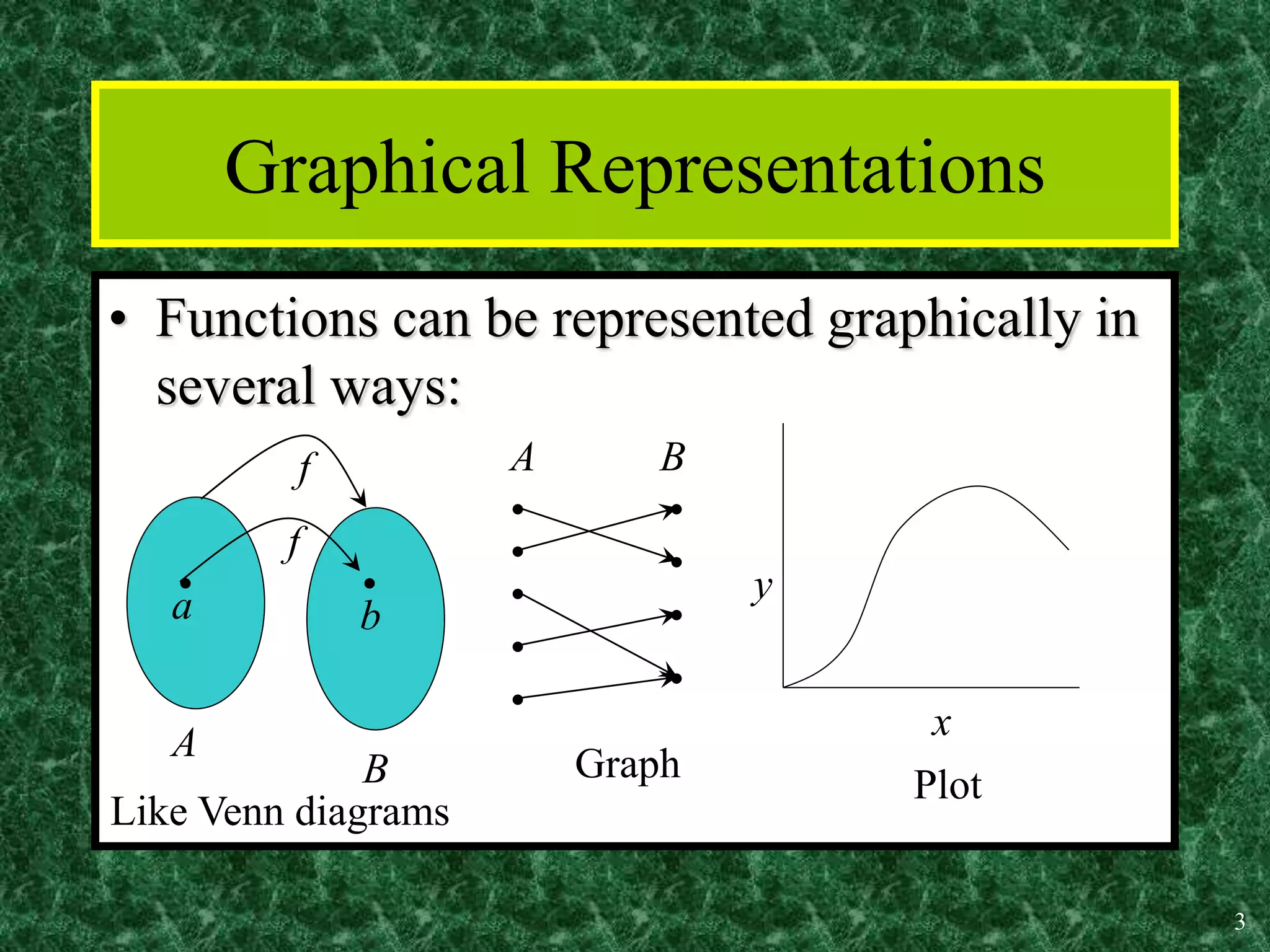
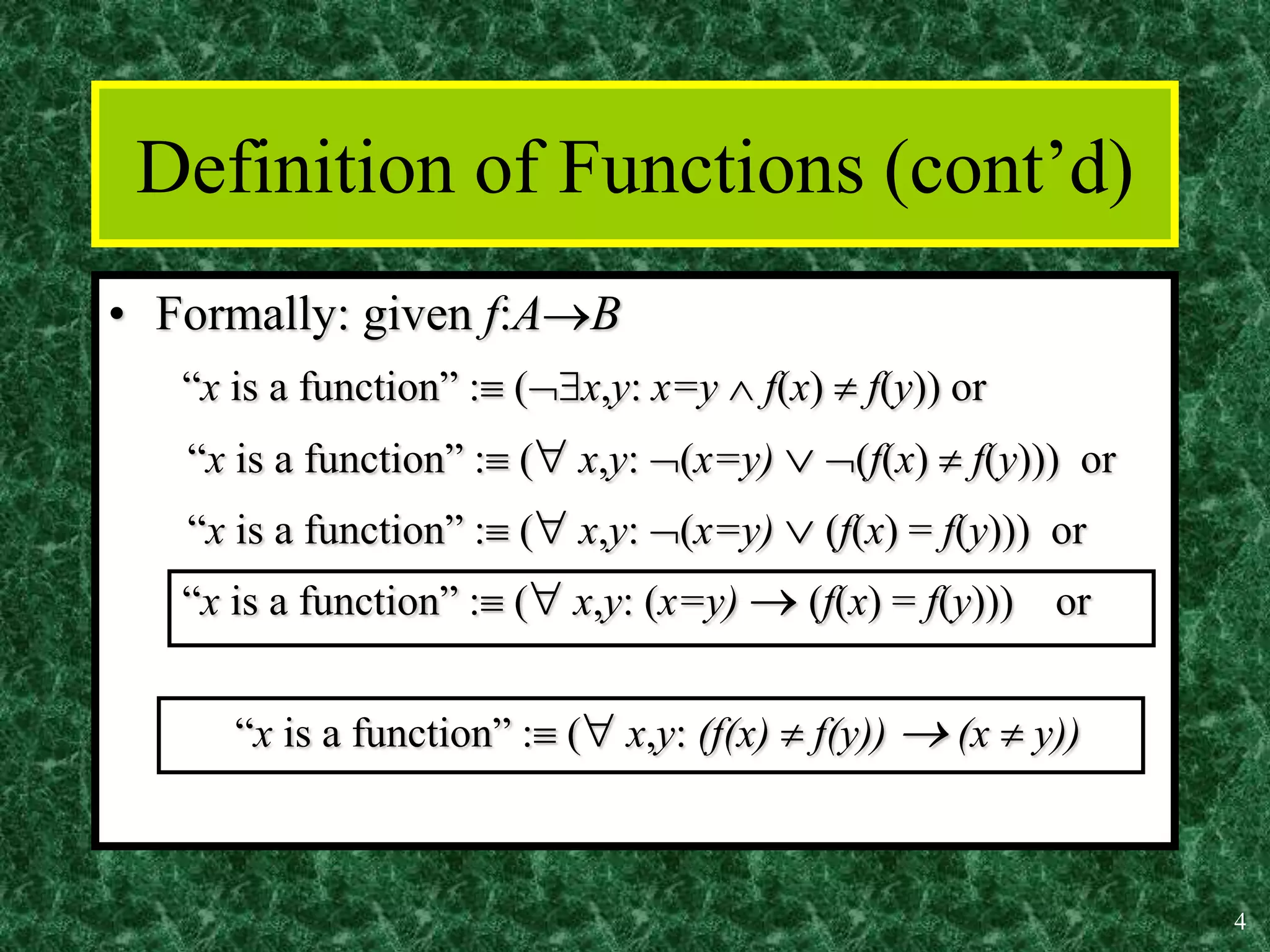
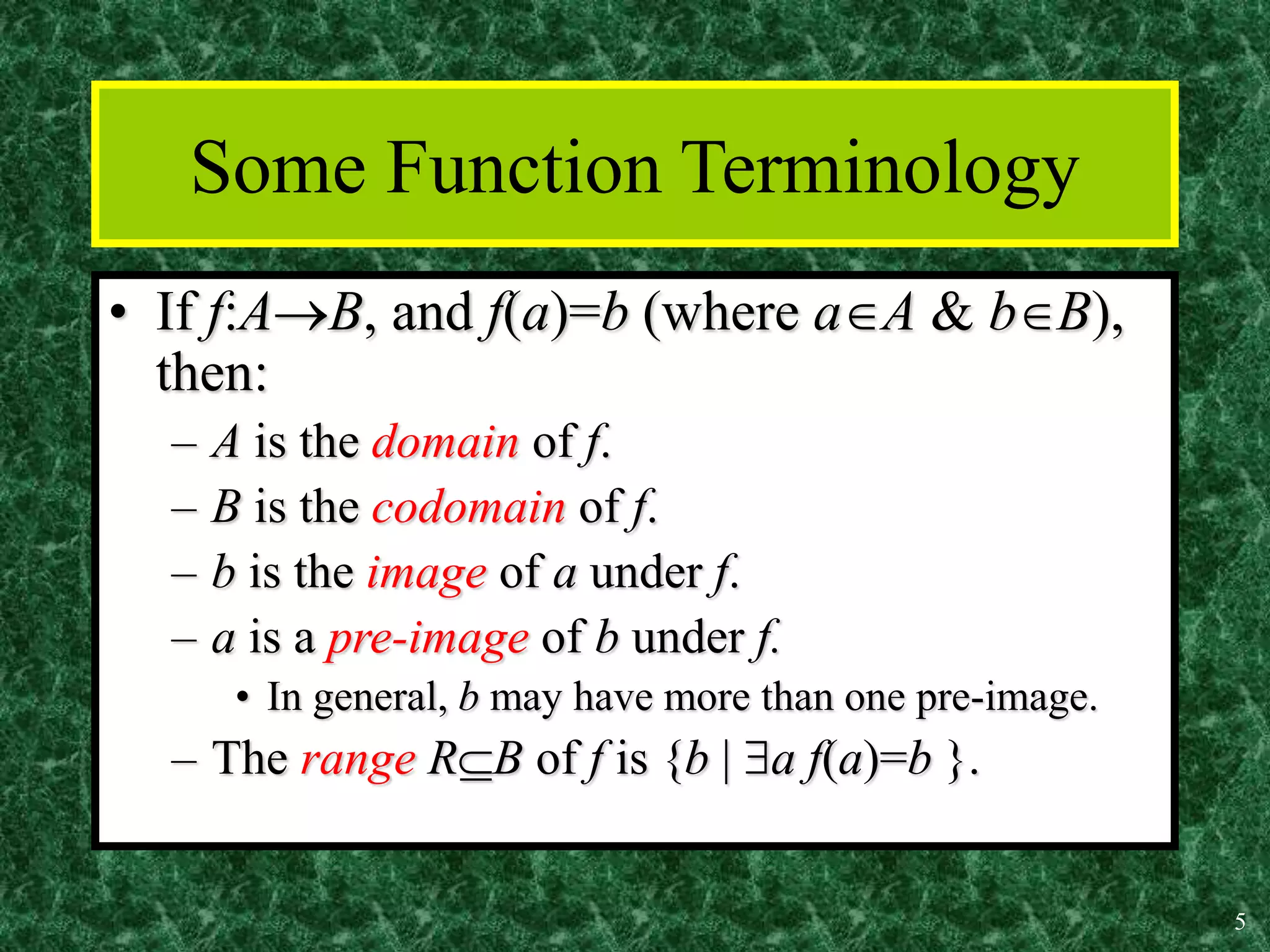
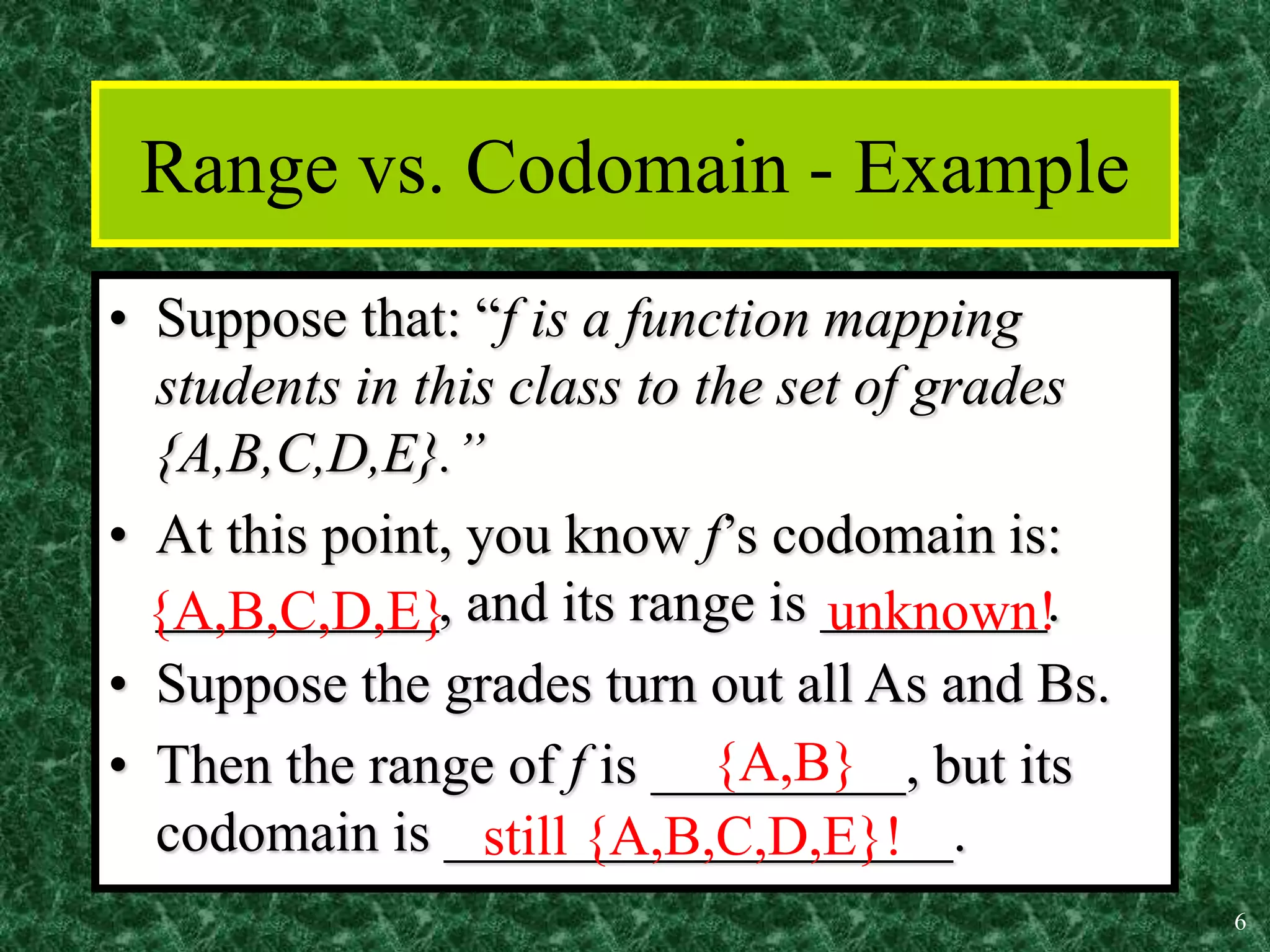
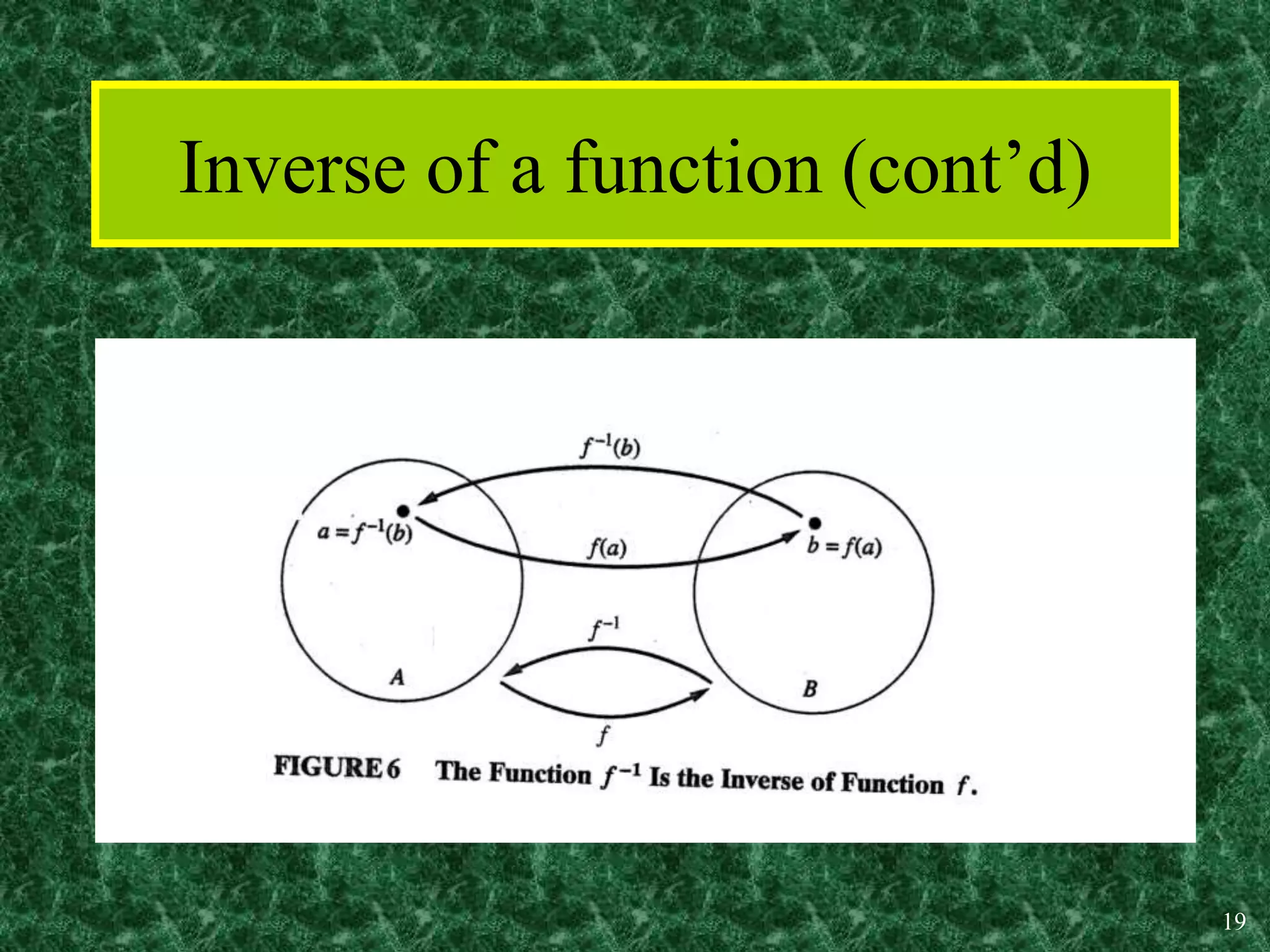
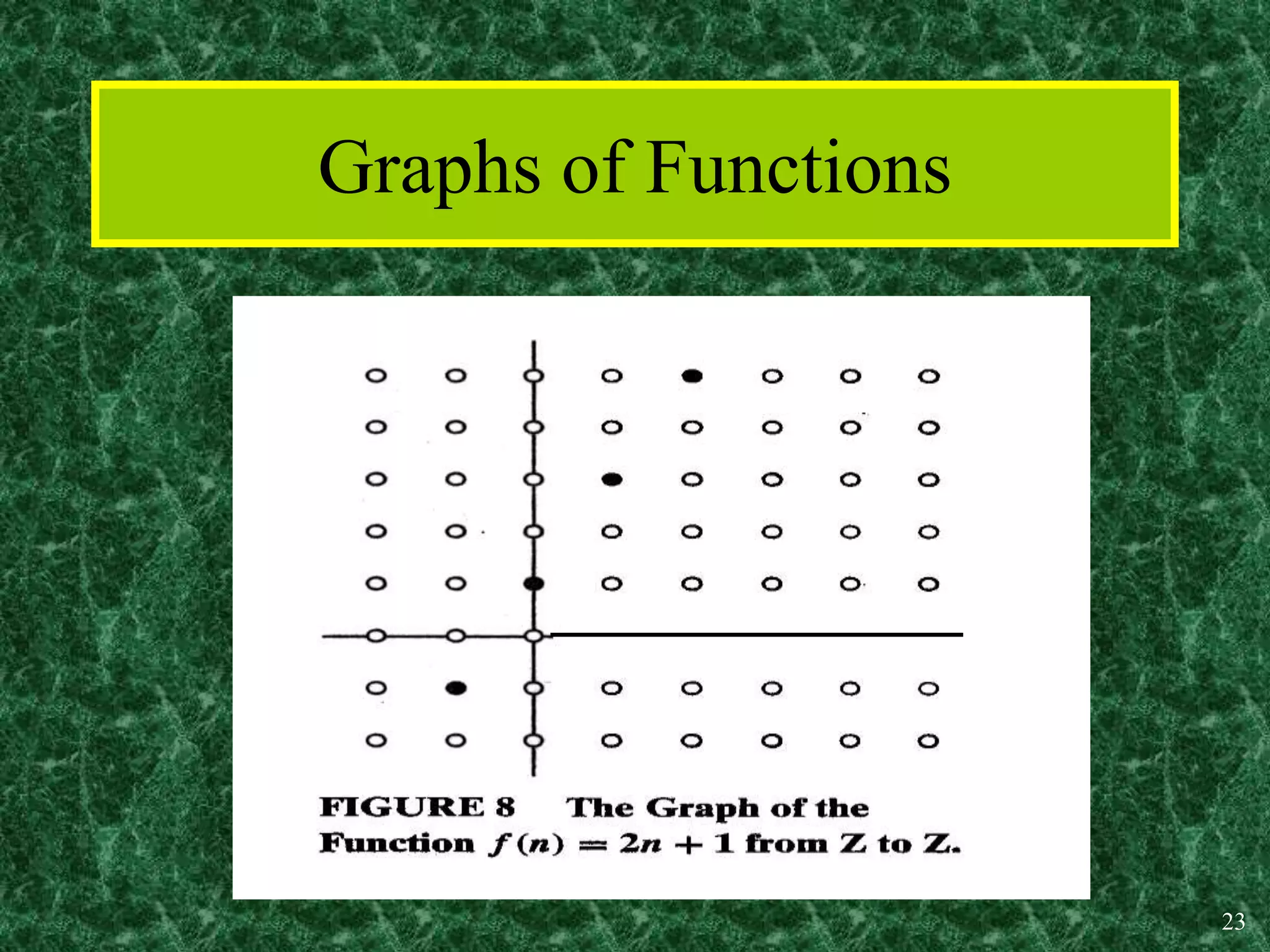
1. A function is a mapping or assignment of elements from one set (the domain) to elements in another set (the codomain or range) such that each element of the domain is mapped to exactly one element of the codomain. Functions can be represented graphically.
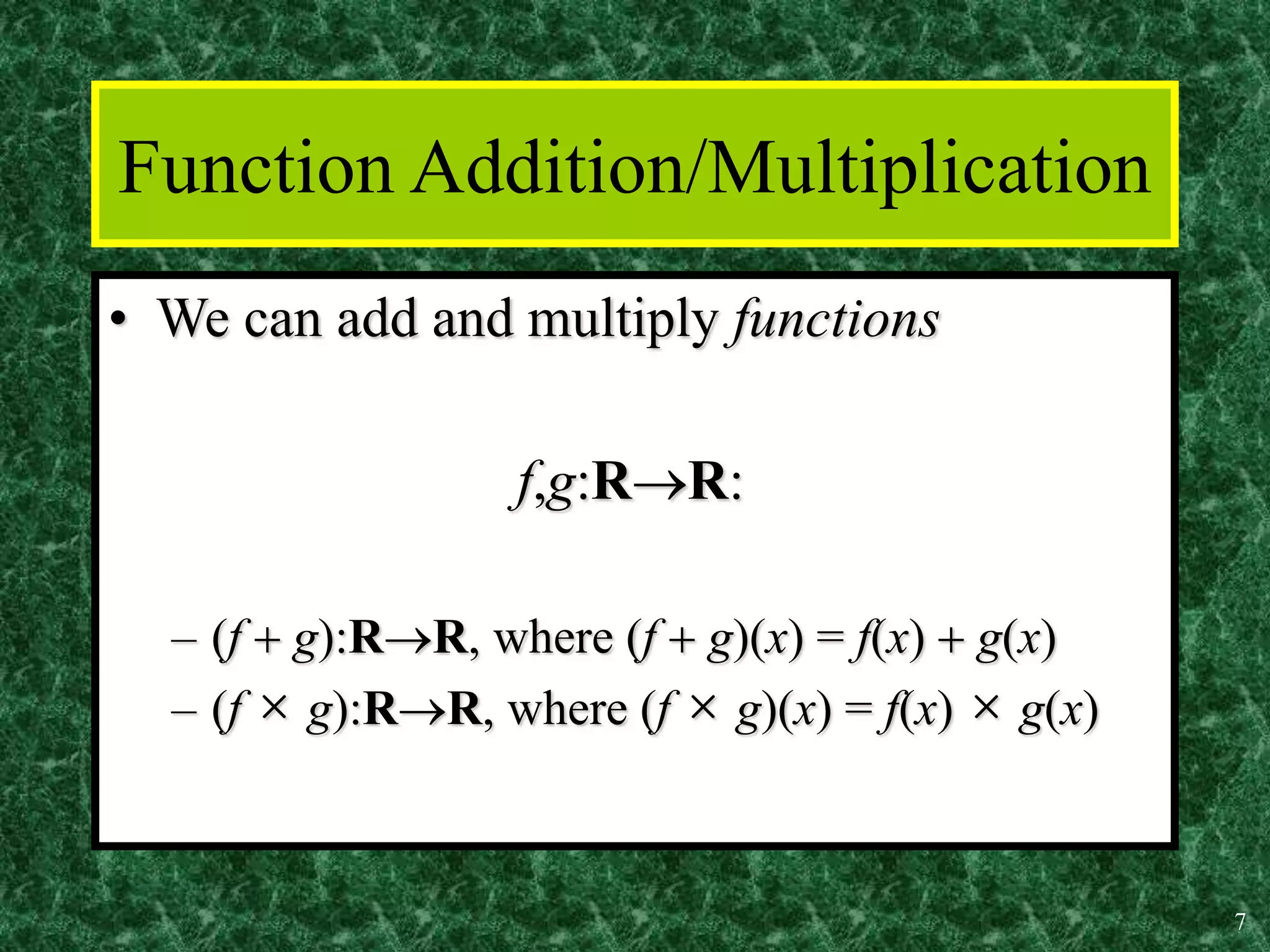
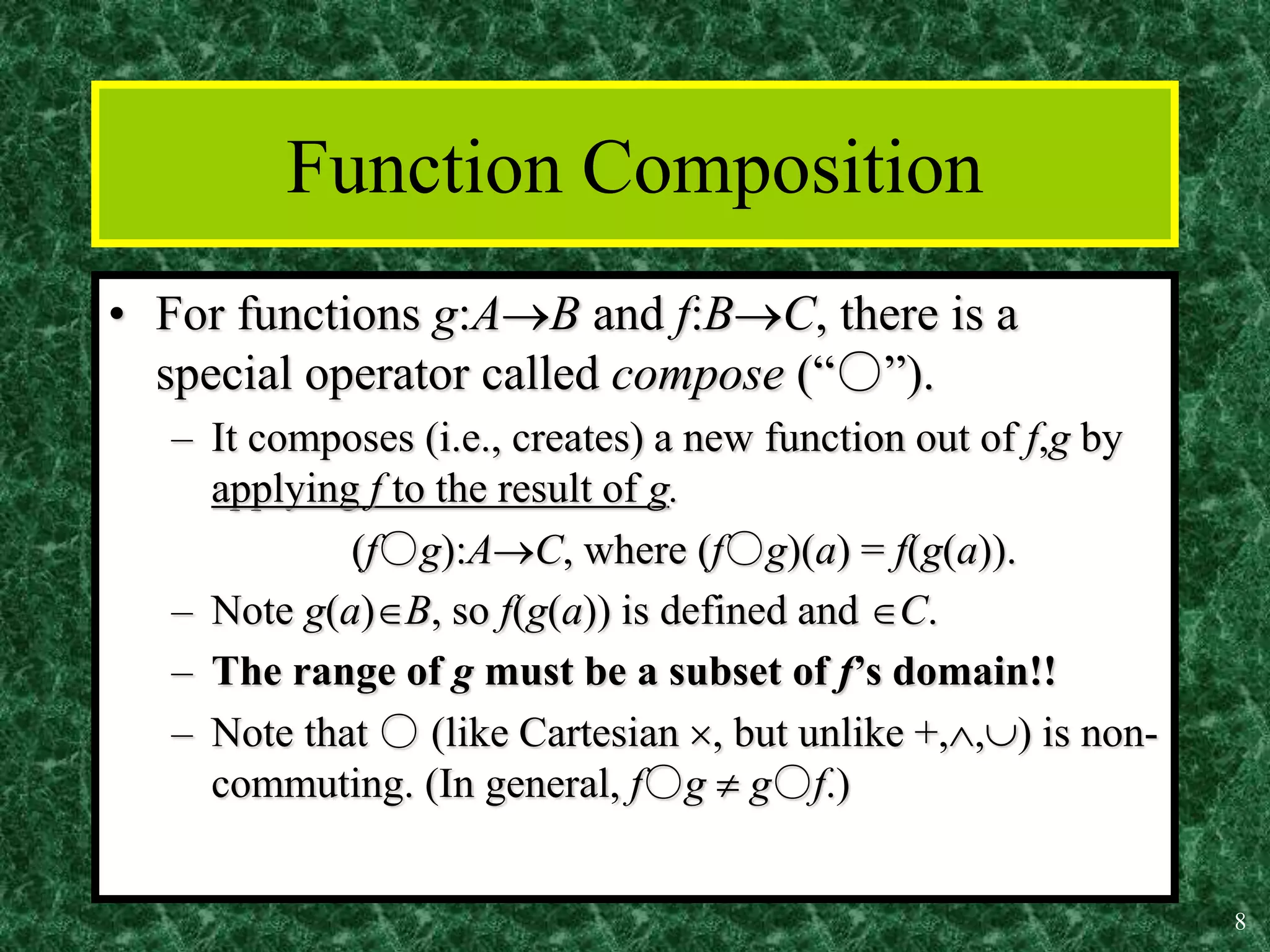
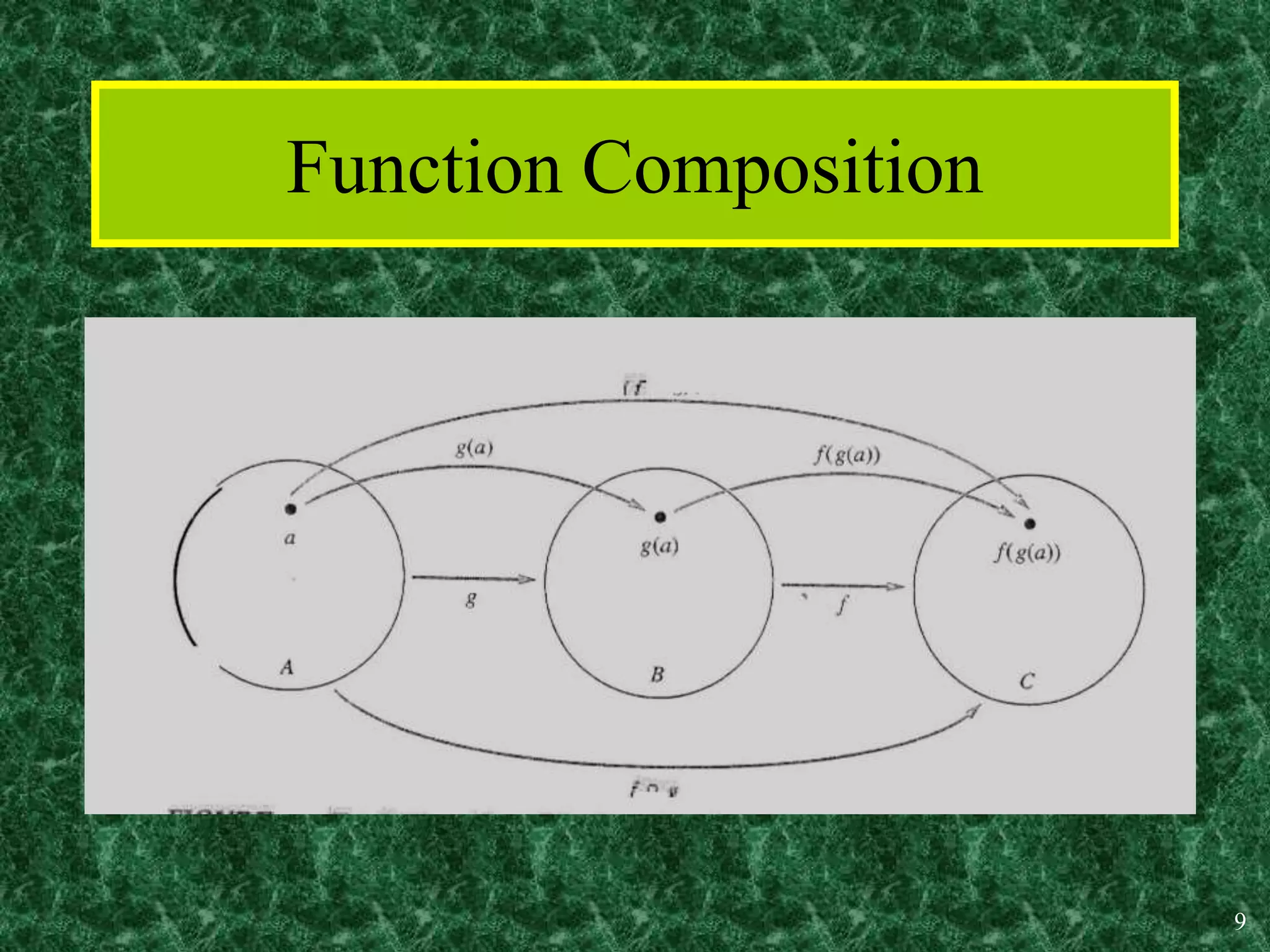
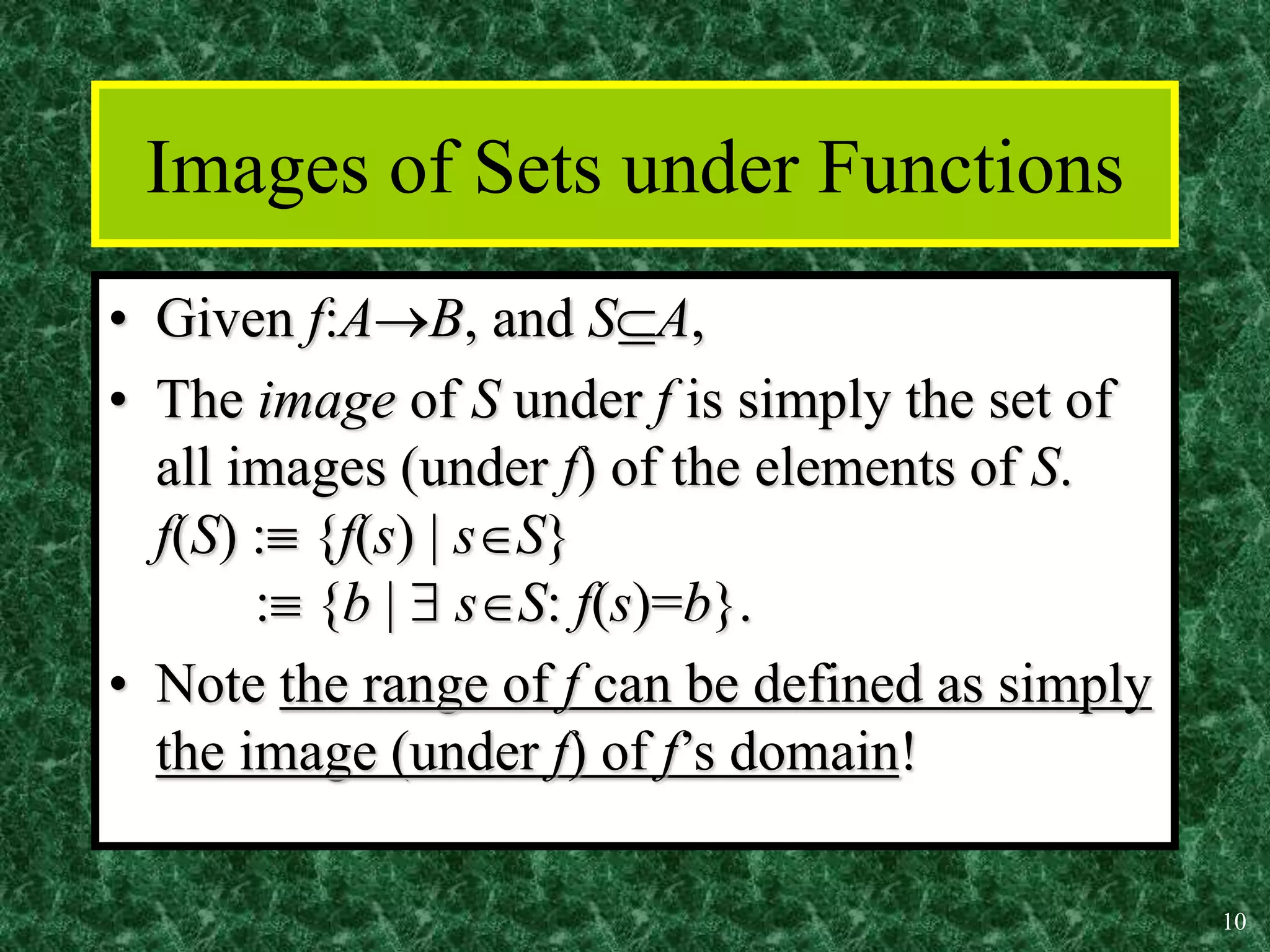
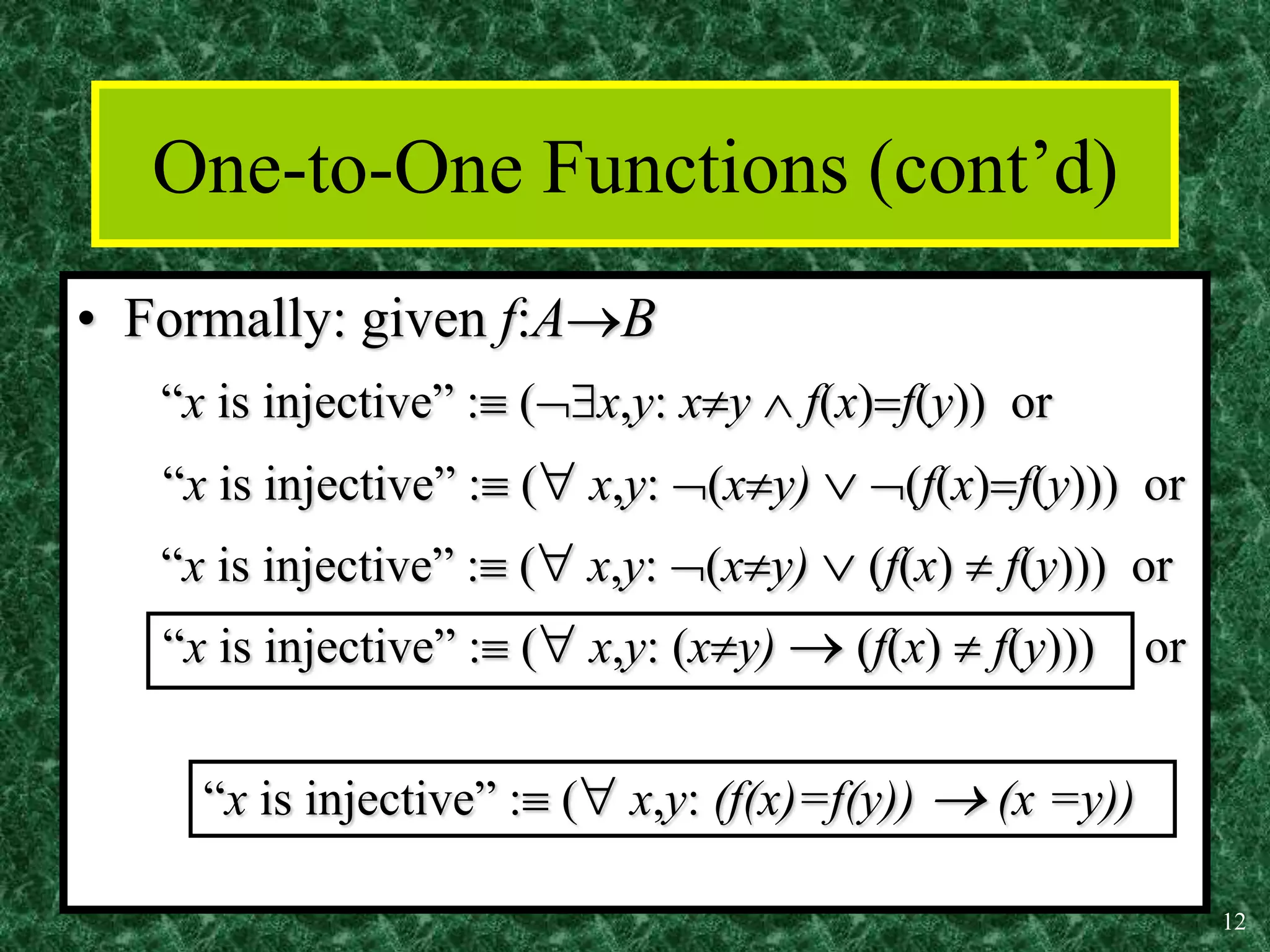
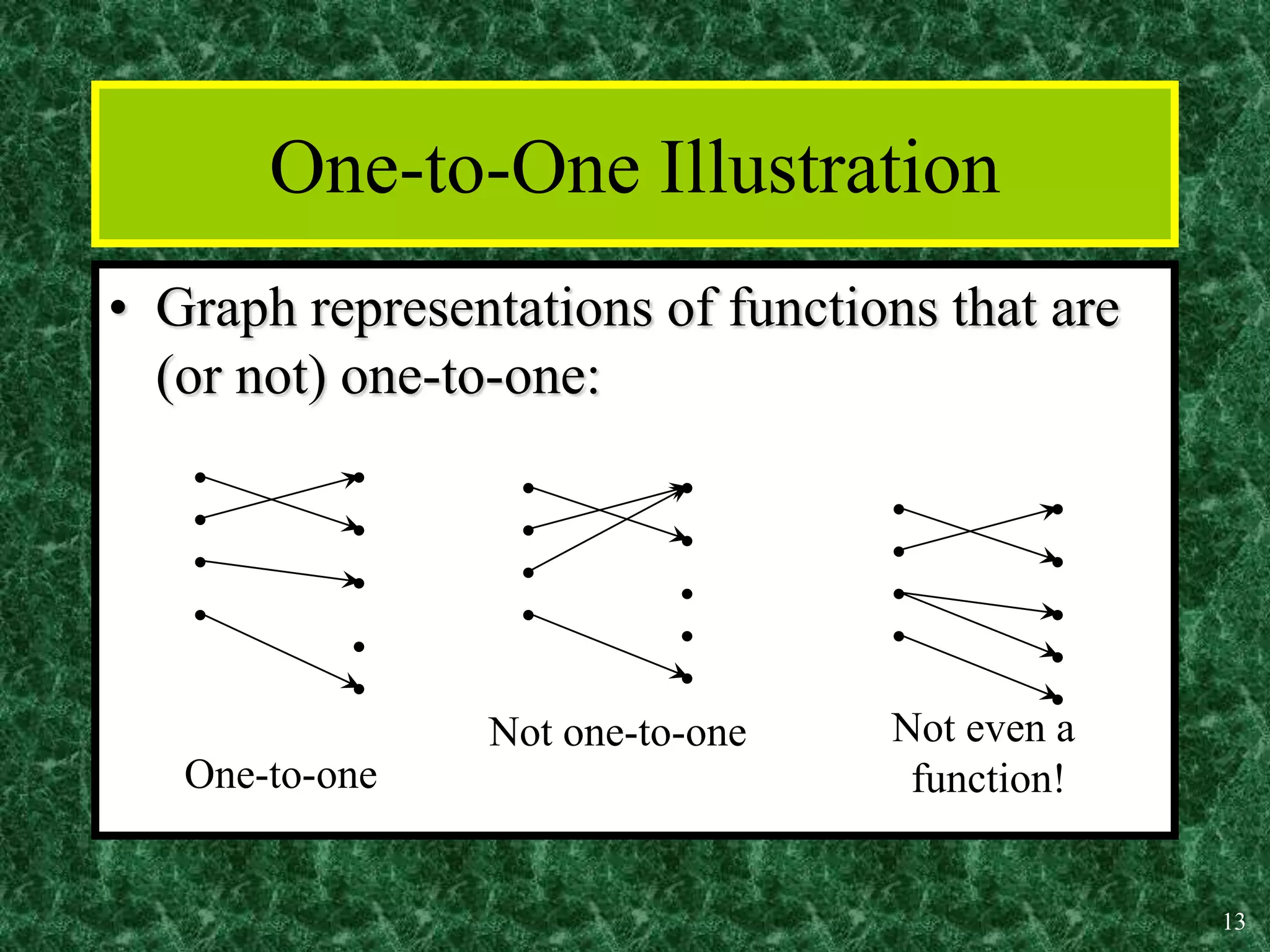
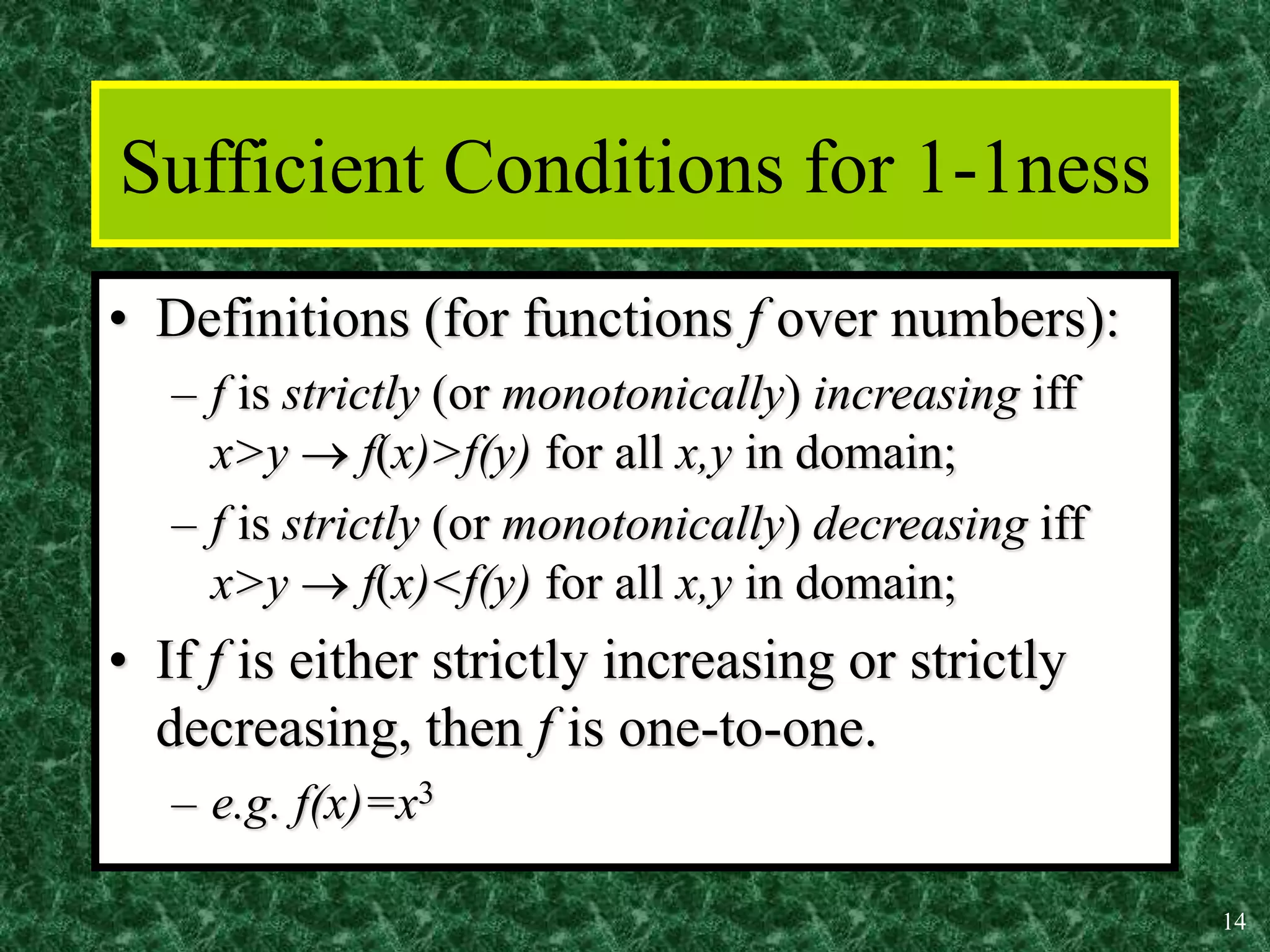
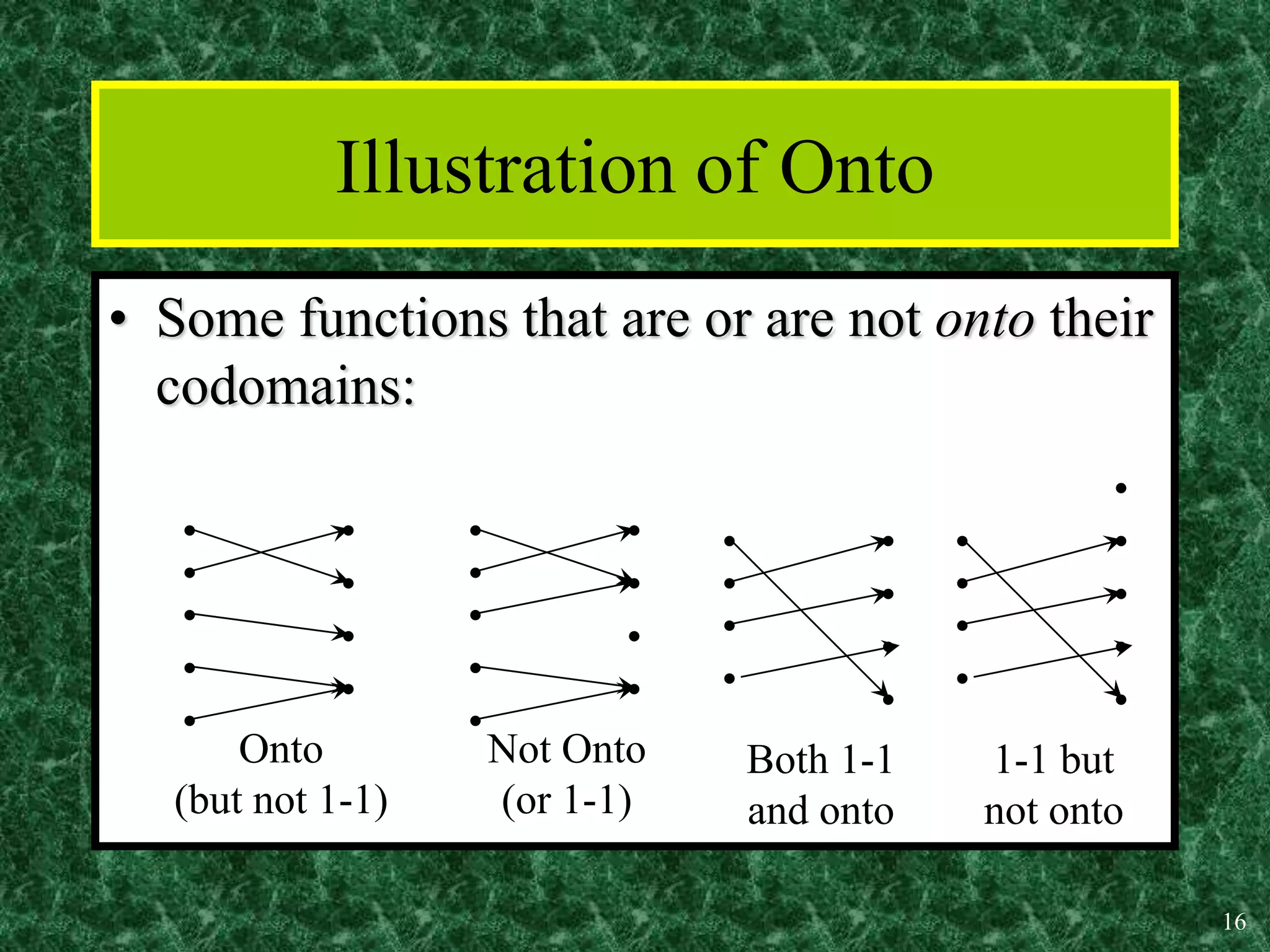
2. Key properties of functions include being one-to-one (injective), onto (surjective), and bijective (both one-to-one and onto). Operations like addition, multiplication, composition and inverses can be defined for functions.
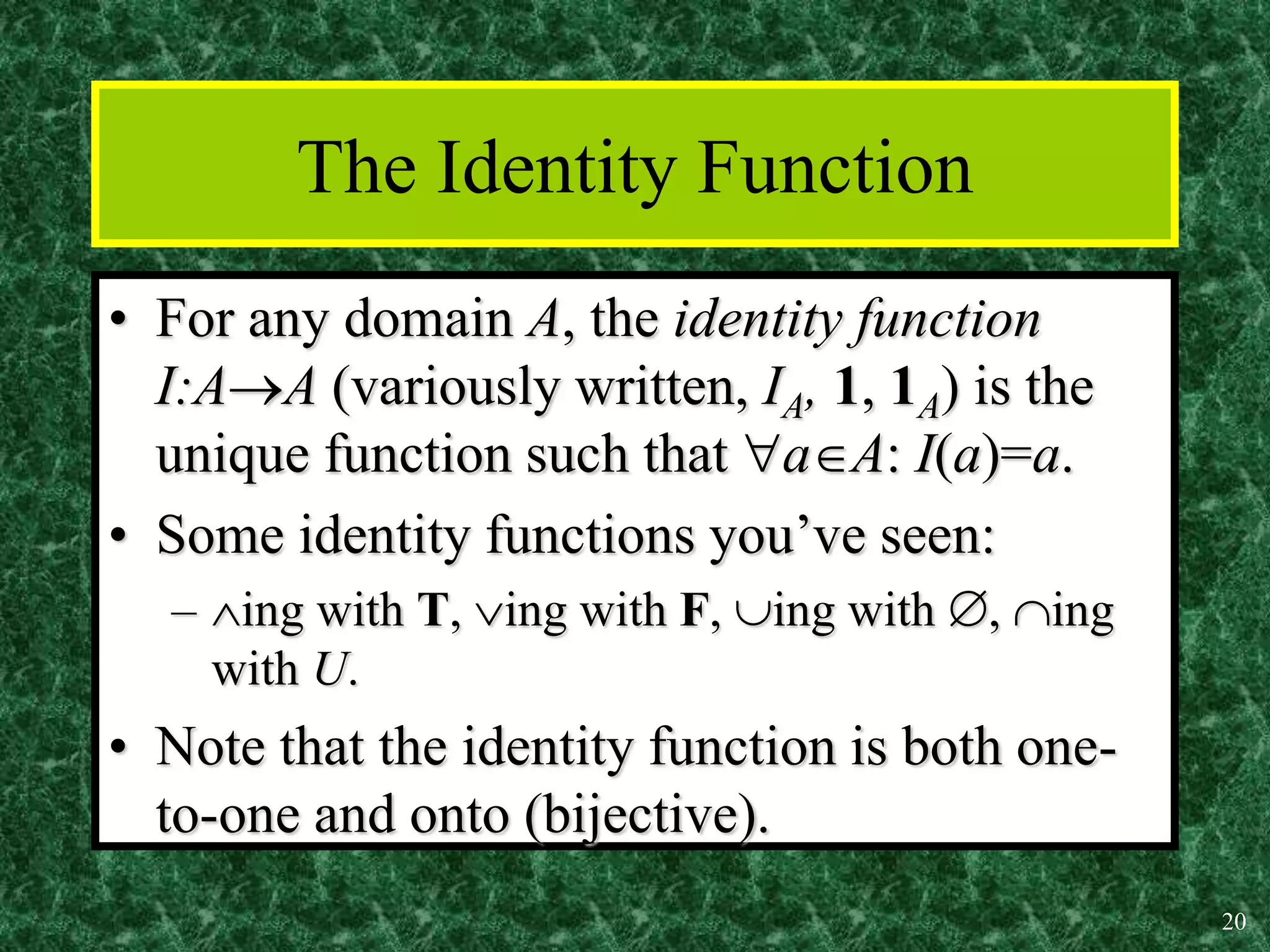
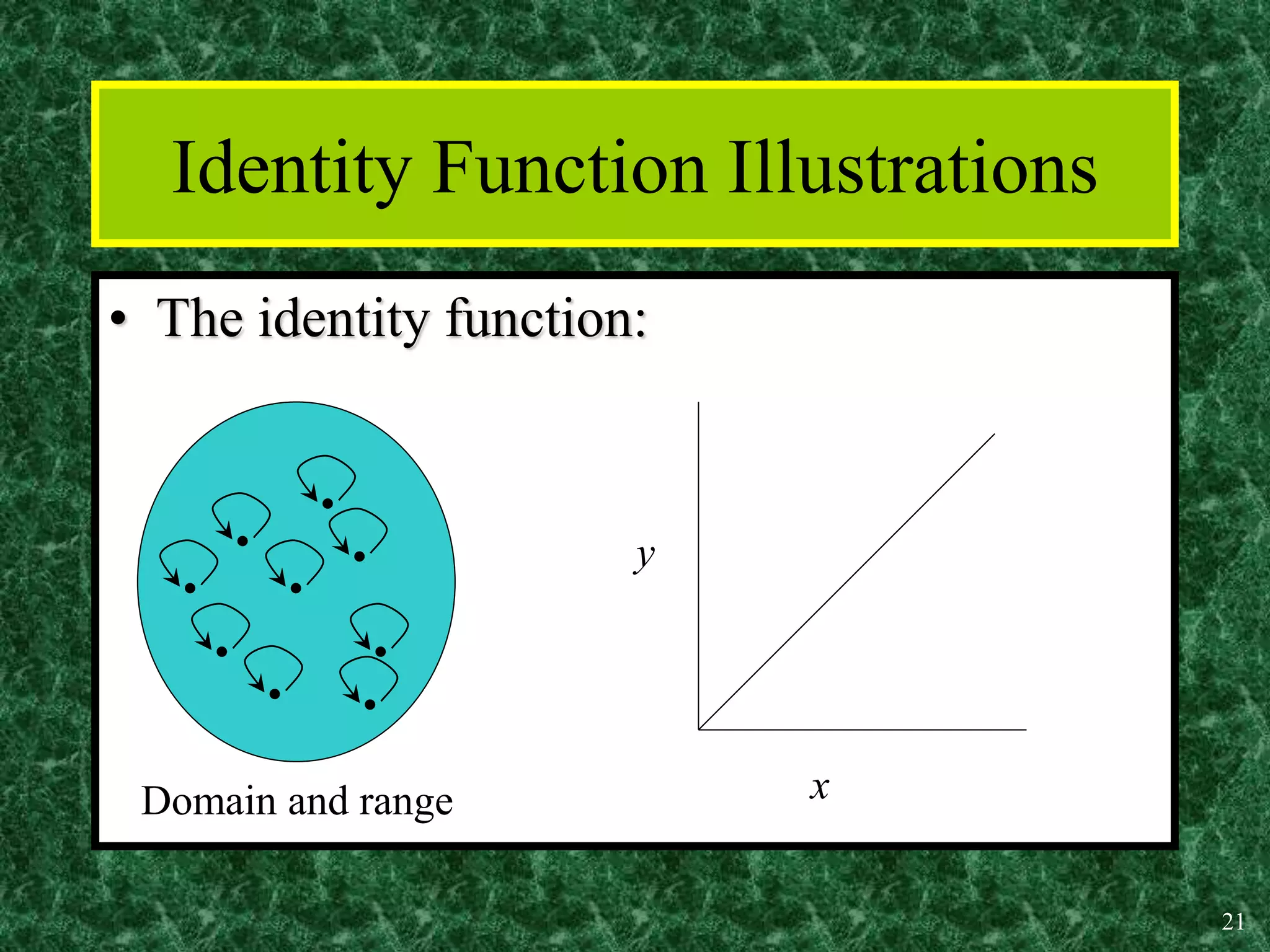
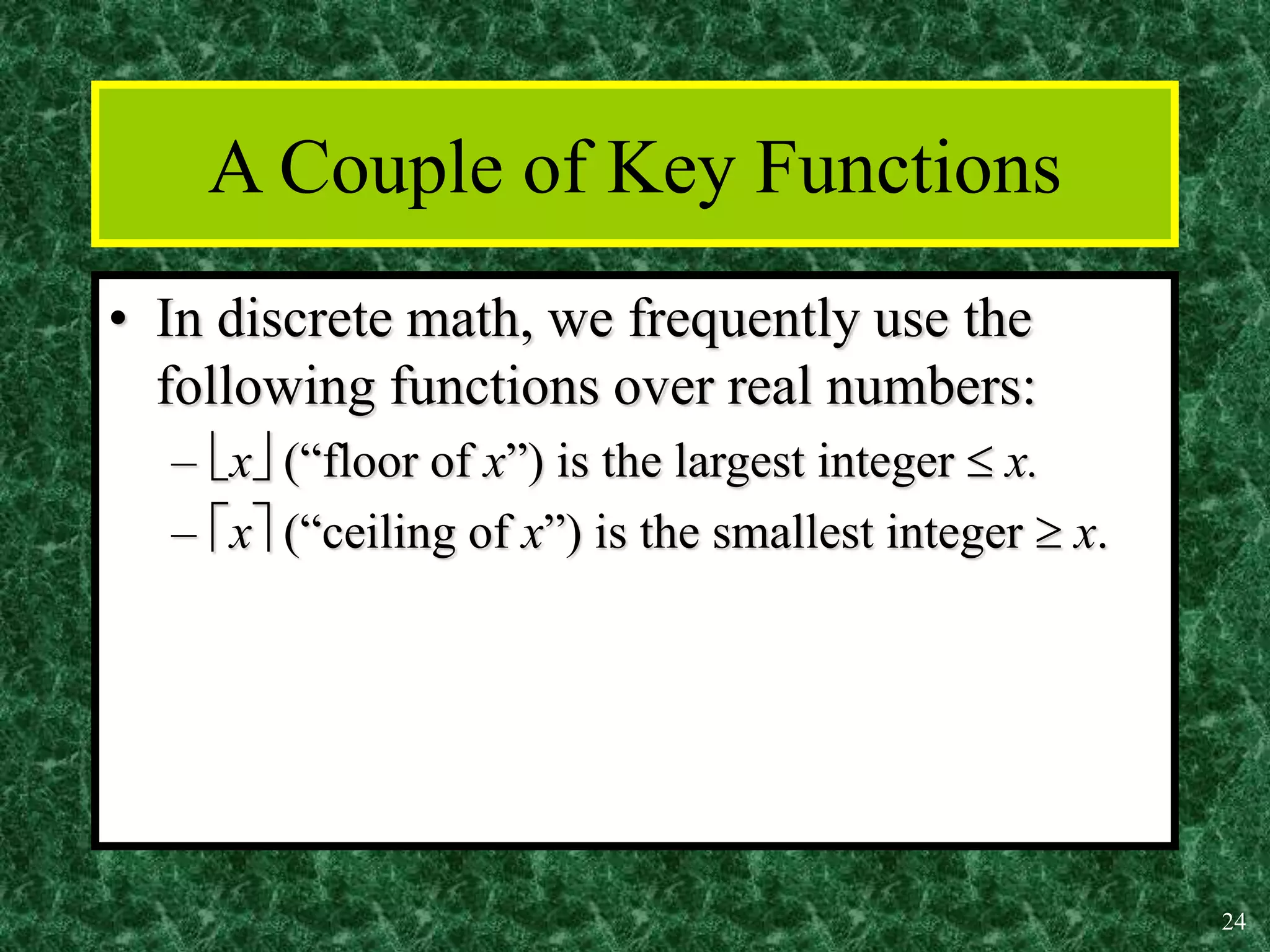
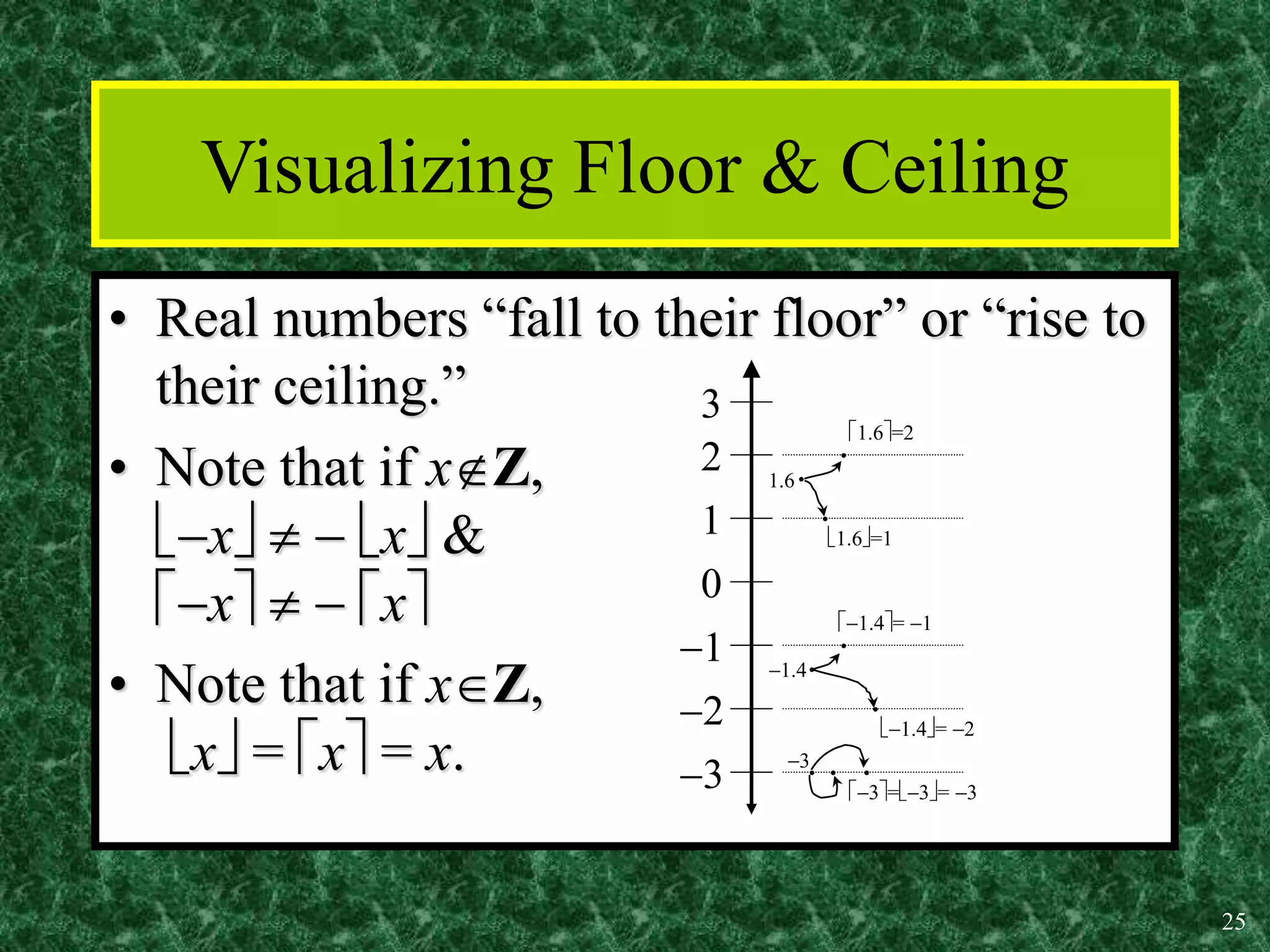
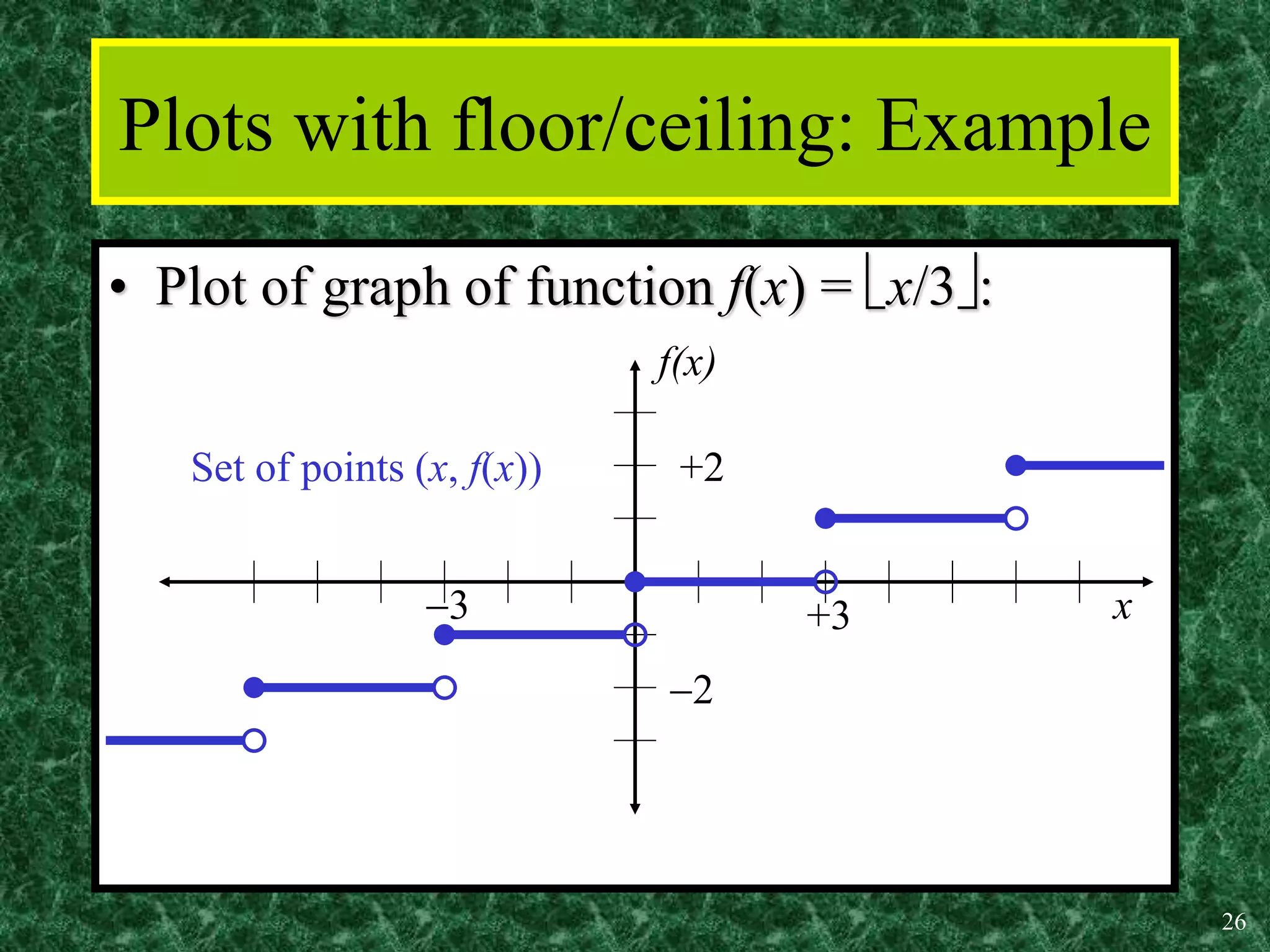
3. Common functions used in discrete math include the floor, ceiling, and identity functions.